Abstract
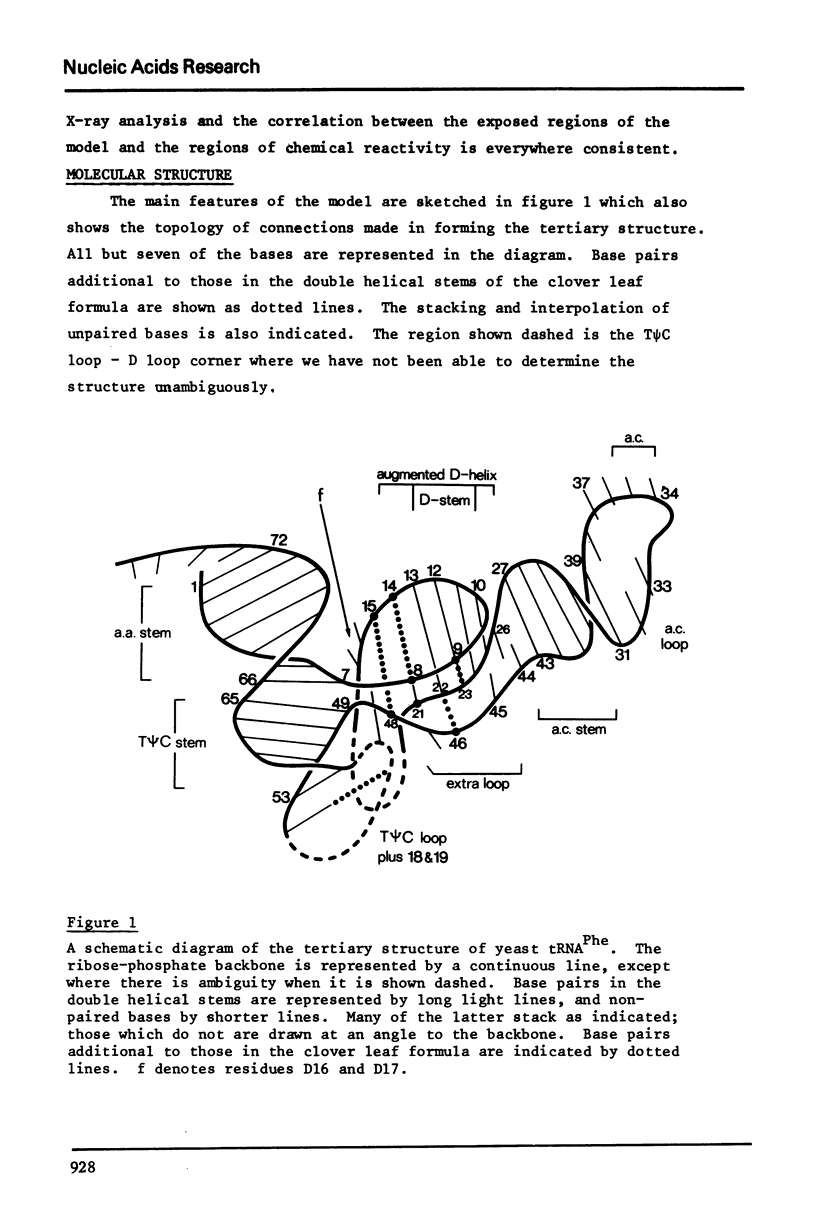
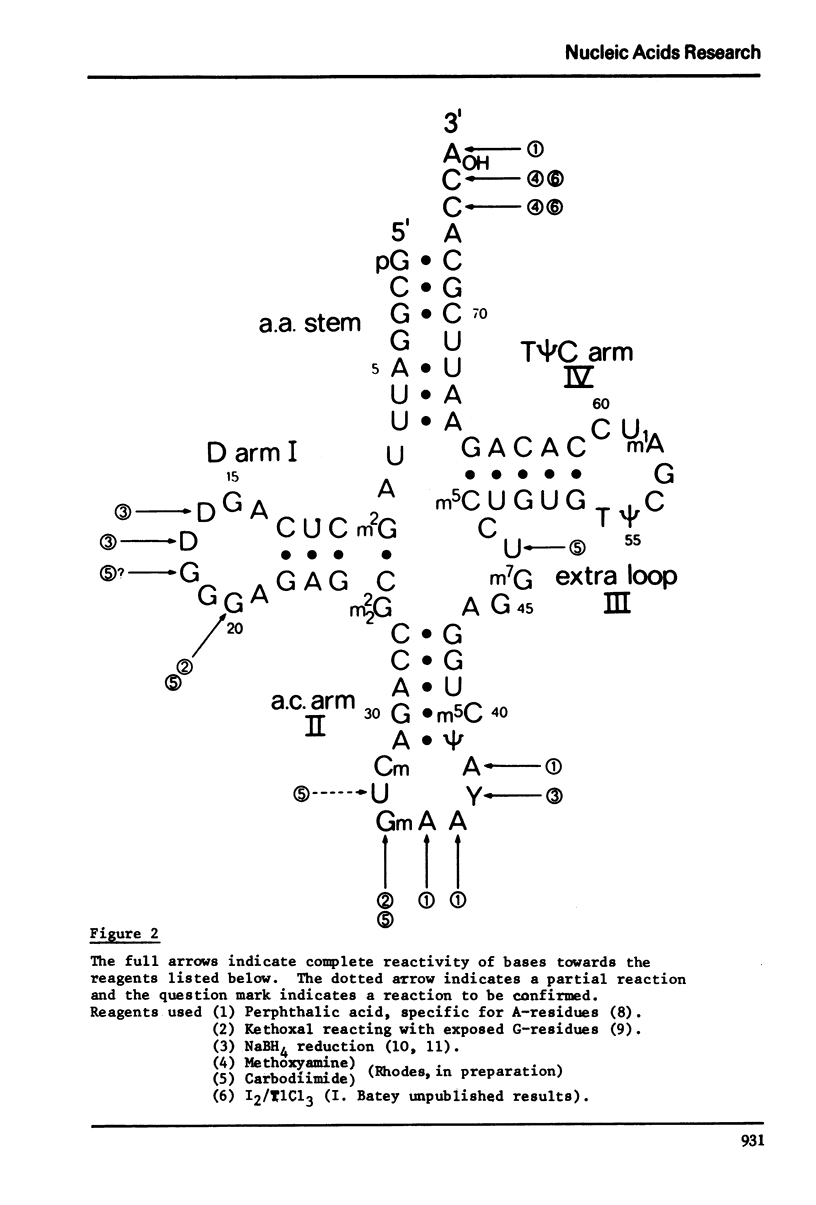
The bases of yeast tRNAPhe which react with carbodiimide and methoxyamine have been determined and this information has been combined with chemical modification studies of other workers to produce a composite picture of base accessibility in this tRNA. The results are compared with the three-dimensional structure which we have recently determined. The bases which react chemically lie in exposed positions in the three-dimensional model and those which do not are either in the double helical stem regions or else are involved in maintaining the tertiary structure through pairing or stacking interactions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cashmore A. R., Brown D. M., Smith J. D. Selective reaction of methoxyamine with cytosine bases in tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 28;59(2):359–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. E., Cashmore A. R., Brown D. M. Selective modification of uridine and guanosine residues in tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 28;68(3):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. E., Ish-Horowicz D. Selective modification of cytidine, uridine, guanosine and pseudouridine residues in Escherichia coli leucine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):375–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. E. Selective modification of cytidine and uridine residues in Escherichia coli formylmethionine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 15;75(3):533–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer F., Doepner H., Haar F V. D., Schlimme E., Seidel H. On the conformation of transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1384–1391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer F. Three-dimensional structure of tRNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1971;11:391–421. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Involvement of 1-methyladenosine and 7-methylguanosine in the three-dimensional structure of (yeast)tRNAPhe. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jan;18(2):292–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. On the specificity of the reduction of transfer ribonucleic acids with sodium borohydride. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):549–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. Detailed molecular model for transfer ribonucleic acid. Nature. 1969 Nov 22;224(5221):759–763. doi: 10.1038/224759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M. Inactivation of yeast phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid by kethoxal. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 8;10(12):2223–2227. doi: 10.1021/bi00788a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Three forms of the 5.8-S ribosomal RNA species in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 3;41(1):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suddath F. L., Quigley G. J., McPherson A., Sneden D., Kim J. J., Kim S. H., Rich A. Three-dimensional structure of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA at 3.0angstroms resolution. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):20–24. doi: 10.1038/248020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



