Abstract
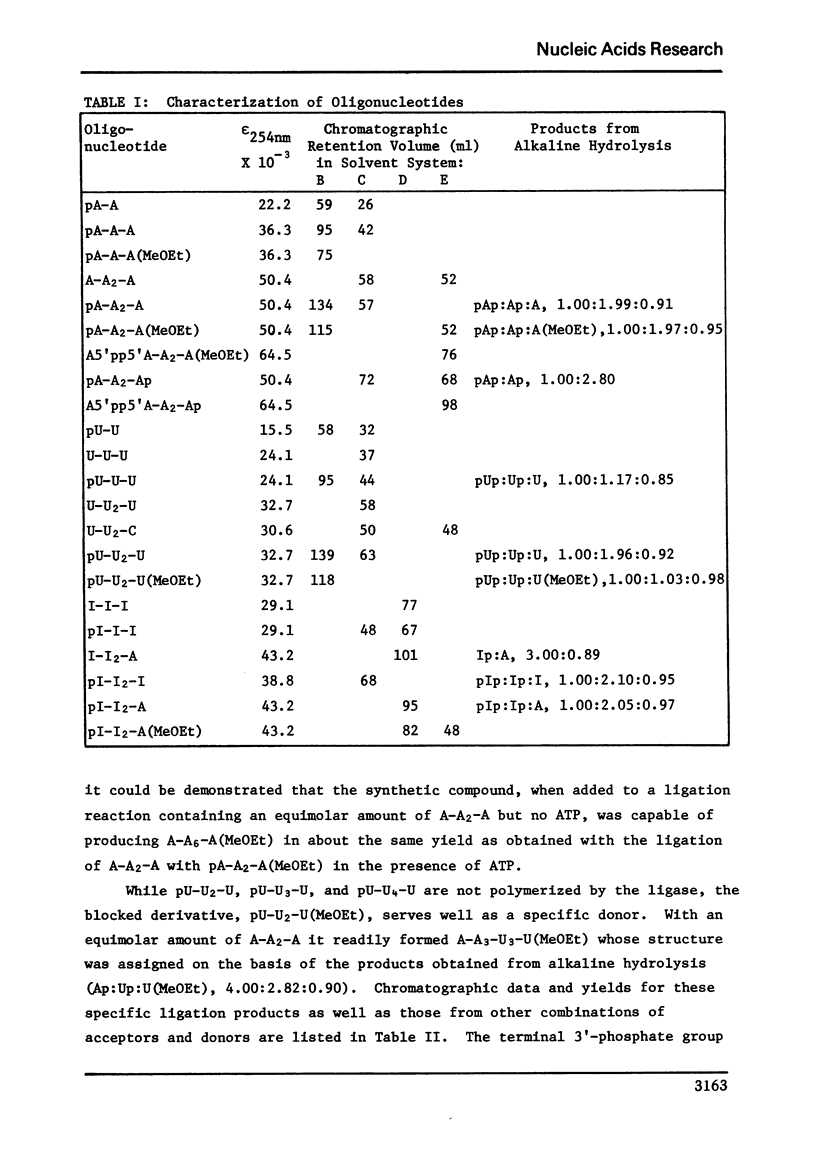
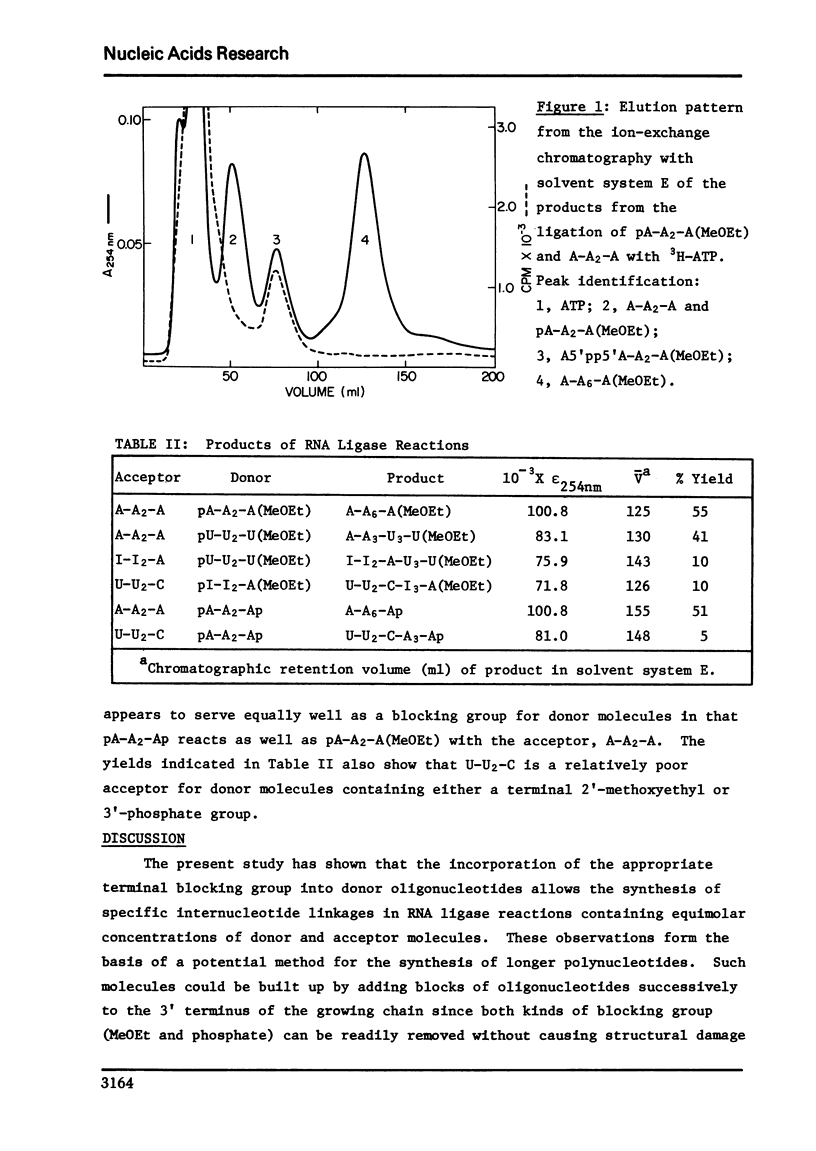
Under the conditions that RNA ligase converts the tetranucleotide, pA-A2-A, to larger polynucleotides, no such polymerization can be detected with the derivative, pA-A2-A(MeOEt), that possesses a terminal 2'-0-(alpha-methoxyethyl) group. The protection against self condensation offered by the methoxyethyl group in this system allows the specific joining of donor and acceptor oligonucleotides in reaction mixtures containing equimolar concentrations of the two species. Thus, the enzyme, together with ATP, converts equimolar quantities of A-A2-A and pA-A2-A(MeOEt) to A-A6-A(MeOEt) in 55% yield, while a similar reaction with A-A2-A and pU-U2-U(MeOEt) results in a 40% yield of A-A3-U3-U(MeOEt). The intermediate in these ligations is a disubstituted pyrophosphate composed of the donor molecule and the adenylate moiety deriving from ATP. In the case of the intermediate arising from the blocked adenosine tetranucleotide, the assigned structure, A5'pp5'A-A2-A(MeOEt), has been confirmed by chemical synthesis. The pyrophosphate derivative is able to participate in joining reactions in the absence of ATP. These observations constitute an efficient approach to the synthesis of larger polynucleotides from a specific series of oligonucleotide blocks since (i), the methoxyethyl group can be easily introduced into each oligonucleotide using the single addition reaction catalyzed by polynucleotide phosphorylase in the presence of a 2'-0-(alpha-methoxyethyl)nucleoside 5'-diphosphate, and (ii), the blocking group may be readily removed under mild conditions after each successive ligation reaction. Two other octanucleotides, I-I2-A-U3-U and U-U2-C-I3-A, have also been synthesized by this method, and these molecules correspond (with I substituting for G) to sequences appearing near the 3' terminus of the 6S RNA transcribed from phage lambda DNA. The terminal 3'-phosphate group serves equally well as a blocking group for specific ligation reactions in that the ligase converts equimolar amounts of A-A2-A and pA-A2-Ap to A-A6-Ap in 50% yield.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asteriadis G. T., Armbruster M. A., Gilham P. T. Separation of oligonucleotides, nucleotides, and nucleosides on columns of polystyrene anion-exchangers with solvent systems containing ethanol. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):64–74. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. N., Gilham P. T. "Single Addition" substrates for the synthesis of specific oligoribonucleotides with polynucleotide phosphorylase. Synthesis of 2'-(alpha-methoxyethy) nucleoside 5'-diphosphates. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3152–3158. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. N., Mackey J. K., Wiebers J. L., Gilham P. T. 2'-O-(alpha-methoxyethyl)nucleoside 5'-diphosphates as "single-addition" substrates in the synthesis of specific oligoribonucleotides with polynucleotide phosphorylase. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):3956–3962. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston J. W., Silber R., Malathi V. G., Hurwitz J. Studies on ribonucleic acid ligase. Characterization of an adenosine triphosphate-inorganic pyrophosphate exchange reaction and demonstration of an enzyme-adenylate complex with T4 bacteriophage-induced enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7447–7456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., Kallenbach N. R. Determination of recognition sites of T4 RNA ligase on the 3'-OH and 5' -P termini of polyribonucleotide chains. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):452–454. doi: 10.1038/254452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., Klein T., Littauer U. Z. T4 RNA ligase: substrate chain length requirements. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 15;46(1):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., Littauer U. Z. Covalent joining of phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid half-molecules by T4 RNA ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3741–3745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith G., Gilham P. T. Stepwise degradation of polyribonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3601–3606. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Last J. A., Anderson W. F. Purification and properties of bacteriophage T4-induced RNA ligase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 May;174(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M., Radding C. M. Nucleotide sequence of a ribonucleic acid transcribed in vitro from lambda phage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5120–5139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linné T., Oberg B., Philipson L. RNA ligase activity in phage-infected bacteria and animal cells. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 15;42(1):157–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackey J. K., Gilham P. T. New approach to the synthesis of polyribonucleotides of defined sequence. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):551–553. doi: 10.1038/233551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka E., Nishikawa S., Sugiura M., Ikehara M. Joining of ribooligonucleotides with T4 RNA ligase and identification of the oligonucleotide-adenylate intermediate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jun;3(6):1613–1623. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.6.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silber R., Malathi V. G., Hurwitz J. Purification and properties of bacteriophage T4-induced RNA ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sninsky J. J., Bennett G. N., Gilham P. T. 'Single addition' and 'transnucleotidation' reactions catalyzed by polynucleotide phosphorylase. Effect of enzymatic removal of inorganic phosphate during reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Dec;1(12):1665–1674. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.12.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snopek T. J., Sugino A., Agarwal K. L., Cozzarelli N. R. Catalysis of DNA joining by bacteriophage T4 RNA ligase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):417–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C., Uhlenbeck O. C., Bedows E., Gumport R. I. T4-induced RNA ligase joins single-stranded oligoribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



