Abstract
Hen oviduct form B DNA-dependent RNA polymerase has been extensively purified and its properties analysed. It seems likely to consist of a mixture of two forms of the type observed in tissues from other species. Furthermore using S1 nuclease to digest single-stranded DNA, we show that although form B can transcribe double-stranded DNA template it has a very strong preference for single-stranded regions. Also the rate of elongation on native DNA in vitro was measured and is an order of magnitude slower than that reported to be operative in vivo.
Full text
PDF


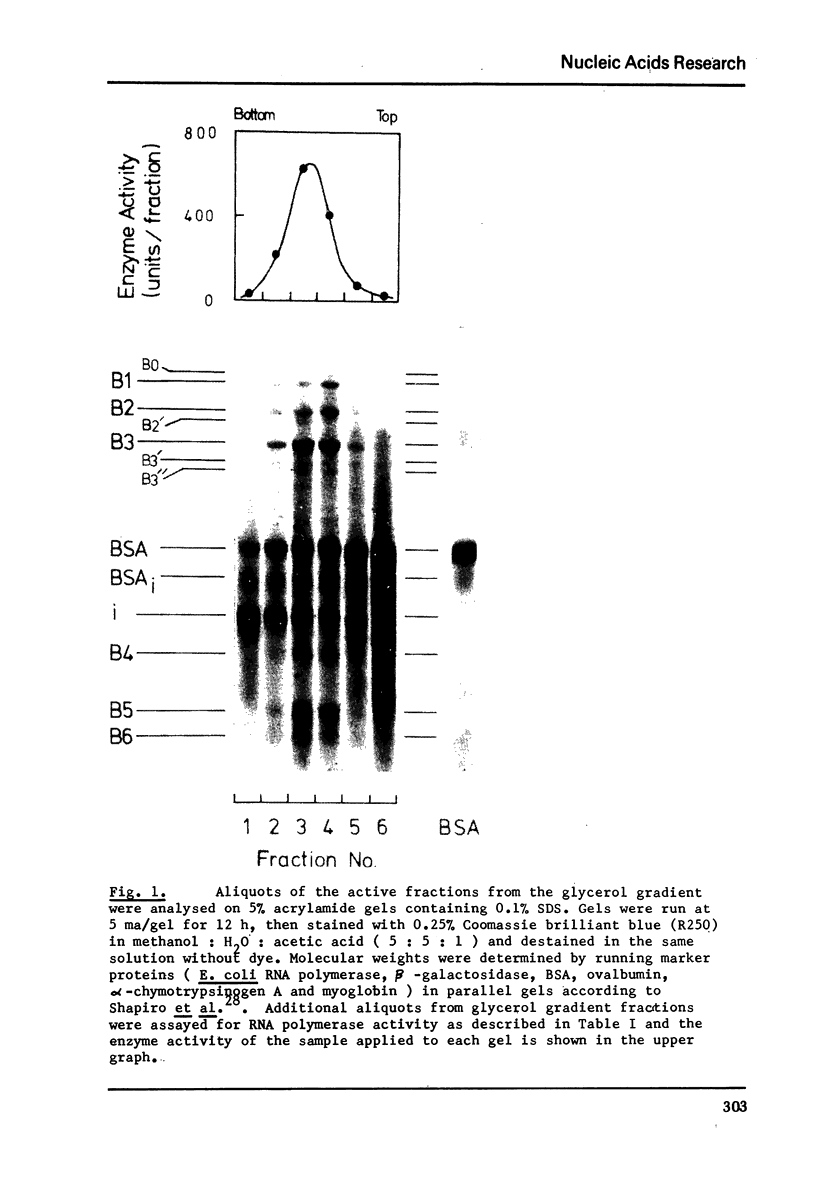

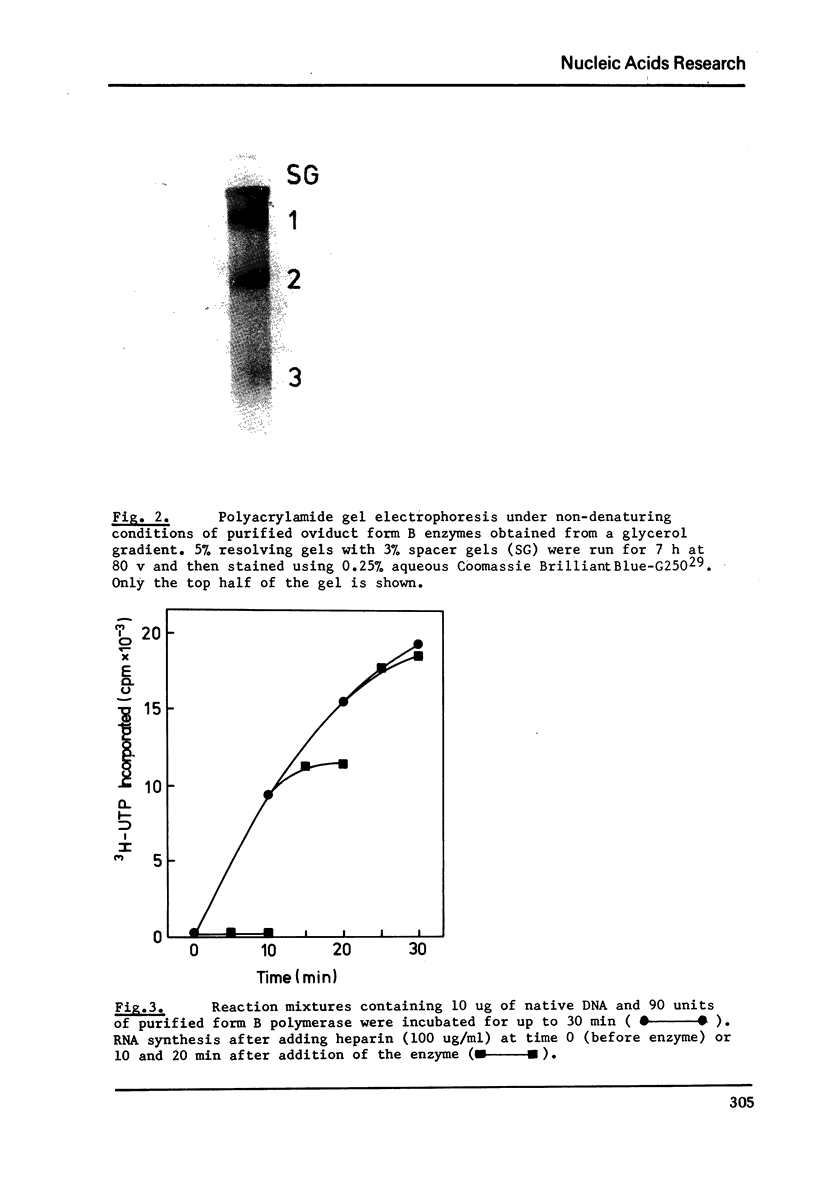

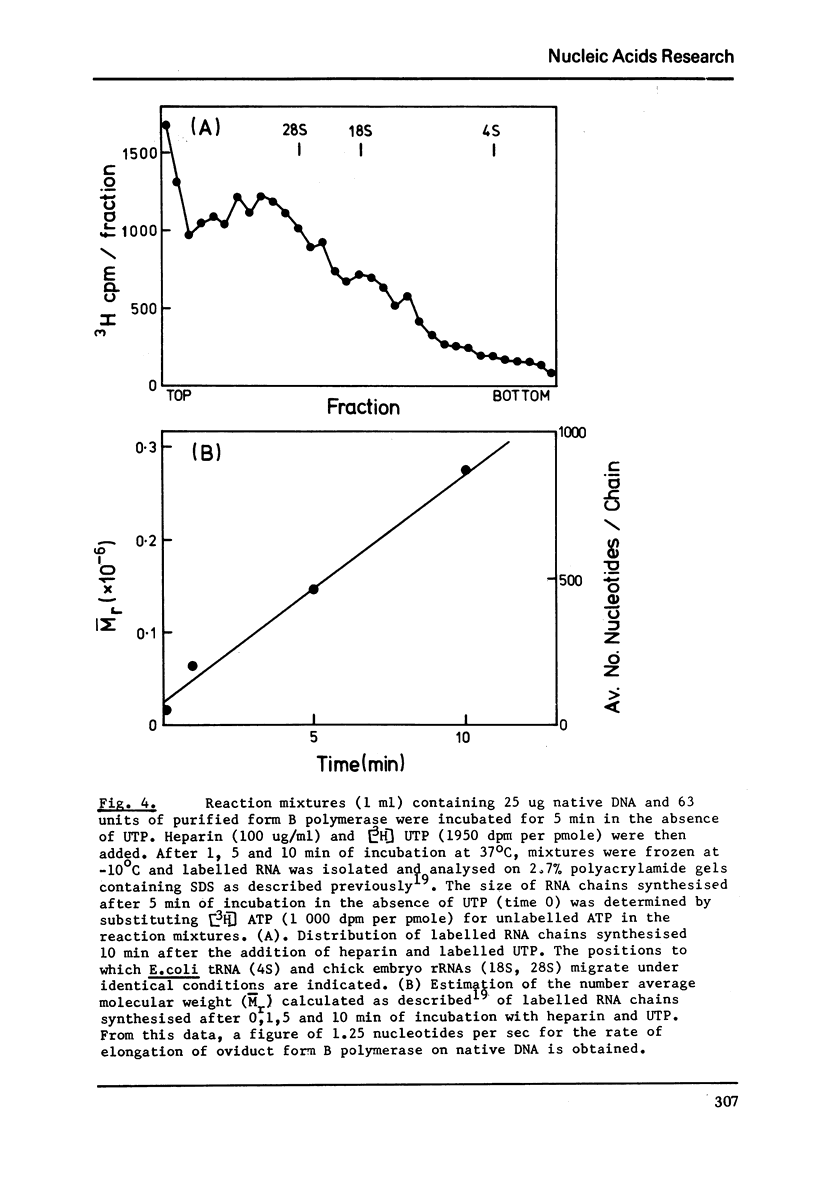

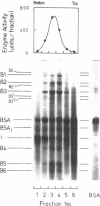
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. A new method for the large scale purification of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H.W. Purification of the rat liver form B DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. F., Haines M. E., Carey N. H. Modification of the template capacity of chick-oviduct chromatin for form-B RNA polymerase by estradiol. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 1;32(3):513–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. F. Transcription of high-molecular-weight RNA from hen-oviduct chromatin by bacterial and endogenous form-B RNA polymerases. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dezélée S., Sentenac A. Role of DNA-RNA hybrids in eukaryotes. Purification and properties of yeast RNA polymerase B. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):41–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Mauro E., Hollenberg C. P., Hall B. D. Transcription in yeast: a factor that stimulates yeast RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2818–2822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diezel W., Kopperschläger G., Hofmann E. An improved procedure for protein staining in polyacrylamide gels with a new type of Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):617–620. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T. Mammalian RNA polymerases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1973;13:93–126. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Altered characteristics of mammalian RNA polymerase following solubilization from nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Sep 6;32(5):831–838. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C. The cocoonase zymogen cells of silk moths: a model of terminal cell differentiation for specific protein synthesis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1972;7:125–191. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 3. Purification of calf-thymus BI and BII enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Nuret P., Chambon P. Structural evidence for two alpha-amanitin sensitive RNA polymerases in calf thymus. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Purification of RNA polymerase B activity from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondal H., Ganguly A., Das A., Mandal R. K., Biswas B. B. Ribonucleic acid polymerase from eukaryotic cells. Effects of factors and rifampicin on the activity of RNA polymerase from chromatin of coconut nuclei. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 23;28(1):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., McGuire W. L. Studies on the mechanism of action of progesterone in regulation of the synthesis of specific protein. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):654–664. doi: 10.1172/JCI105761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponta H., Ponta U., Wintersberger E. Purification and properties of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases from yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 18;29(1):110–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifart K. H., Juhasz P. P., Benecke B. J. A protein factor from rat-liver tissue enhancing the transcription of native templates by homologous RNA polymerase B. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):181–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Keller W. Mammalian deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases. I. Purification and properties of an -amanitin-sensitive ribonucleic acid polymerase and stimulatory factors from HeLa and KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3777–3788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Blatti S. P., Rutter W. J. Molecular structures of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases (II) from calf thymus and rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2994–2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]