Abstract
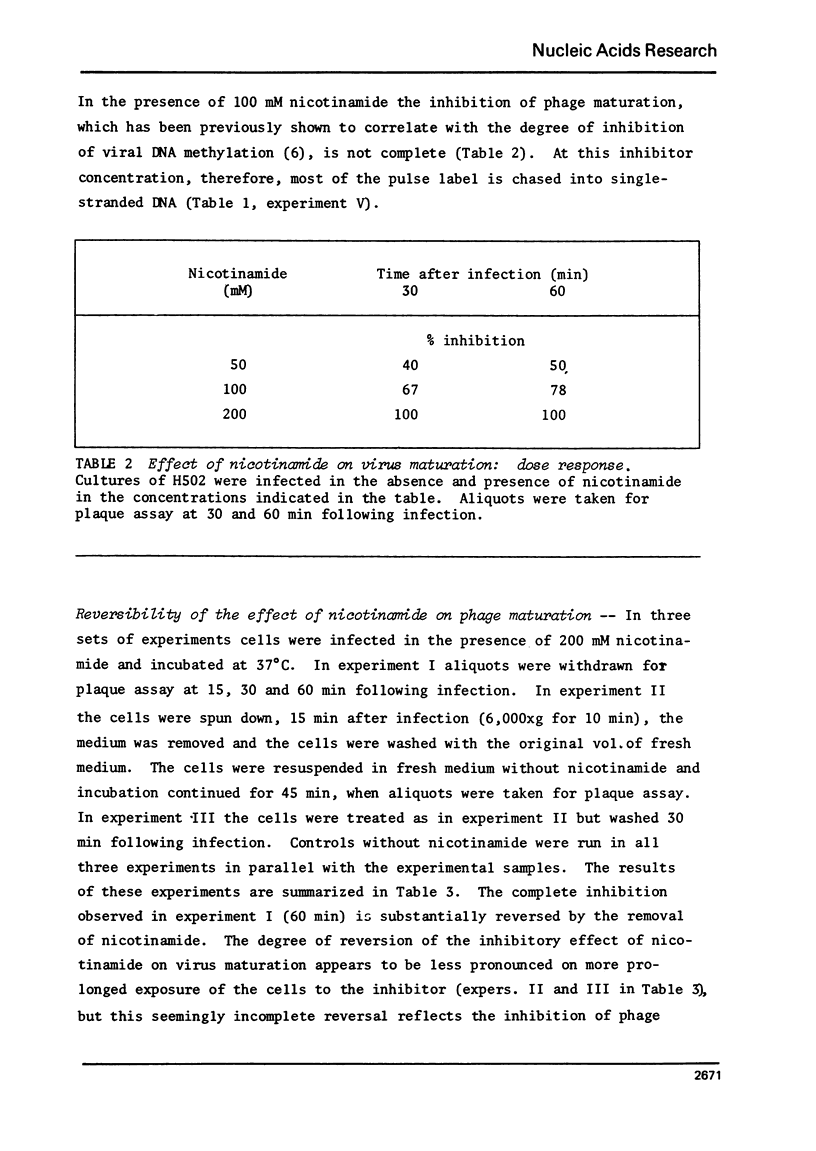
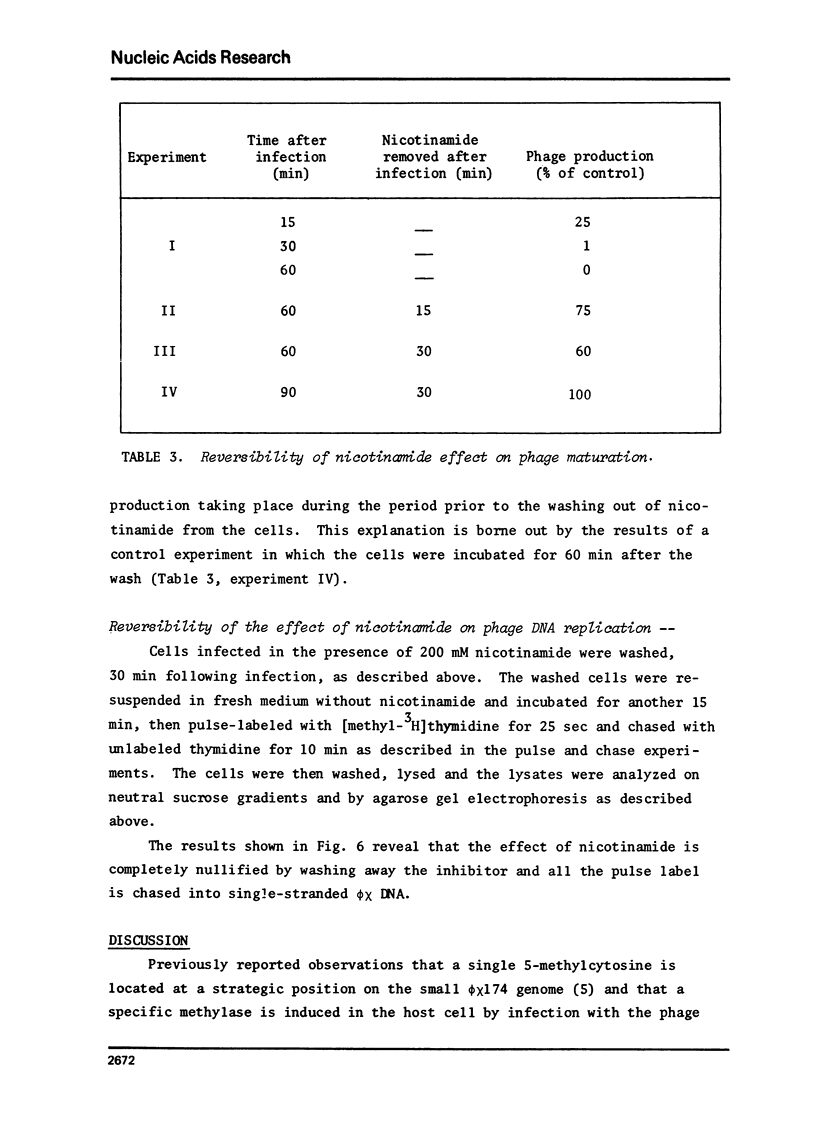
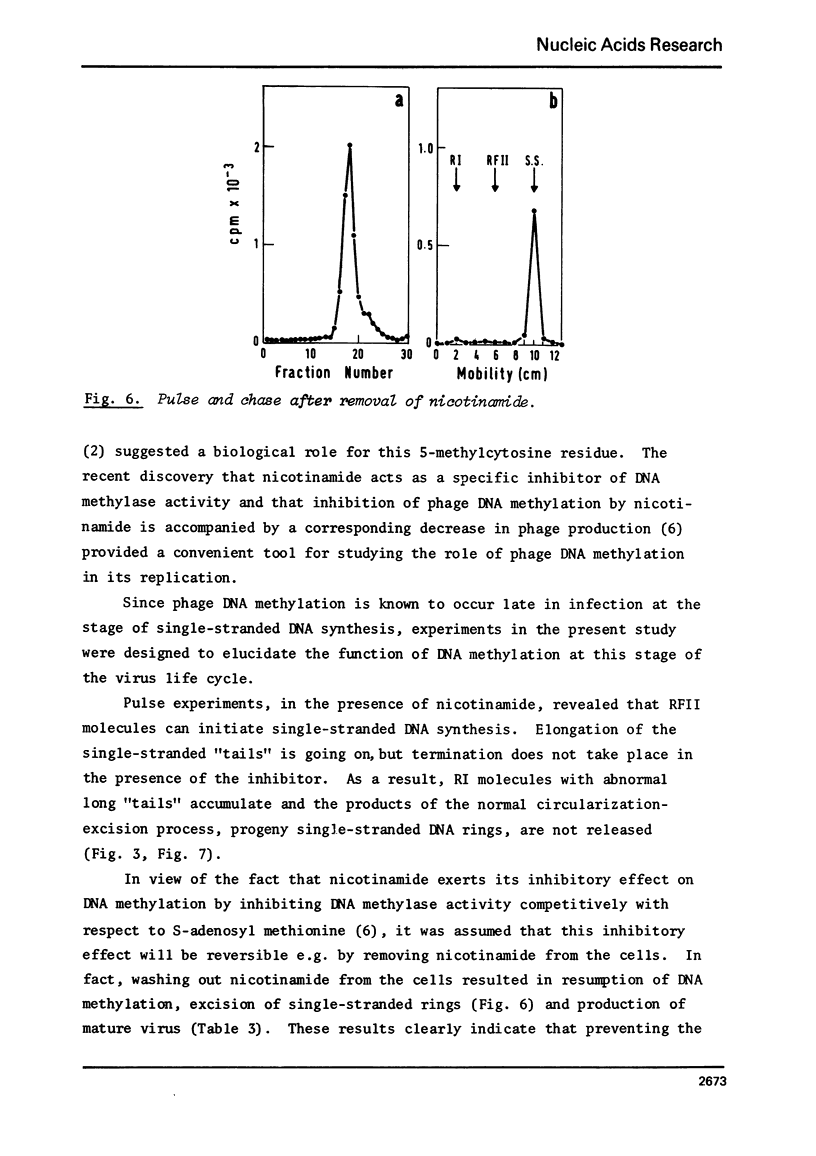
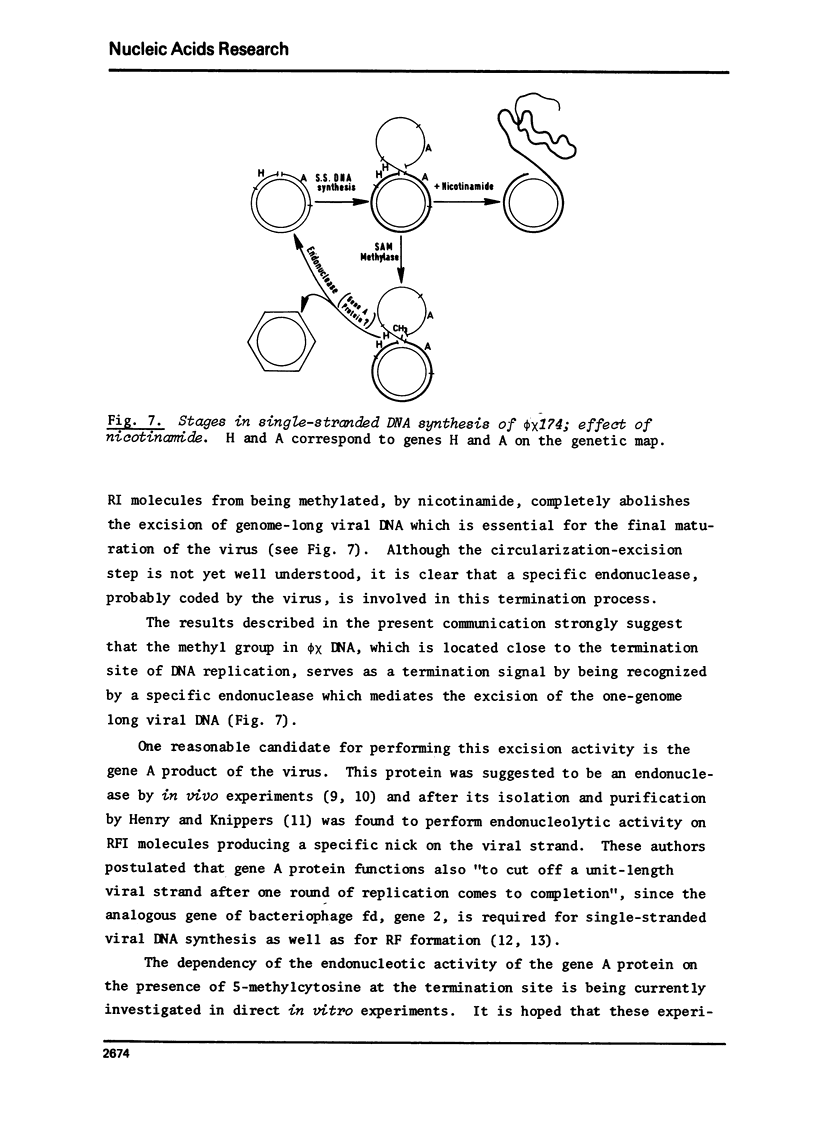
In vivo inhibition of bacteriophage phiX174 DNA methylation by nicotinamide resulted in the accumulation of replicative intermediates with multiple-genome length single-stranded "tails". These abnormal replicative intermediates could not be chased into viral single-stranded circular DNA. The effect of nicotinamide on phage maturation and accumulation of abnormal replicative intermediates could be reversed by washing out the inhibitor. The results suggest that the single methyl group present in the viral DNA serves as a recognition site for a specific endonuclease, probably the gene A protein product, that is responsible for the excision of the single-stranded one-genome long viral DNA, before final maturation of the virus occurs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Francke B., Ray D. S. Cis-limited action of the gene-A product of bacteriophage phiX174 and the essential bacterial site (E. coli-electron microscopy-cis-acting protein-specifically-nicked RF). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):475–479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke B., Ray D. S. Formation of the parental replicative form DNA of bacteriophage phi-X174 and initial events in its replication. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 14;61(3):565–586. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry T. J., Knippers R. Isolation and function of the gene A initiator of bacteriophage phi-chi 174, a highly specific DNA endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1549–1553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knippers R., Razin A., Davis R., Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with Bacteriophage phi-X174. XXIX. In vivo studies on the synthesis of the single-stranded DNA of progeny phi-X174 bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):237–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knippers R., Salivar W. O., Newbold J. E., Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phiX174. XXVI. Transfer of the parental DNA of bacteriophage phiX174 into progeny bacteriophage particles. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 14;39(3):641–654. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. S., Sinsheimer R. L. Location of the 5-methylcytosine group on the bacteriophage phi X174 genome. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):872–877. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.872-877.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A. DNA methylase induced by bacteriophage phiX174. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3773–3775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Goren D., Friedman J. Studies on the biological role of DNA methylation: inhibition of methylation and maturation of the bacteriophage phichi174 by nicotinamide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1967–1974. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Sedat J. W., Sinsheimer R. L. In vivo methylation of replicating bacteriophage phi chi174 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 15;78(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90465-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Sedat J. W., Sinsheimer R. L. Structure of the DNA of bacteriophage phiX174. VII. Methylation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 28;53(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90298-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng B. Y., Marvin D. A. Filamentous bacterial viruses. VI. Role of fd gene 2 in deoxyribonucleic acid replication. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):384–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.384-391.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


