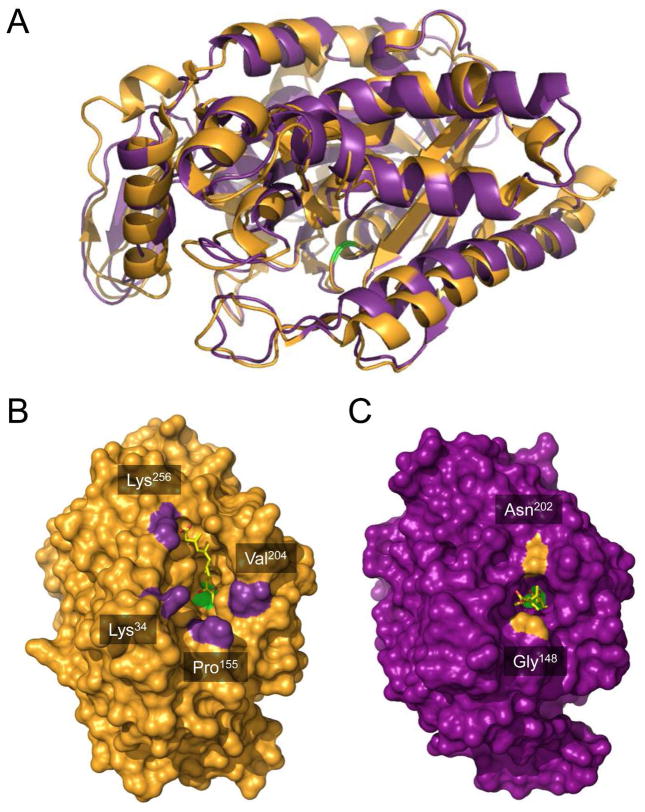
Figure 4.
Comparison of hymeglusin-bound structures of eukaryotic HMG-CoA synthase and bacterial mvaS. (A) The crystal structure of hymeglusin-bound Brassica juncea HMG-CoA synthase (PDB code 2F9A, shown in orange cartoon) was superimposed with that of hymeglusin-bound E. faecalis mvaS (PDB code 3V4X, shown in purple cartoon). Positions of the respective catalytic cysteine residues are highlighted with green color. (B) Brassica juncea HMG-CoA synthase shown as a molecular surface in an identical orientation to panel A. Bound hymeglusin is shown as a yellow ball-and-stick. The positions of landmark residues that define the boundaries of the active site entrance are indicated and highlighted in purple. (C) Enterococcus faecalis mvaS shown as a molecular surface in an identical orientation to panel A. Bound hymeglusin is shown as a yellow ball-and-stick. The positions of landmark residues that define the boundaries of the active site entrance are indicated and highlighted in orange.