Abstract
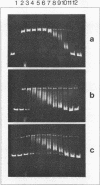
A DNA-relaxing enzyme which catalyzes the conversion of superhelical DNA to a non-superhelical covalently closed form has been purified from Micrococcus luteus to near homogeneity by two chromatographic steps. The enzyme is a single polypeptide chain. As determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate - polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and gel filtration on Sephadex G 150, the molecular weight is 115,000. The DNA-relaxing activity determined as a function of enzyme concentration follows a sigmoidal curve. The enzyme requires Mg++ for activity. In the presence of 4.5 mM Mg++ addition of 50-250 mM KCl yields incompletely relaxed DNA molecules (intermediates); intermediates are also observed in the absence of KCl, when the reaction is carried out at 0 degree C or at Mg++ concentrations exceeding 10 mM.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baase W. A., Wang J. C. An omega protein from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4299–4303. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W. R., Ressner E. C., Kates J., Patzke J. V. A DNA nicking-closing enzyme encapsidated in vaccinia virus: partial purification and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1841–1845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrington M. G., Morgan A. R. The purification from Escherichia coli of a protein relaxing superhelical DNA. Can J Biochem. 1976 Apr;54(4):301–306. doi: 10.1139/o76-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., Dulbecco R. An activity from mammalian cells that untwists superhelical DNA--a possible swivel for DNA replication (polyoma-ethidium bromide-mouse-embryo cells-dye binding assay). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Evidence for an intermediate with a single-strand break in the reaction catalyzed by the DNA untwisting enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3488–3491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., McConaughy B. L. Purification and characterization of the DNA untwisting enzyme from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4638–4642. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Canelo E. S., Sinsheimer R. L. DNA of bacteriophage PM2: a closed circular double-stranded molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1164–1168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Upholt W. B., Vinograd J. A buoyant method for the determination of the superhelix density of closed circular DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. C., Kushner S. R., Grossman L. Enzymatic repair of DNA, 1. Purification of two enzymes involved in the excision of thymine dimers from ultraviolet-irradiated DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):144–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Characterization of purified DNA-relaxing enzyme from human tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2550–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung V. T., Wang J. C. Purification and characterization of an omega protein from Micrococcus luteus. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5398–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman R. M. A deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus luteus (Micrococcus lysodeikticus) isolated on deoxyribonucleic acid-cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6222–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Morgan A. R. Partial purification of "omega" protein from calf thymus. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5205–5209. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Shure M., Tang D., Vinograd J., Vosberg H. P. Action of nicking-closing enzyme on supercoiled and nonsupercoiled closed circular DNA: formation of a Boltzmann distribution of topological isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4280–4284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebring E. D., Kelly T. J., Jr, Thoren M. M., Salzman N. P. Structure of replicating simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid molecules. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):478–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.478-490.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P., Grossman L. I., Vinograd J. Isolation and partial characterisation of the relaxation protein from nuclei of cultured mouse and human cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):79–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P., Vinograd J. Purification and demonstration of the enzymatic character of the nicking-closing protein from mouse L cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):456–464. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91167-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]