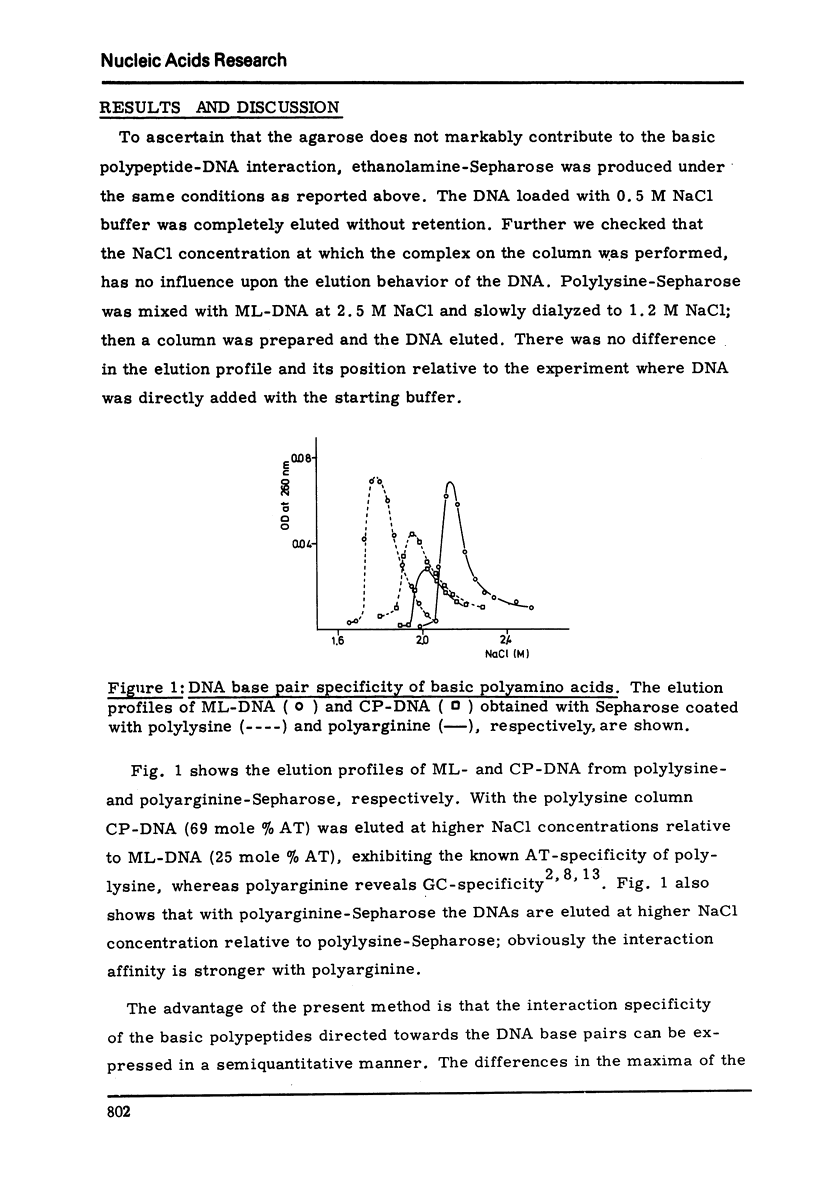
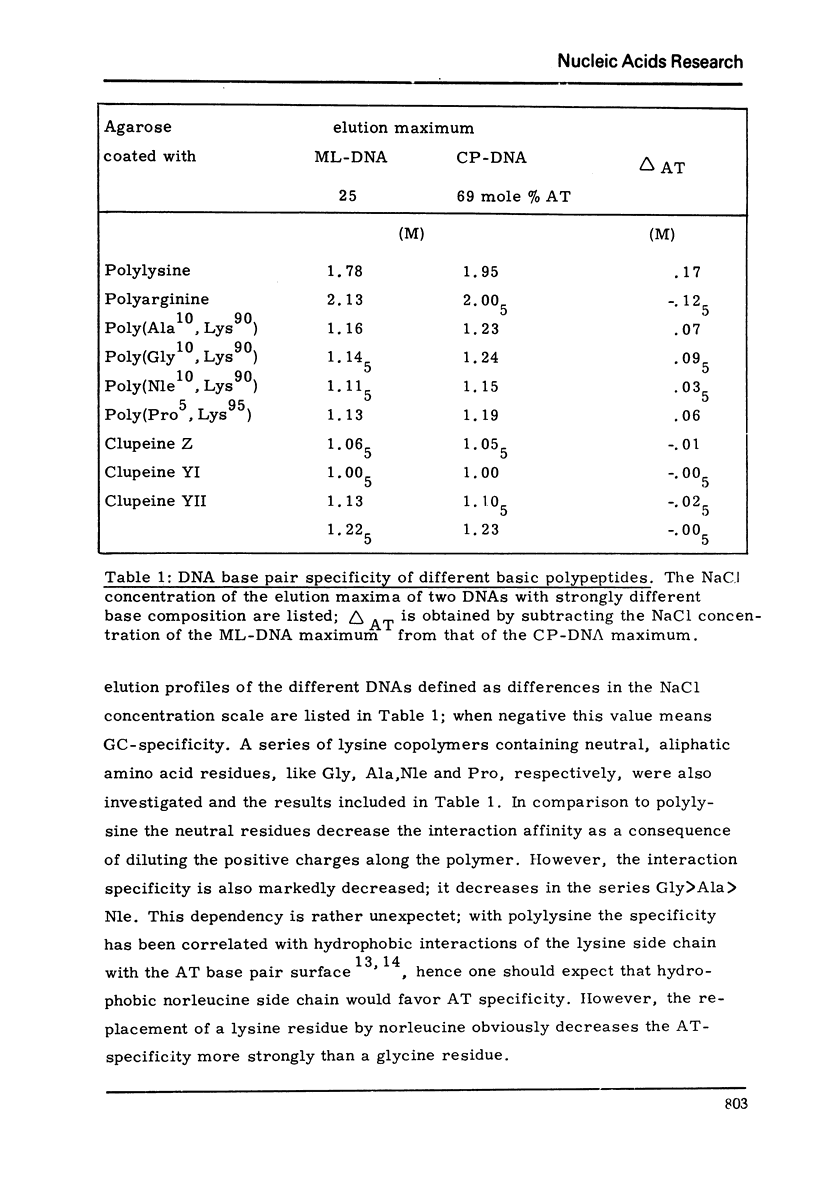
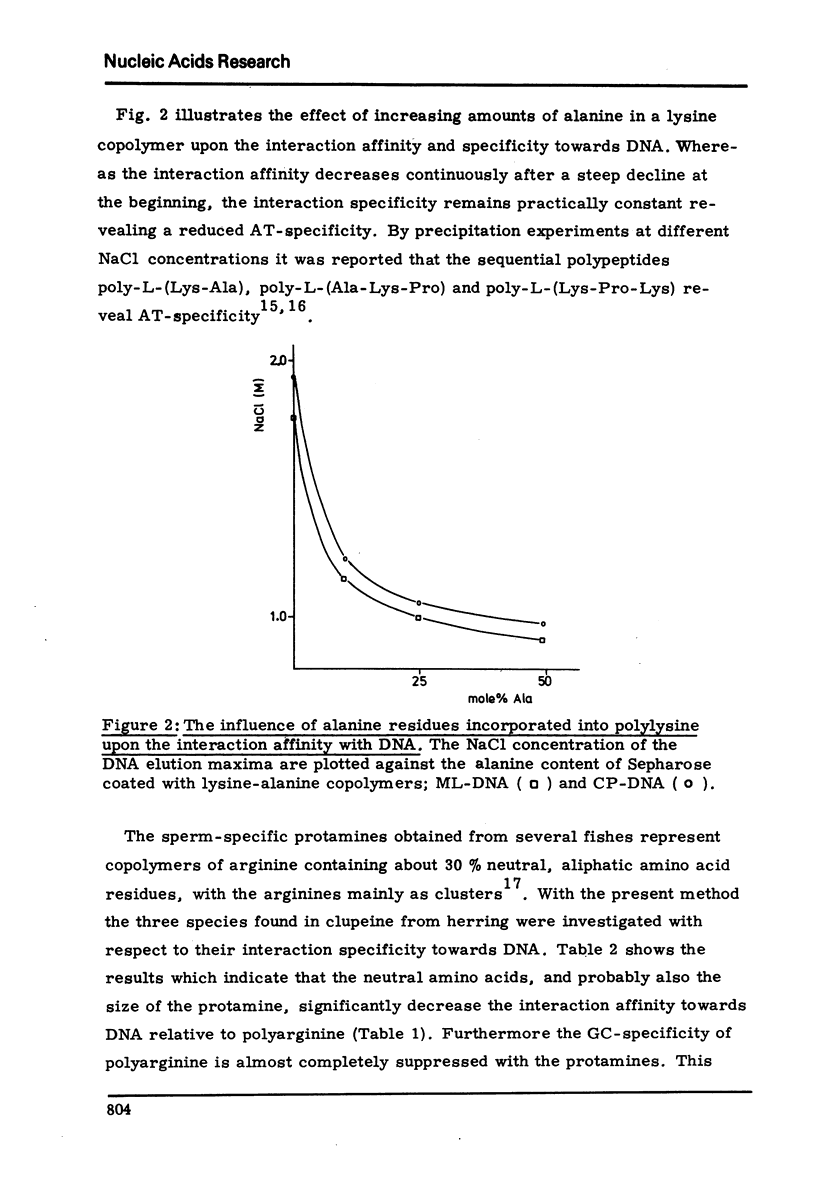
Abstract
An approach is described for evaluation of the specificity of basic polypeptides concerning the base pair composition of DNA. The polypeptides were covalently bound to CNBr activated agarose and two DNAs strongly different in base composition but of equal molecular weight were loaded and detached by a NaCl gradient. The difference in the NaCl concerntrations between the elution maxima of the two DNAs was taken as a measure for the recognition specificity. The results obtained confirmed the known AT- und GC-specificity of polylysine and polyarginine, respectively. Neutral residues incorporated into polylysine generally reduce the interaction affinity and also the AT-specificity of their host. This behavior is very pronounced with three homogeneous fractions of clupeine containing about one third of neutral aliphatic amino acids within clusters of arginine; the base pair specificity of these arginine copolymers was found to be practically nil.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arfmann H. A., Labitzke R., Lawaczeck R., Wagner K. G. Aromatic amino acid-lysine copolymers. Conformation and specificity of nucleotide interaction. Biochimie. 1974;56(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayad S. R., Blamire J. Fractionation of Bacillus subtilis DNA by use of poly-L-lysine kieselguhr columns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 15;30(3):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90436-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayad S. R., Parker M. C. Interactions between histone and DNA from calf and human tissues using activated sepharose column chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1973 Aug 1;82(2):343–348. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)91840-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. J., Felsenfeld G. Association of arginine-rich histones with G-C-rich regions of DNA in chromatin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 20;240(103):226–229. doi: 10.1038/newbio240226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helleiner C. W. Fractionation of DNA on columns of poly-L-lysine supported on kieselguhr. Can J Biochem. 1969 Dec;47(12):1199–1202. doi: 10.1139/o69-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helleiner C. W. The behavior of DNA on basic polyamino acid Kieselguhr columns. J Chromatogr. 1972 Oct 18;72(2):400–402. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)89528-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D., Loeser R., Herrlich P., Roeschenthaler R. The separation of nucleic acids on basic polyamino acid-kieselguhr columns. J Chromatogr. 1970 Oct 7;52(1):158–161. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96558-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Sober H. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions. 3. Cation effect on binding strength and specificity. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3307–3314. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng M., Felsenfeld G. The preferential interactions of polylysine and polyarginine with specific base sequences in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1325–1332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panusz H., Bartkowiak J., Krzywiec A., Joustra M., Plucienniczak A. The fractionation of calf thymus DNA on histone KAP-Sepharose 4B columns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Sep;1(9):1143–1151. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.9.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plucienniczak A., Bartkowiak J., Krzywiec A., Panusz H. The fractionation of calf thymus DNA by multiple formation of sedimentable complexes with homologous lysine-rich histone KAP. Derivative melting curves and ultracentrifugation in CsCl concentration gradients. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Dec;1(12):1675–1690. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.12.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privat J. P., Spach G., Leng M. Etude des interactions entre l'acide désoxyribonucléique et le polypeptide alterné (L-lysyl-L-alanyle)n. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):90–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPITNIK P., LIPSHITZ R., CHARGAFF E. Studies on nucleoproteins. III. Deoxyribonucleic acid complexes with basic polyelectrolytes and their fractional extraction. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):765–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. T., Leng M., Felsenfeld G. Deoxyribonucleic acid-polylysine complexes. Structure and nucleotide specificity. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3219–3232. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hippel P. H., McGhee J. D. DNA-protein interactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):231–300. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner K. G., Arav R. On the interaction of nucleotides with poly-L-lysine and poly-L-arginine. I. The influence of the nucleotide base on the binding behavior. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1771–1777. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner K. G., Arfmann H. A. Properties of basic amino-acid residues. Nucleotide--poly(amino acid)interaction. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):27–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M. Recognition of nucleotide sequences. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:841–880. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.004205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


