Abstract
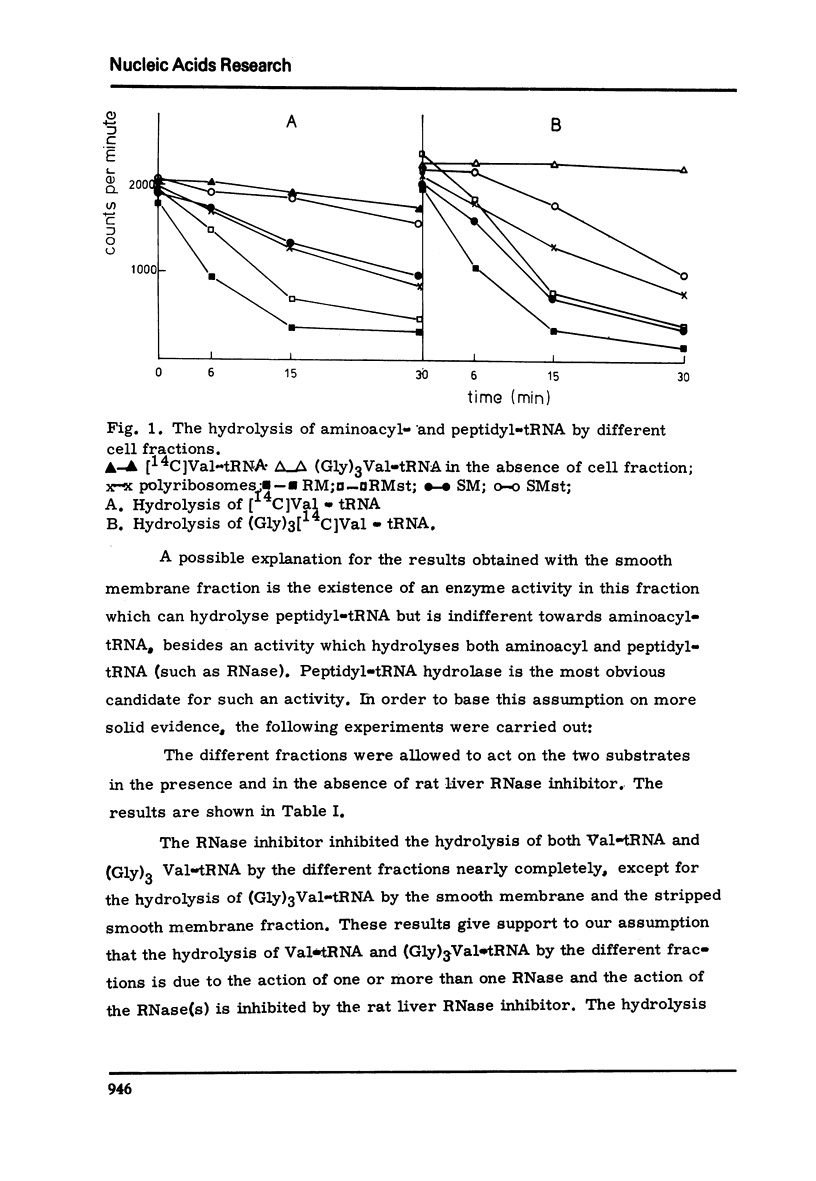
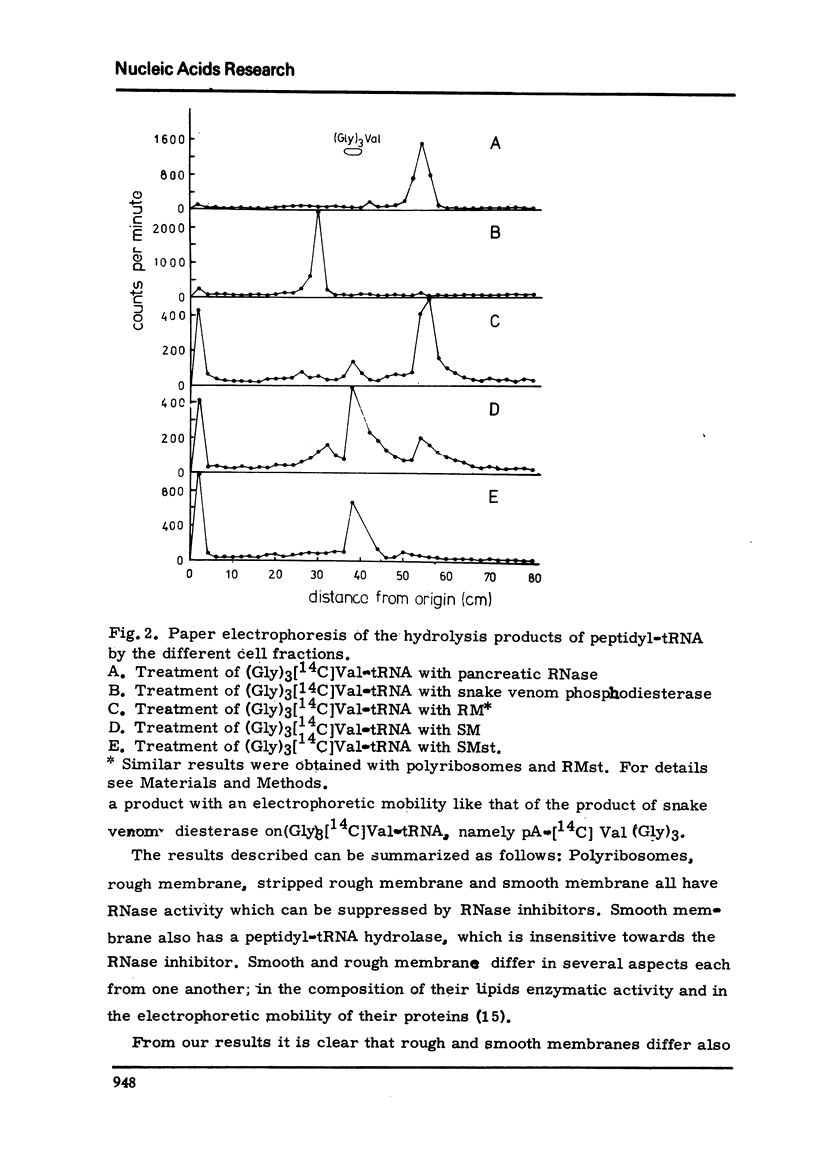
Peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase and RNase activities have been studied in those fractions of rat liver, which are used in in vitro reconstitution of rough membrane, because these enzymes may interfere with the in vitro reconstitution. It was found that smooth membrane has an active peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase, while the other fractions tested, polyribosomes, rough membrane, stripped rough membrane and the post-microsomal supernatant had no, or very low, peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase activity. Polyribosomes, rough and stripped rough membrane have RNase activity; this activity could be completely inhibited by rat liver RNase inhibitor. It is shown that RNase inhibitor is an obligatory component in in vitro experiments, in which rough membrane is reconstituted from stripped rough membrane, ribosomes and mRNA.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baglioni C., Bleiberg I., Zauderer M. Assembly of membrane-bound polyribosomes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 7;232(27):8–12. doi: 10.1038/newbio232008a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H., Bont W. S., de Vries M., Benedetti E. L. Isolation and properties of polyribosomes and fragments of the endoplasmic reticulum from rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):177–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1030177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgese N., Mok W., Kreibich G., Sabatini D. D. Ribosomal-membrane interaction: in vitro binding of ribosomes to microsomal membranes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 25;88(3):559–580. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuzin F., Kretchmer N., Greenberg R. E., Hurwitz R., Chapeville F. Enzymatic hydrolysis of N-substituted aminoacyl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2079–2086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groot N., Groner Y., Lapidot Y. Peptidyl-tRNA. VII. Substrate specificity of peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 20;186(2):286–296. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribnau A. A., Schoenmakers J. G., Bloemendal H. Purification of rat liver RNase inhibitor and its effect on polyribosome integrity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks S. J., Drysdale J. W., Munro H. N. Preferential synthesis of ferritin and albumin by different populations of liver polysomes. Science. 1969 May 2;164(3879):584–585. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3879.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidot Y., Rappoport S. The synthesis of oligopeptidyl-tRNA. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:688–695. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidot Y., de Groot N. The chemical synthesis and the biochemical properties of peptidyl-tRNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1972;12:189–228. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60663-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A., Efron D., Weeks D. P. The wheat embryo cell-free system. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:749–754. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. E., Wool I. G. Active hybrid 80 s particles formed from subunits of rat, rabbit and protozoan (Tetrahymena pyriformis) ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 14;43(1):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. A small particulate component of the cytoplasm. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jan;1(1):59–68. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulin D., Yot P., Chapeville F. Enzymatic hydrolysis of N-substituted aminoacyl-tRNA. FEBS Lett. 1968 Aug;1(3):163–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitot H. C., Shires T. K. Introductory remarks: membrane-polysome interactions. Fed Proc. 1973 Jan;32(1):76–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragland W. L., Shires T. K., Pitot H. C. Polyribosomal attachment to rat liver and hepatoma endoplasmic reticulum in vitro. A method for its study. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):271–278. doi: 10.1042/bj1210271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M. Biosynthesis of serum proteins and ferritin by free and attached ribosomes of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4308–4315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolleston F. S. The binding of ribosomal subunits to endoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):721–731. doi: 10.1042/bj1290721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roobol A., Rabin B. R. The binding of polysomes to smooth membranes of rat liver promoted by steroid hormones and extracts from either rough endoplasmic reticulum or from polysomes of the opposite sex. FEBS Lett. 1971 Apr 30;14(3):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Zamir A., Elson D. On the specificity and stability of an enzyme that hydrolyzes N-substituted aminoacyl-transfer RNA's. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):701–707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. J., Rabin B. R. The effects of aflatoxin B(1) and steroid hormones on polysome binding to microsomal membranes as measured by the activity of an enzyme catalysing disulphide interchange. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jul;4(2):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



