Abstract
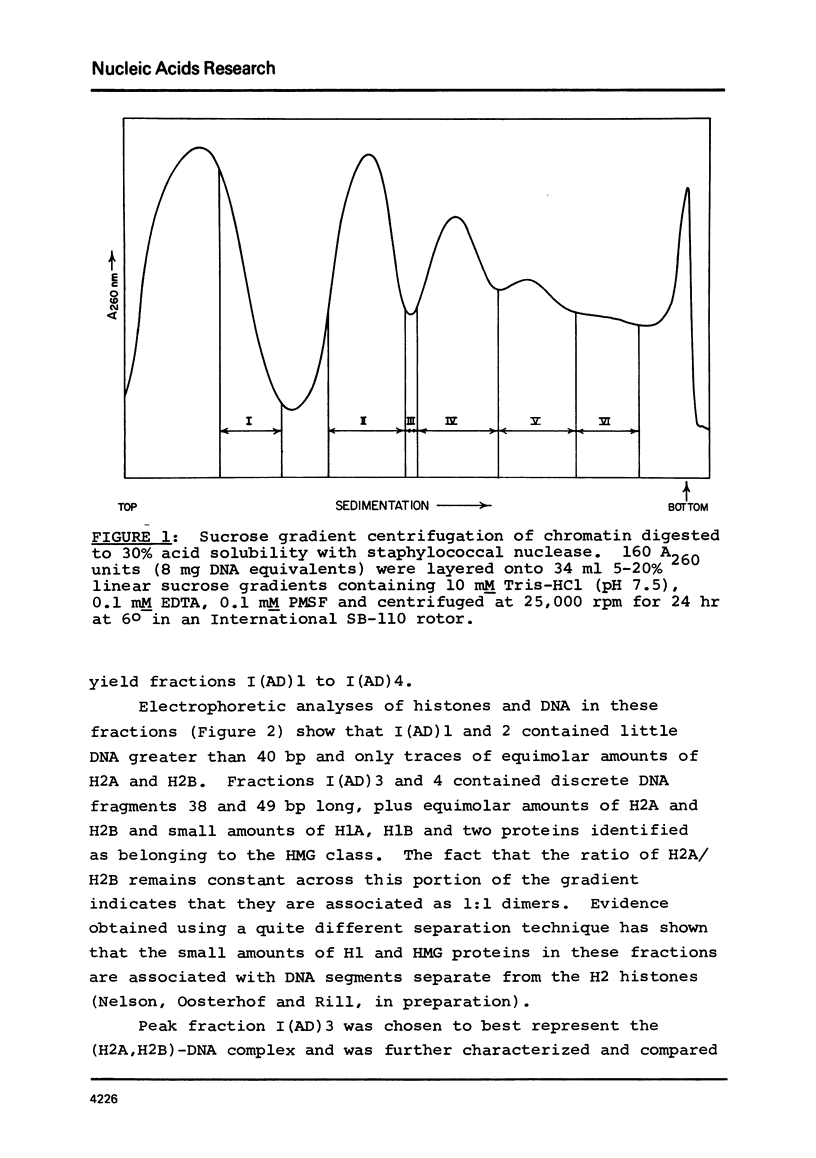
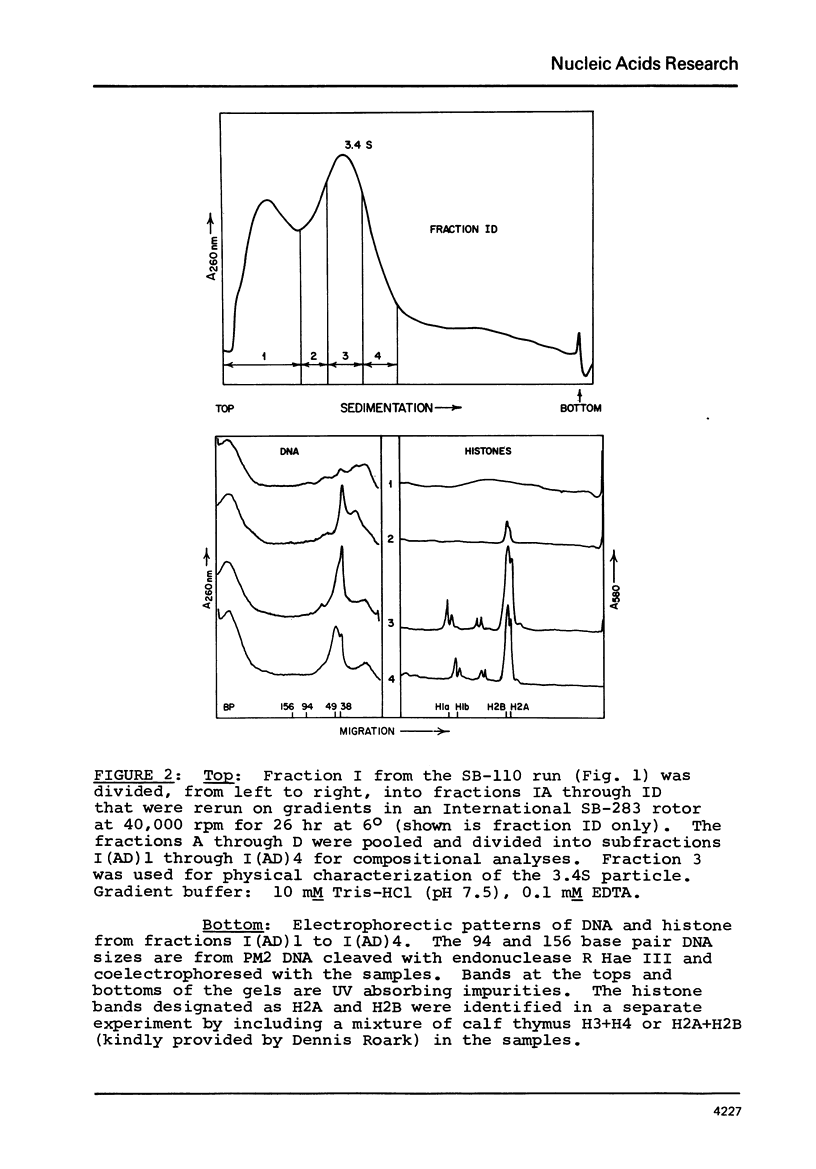
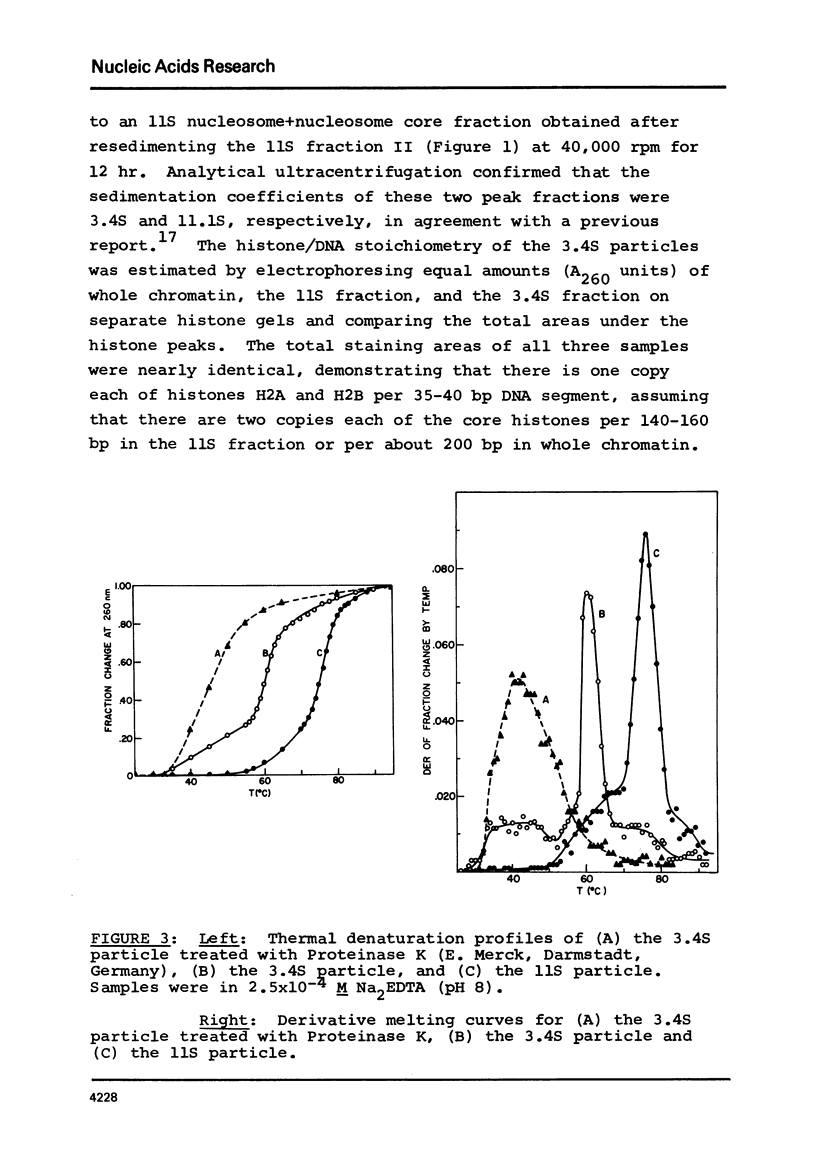
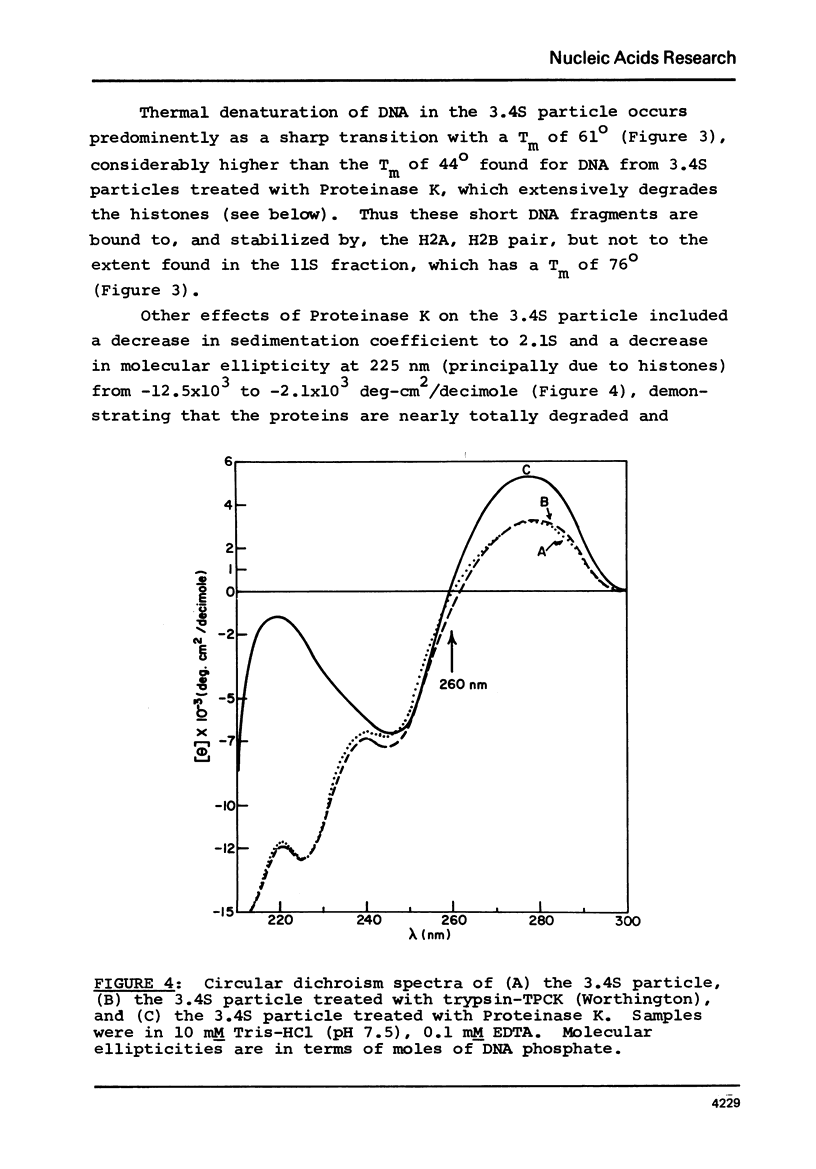
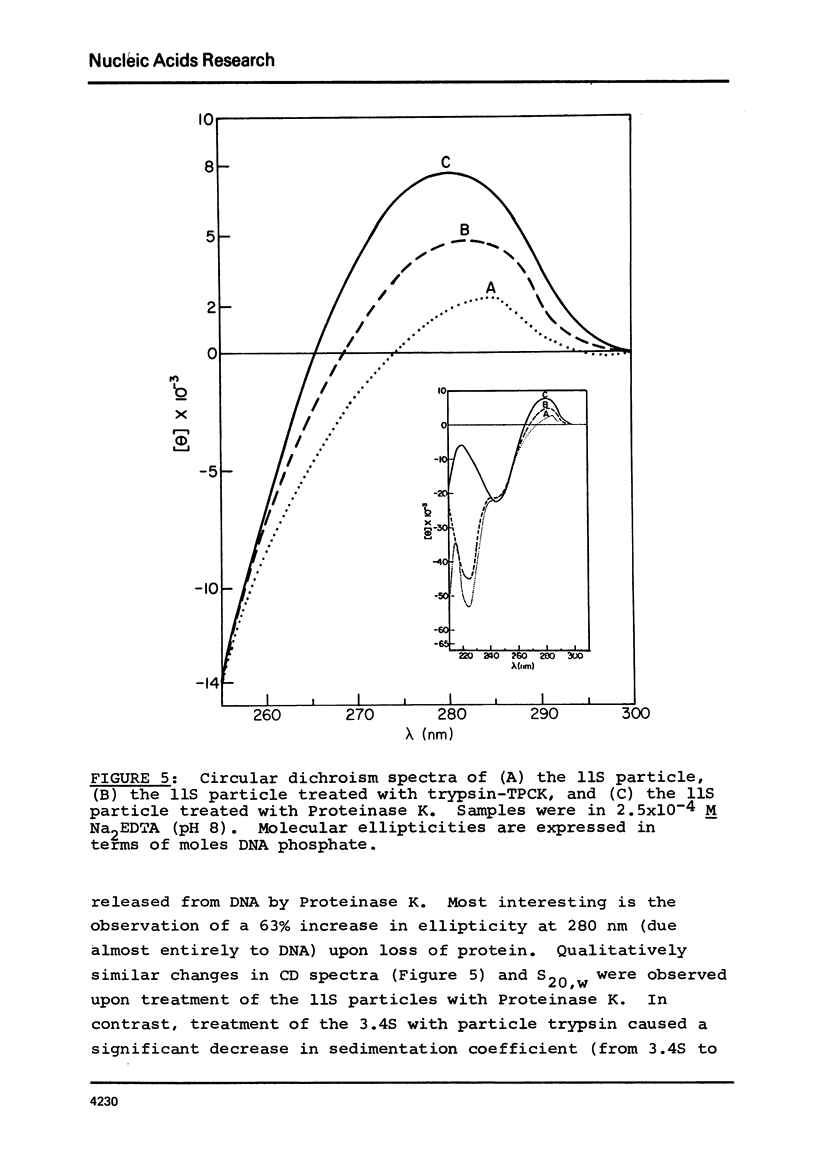
Two specific slow sedimenting nucleoprotein particles containing equimolar amounts of histones H2A and H2B and 38 or 49 base pair (bp) lengths of DNA have been isolated by centrifugation on sucrose gradients. The 3.4S particles containing 38 bp DNA and H2A+H2B thermally denature at 61 degrees, considerably higher than Proteinase K treated particles (44 degrees), but lower than 11S nucleosomes (76 degrees). Treatment with Proteinase K increases the circular dichroism of 3.4S particles at 280 nm by 63% and decreases the sedimentation coefficient to 2.1S. These results indicate that H2A and H2B are proximate along DNA in nucleosomes and alone can alter the optical activity and perhaps conformation of local regions of DNA.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R., Cedar H., Felsenfeld G. Synthesis of globin ribonucleic acid from duck-reticulocyte chromatin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2029–2032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axel R., Melchior W., Jr, Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. Specific sites of interaction between histones and DNA in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4101–4105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Pollard H. B. The presence of F3-F2a1 dimers and F1 oligomers in chromatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):282–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalkley R. Histone propinquity using imidoesters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 19;64(2):587–594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Jr, Isenberg I. Interactions of histone LAK (f2a2) with histones KAS (f2b) and GRK (f2a1). Biochemistry. 1974 May 7;13(10):2098–2104. doi: 10.1021/bi00707a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. I. Isolation of a histone IIb1-IIb2 complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 15;54(4):1588–1594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure; oligomers of the histones. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):865–868. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. J., Bonner J. Interaction of histone half-molecules with deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1461–1470. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson H. G., McCarthy B. J. Histone-histone associations within chromatin. Cross-linking studies using tetranitromethane. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 11;14(5):1073–1078. doi: 10.1021/bi00676a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson H. G., Shetlar M. D., McCarthy B. J. Histone-histone interactions within chromatin. Crosslinking studies using ultraviolet light. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):2002–2007. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Kornberg R. D. Action of micrococcal nuclease on chromatin and the location of histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):393–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Subunit structure of chromatin. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):249–251. doi: 10.1038/251249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. Preparation of native chromatin and damage caused by shearing. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Spheroid chromatin units (v bodies). Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Once more into the breach. Nature. 1970 Jul 4;227(5253):1–1. doi: 10.1038/227001a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterhof D. K., Hozier J. C., Rill R. L. Nucleas action on chromatin: evidence for discrete, repeated nucleoprotein units along chromatin fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):633–637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rill R. L., Nelson D. A., Oosterhof D. K., Hozier J. C. Structural repeat units of Chinese hamster ovary chromatin. Evidence for variations in repeat unit DNA size in higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Apr;4(4):771–789. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rill R. L., Oosterhof D. K., Hozier J. C., Nelson D. A. Heterogeneity of chromatin fragments produced by micrococcal nuclease action. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1525–1538. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw B. R., Herman T. M., Kovacic R. T., Beaudreau G. S., Van Holde K. E. Analysis of subunit organization in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skandrani E., Mizon J., Sautière P., Biserte G. Etude de la fraction F2b des histones de thymus de veau. Biochimie. 1972;54(10):1267–1272. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Chromatin structure as probed by nucleases and proteases: evidence for the central role of histones H3 and H4. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. A comparison of the digestion of nuclei and chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2915–2920. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lente F., Jackson J. F., Weintraub H. Identification of specific crosslinked histones after treatment of chromatin with formaldehyde. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Georgiev G. P. Heterogeneity of chromatin subunits in vitro and location of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):477–492. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Release of discrete subunits after nuclease and trypsin digestion of chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1212–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Removal of histone H1 exposes a fifty base pair DNA segment between nucleosomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3307–3314. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock C. L., Frado L. L. Thermal denaturation of subchromosomal particles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):403–410. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80342-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



