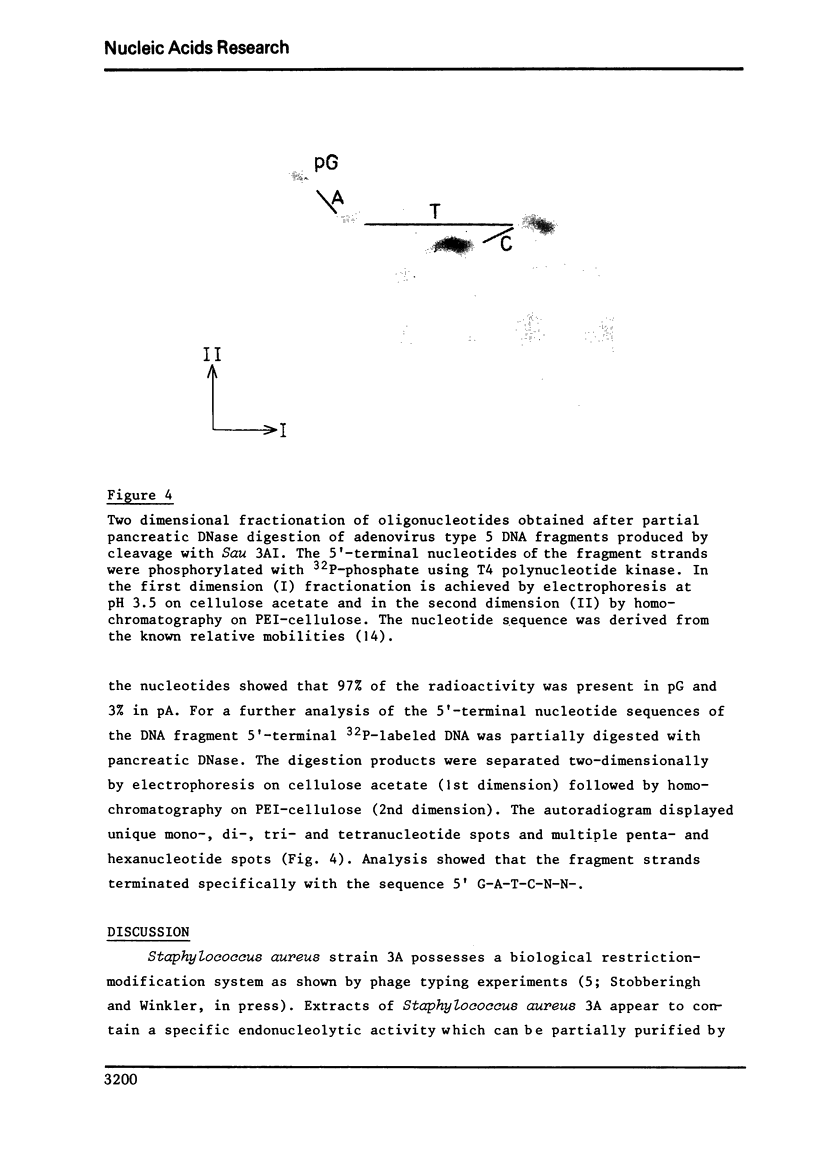
Abstract
A specific endonuclease, Sau 3AI, has been partially purified from Staphylococcus aureus strain 3A by DEAE-cellulose chromatography. The enzyme cleaves adenovirus type 5 DNA many times, SV40 DNA eight times but does not cleave double-stranded phi X174 DNA. It recognizes the sequence (see article) and cleaves as indicated by the arrows. Evidence is presented that this enzyme plays a role in the biological restriction-modification system of Staphylococcus aureus strain 3A.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bron S., Murray K., Trautner T. A. Restriction and modification in B. subtilis. Purification and general properties of a restriction endonuclease from strain R. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 30;143(1):13–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00269416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F. Chromatography of 32P-labelled oligonucleotides on thin layers of DEAE-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Sedat J., Ziff E. Direct determination of DNA nucleotide sequences: structure of a fragment of bacteriophage phiX172 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):377–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klesius P. H., Schuhardt V. T. Use of lysostaphin in the isolation of highly polymerized deoxyribonucleic acid and in the taxonomy of aerobic Micrococcaceae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):739–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.739-743.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKHAM R., SMITH J. D. The structure of ribonucleic acid. I. Cyclic nucleotides produced by ribonuclease and by alkaline hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1952 Dec;52(4):552–557. doi: 10.1042/bj0520552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans D., Smith H. O. Restriction endonucleases in the analysis and restructuring of dna molecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:273–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Nathans D. Letter: A suggested nomenclature for bacterial host modification and restriction systems and their enzymes. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 15;81(3):419–423. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Wilcox K. W. A restriction enzyme from Hemophilus influenzae. I. Purification and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobberinghi E. E., Winkler K. C. Proceedings: Restrictionless mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(2):212–213. doi: 10.1007/BF02565054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussenbach J. S. On the fate of adenovirus DNA in KB cells. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):969–972. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]