Abstract
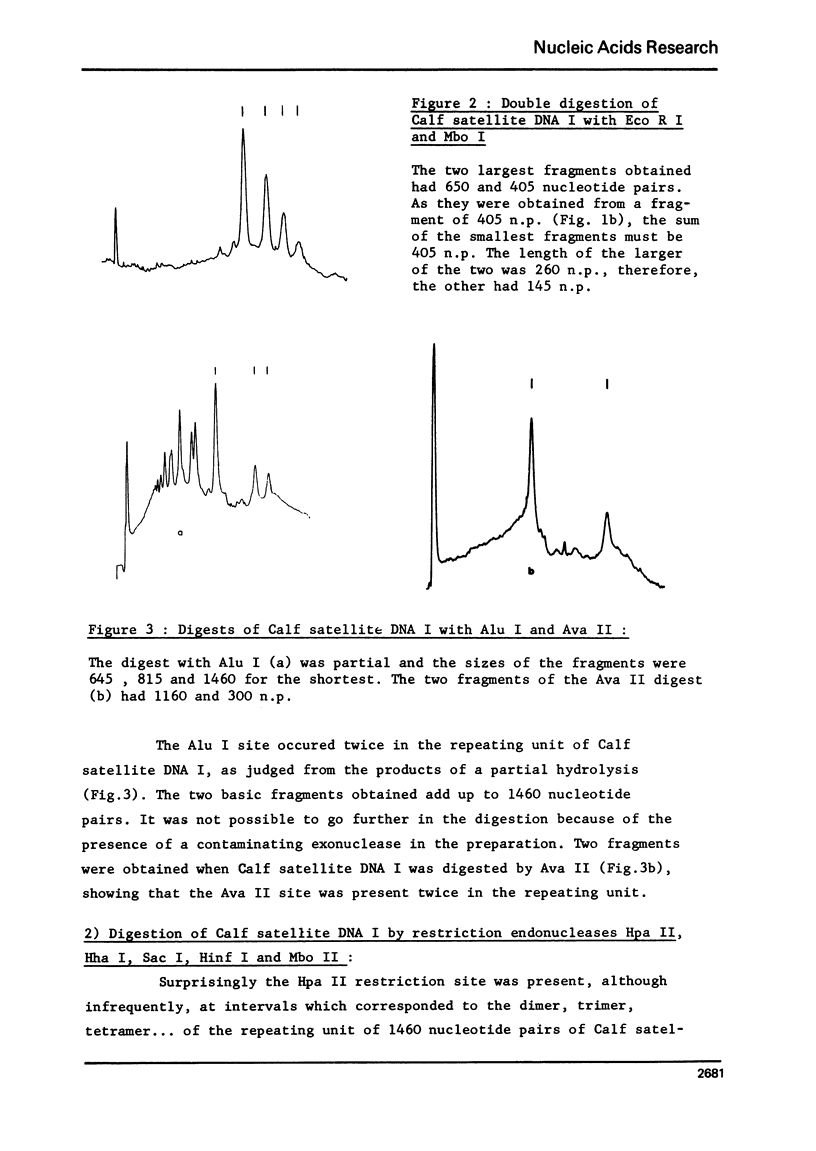
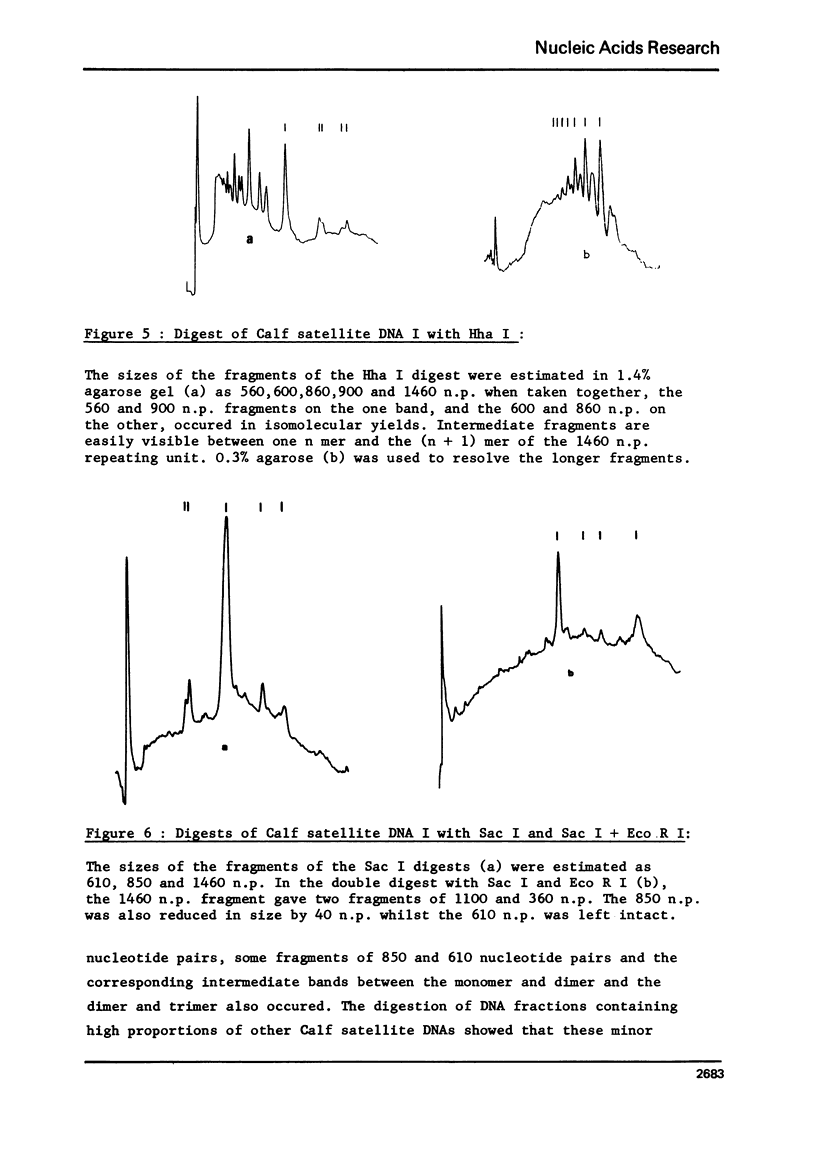
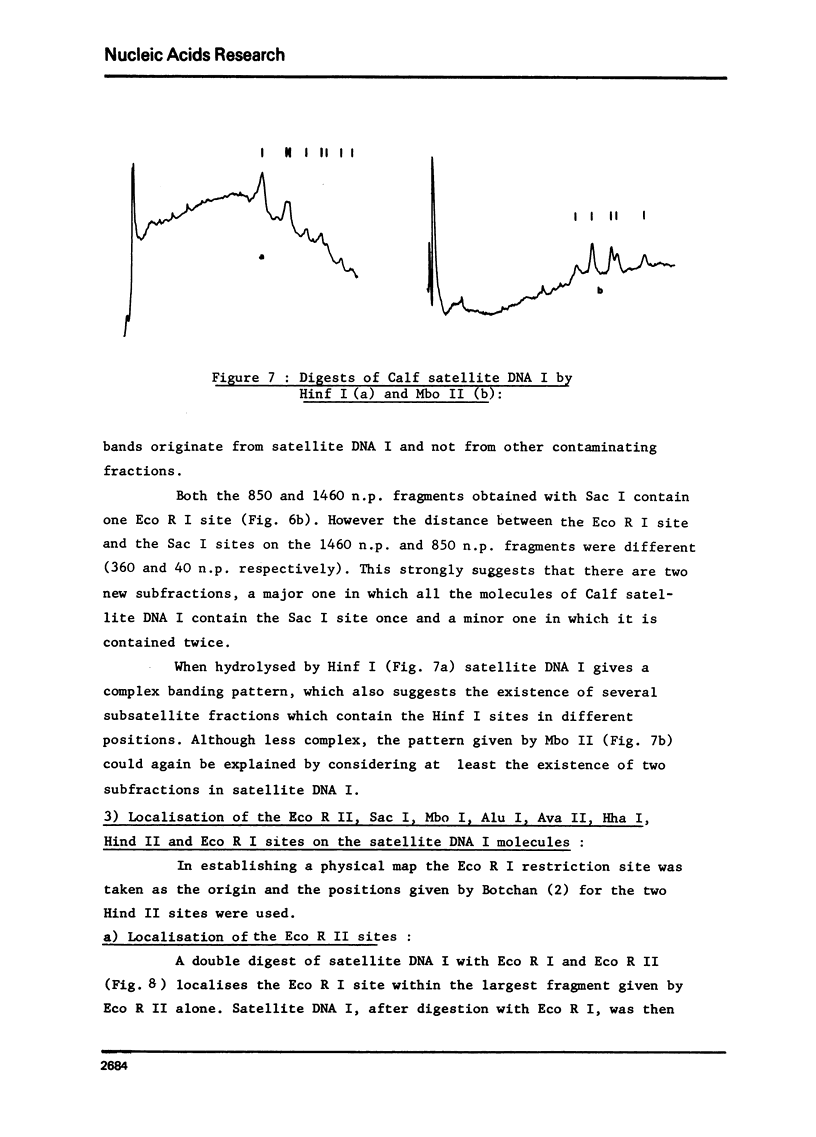
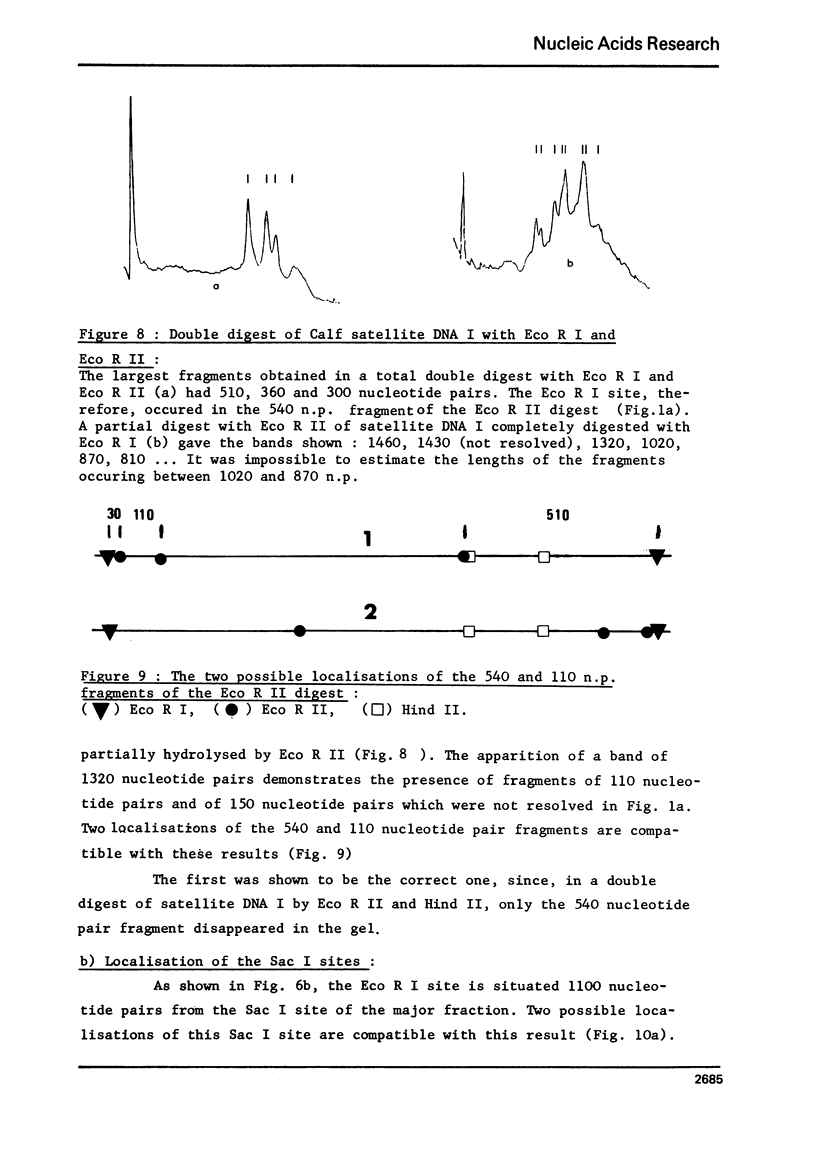
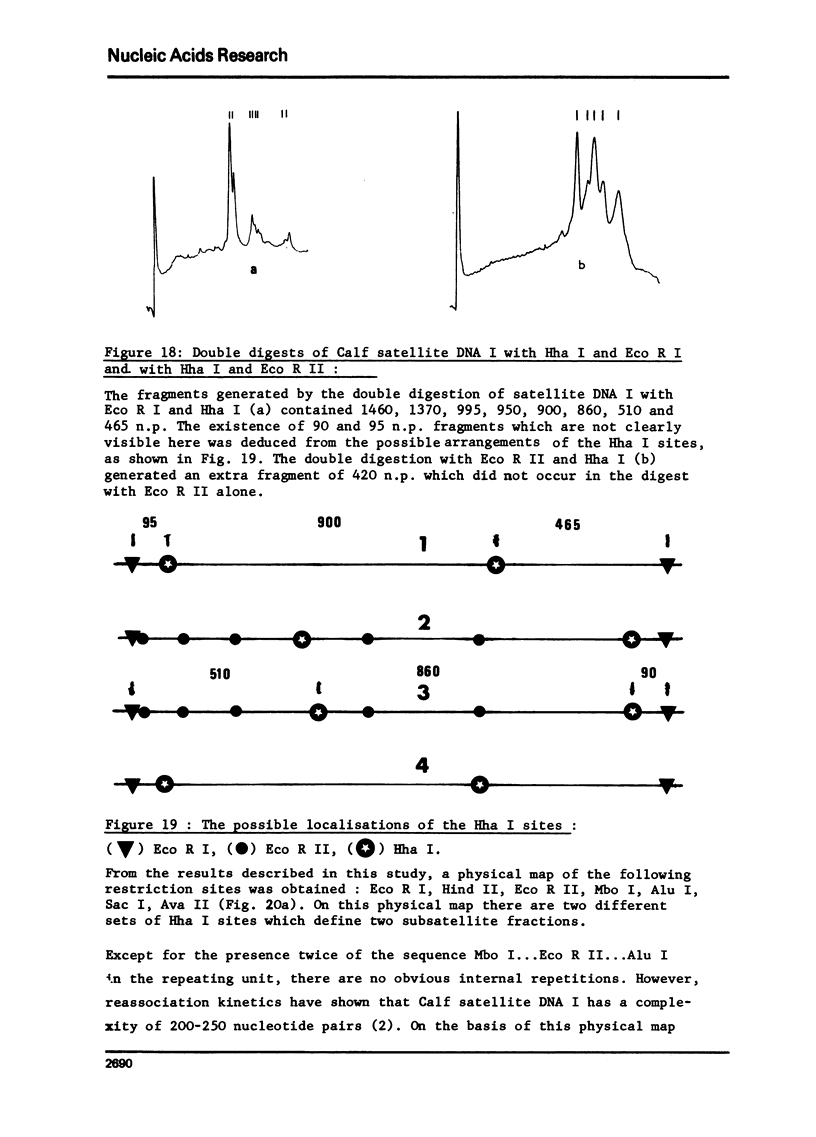
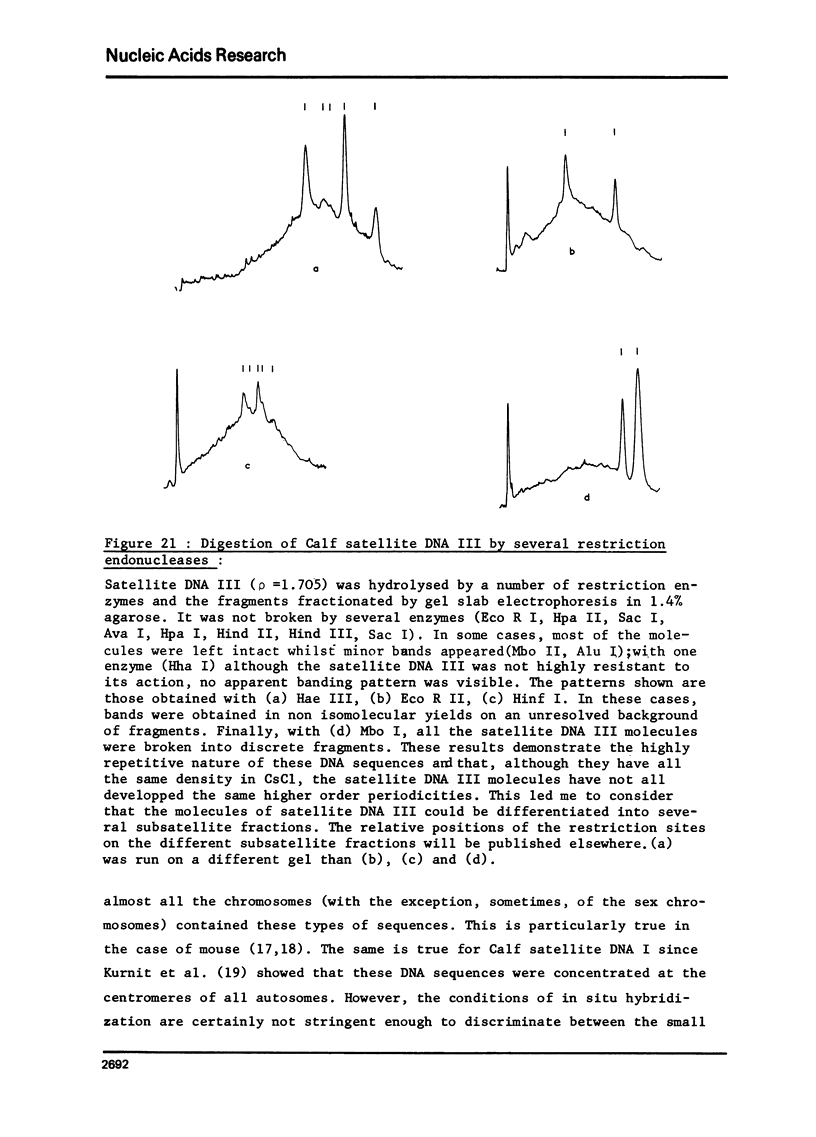
Calf satellite DNA I (p = 1.715) has been hydrolysed by a number or restriction endonucleases. It consists of a repeating unit of 1460 nucleotide pairs within which the sites of Eco R II Mbo I, Sac I, Alu I, Ava II and Hha I were localised in comparison with those of Eco R I and Hind II. The distribution of the Hpa II, Sac I, Hha I, Hinf I and Mbo II sites within calf satellite DNA I, as well as that of several restriction endonuclease sites within calf satellite DNA III (p = 1.705) allowed me to define subsatellite fractions. Furthermore, some of the sites of the CpG containing restriction enzymes Hpa II and Hha I are lacking. The possible implications of these results are discussed.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biro P. A., Carr-Brown A., Southern E. M., Walker P. M. Partial sequence analysis of mouse satellite DNA evidence for short range periodicities. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):71–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90405-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M. R. Bovine satellite I DNA consists of repetitive units 1,400 base pairs in length. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):288–292. doi: 10.1038/251288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K., Nathans D. Specific cleavage of simian virus 40 DNA by restriction endonuclease of Hemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2913–2917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Polan M. L., Gall J. G. Satellite DNA sequences of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):665–692. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Thiery J. P., Bernardi G. An analysis of the bovine genome by Cs2SO4-Ag density gradient centrifugation. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 15;80(1):177–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry K., Poon R., Whitcome P., Idriss J., Salser W., Mazrimas J., Hatch F. Nucleotide sequence of HS-beta satellite DNA from kangaroo rat Dipodomys ordii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2642–2646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Atherton D. D. Satellite DNA sequences in Drosophila virilis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):633–664. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grippo P., Iaccarino M., Parisi E., Scarano E. Methylation of DNA in developing sea urchin embryos. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 14;36(2):195–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90375-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R., Pugh J. E. DNA modification mechanisms and gene activity during development. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. R., Wetmur J. G. Length dependence of the kinetic complexity of mouse satellite DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 19;52(4):1148–1155. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90620-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Hess I., Zachau H. G. Highly regular arrangement of a restriction-nuclease-sensitive site in rodent satellite DNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):501–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W. Chromosomal and nuclear location of mouse satellite DNA in individual cells. Nature. 1970 Mar 7;225(5236):912–915. doi: 10.1038/225912a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnit D. M., Shafit B. R., Maio J. J. Multiple satellite deoxyribonucleic acids in the calf and their relation to the sex chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 15;81(3):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Siegel W., Sklar J. Hemophilus aegyptius restriction edonuclease cleavage map of the simian virus 40 genome and its colinear relation with the hemophilus influenzae cleavage map of SV40. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):105–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Beatty B. R. Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Chromosomal localization of mouse satellite DNA. Science. 1970 Jun 12;168(3937):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3937.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Unequal crossover and the evolution of multigene families. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:507–513. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Base sequence and evolution of guinea-pig alpha-satellite DNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 22;227(5260):794–798. doi: 10.1038/227794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Long range periodicities in mouse satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90404-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Pan J., Zain S., Weissman S. M. The mapping and ordering of fragments of SV40 DNA produced by restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Jun;1(6):727–752. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.6.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D., McCallum M. Mismatching and the reassociation rate of mouse satellite DNA. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):83–85. doi: 10.1038/newbio232083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. M. Origin of satellite DNA. Nature. 1971 Jan 29;229(5283):306–308. doi: 10.1038/229306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink P. C., Brown D. D. Denaturation map of the ribosomal DNA of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



