Abstract
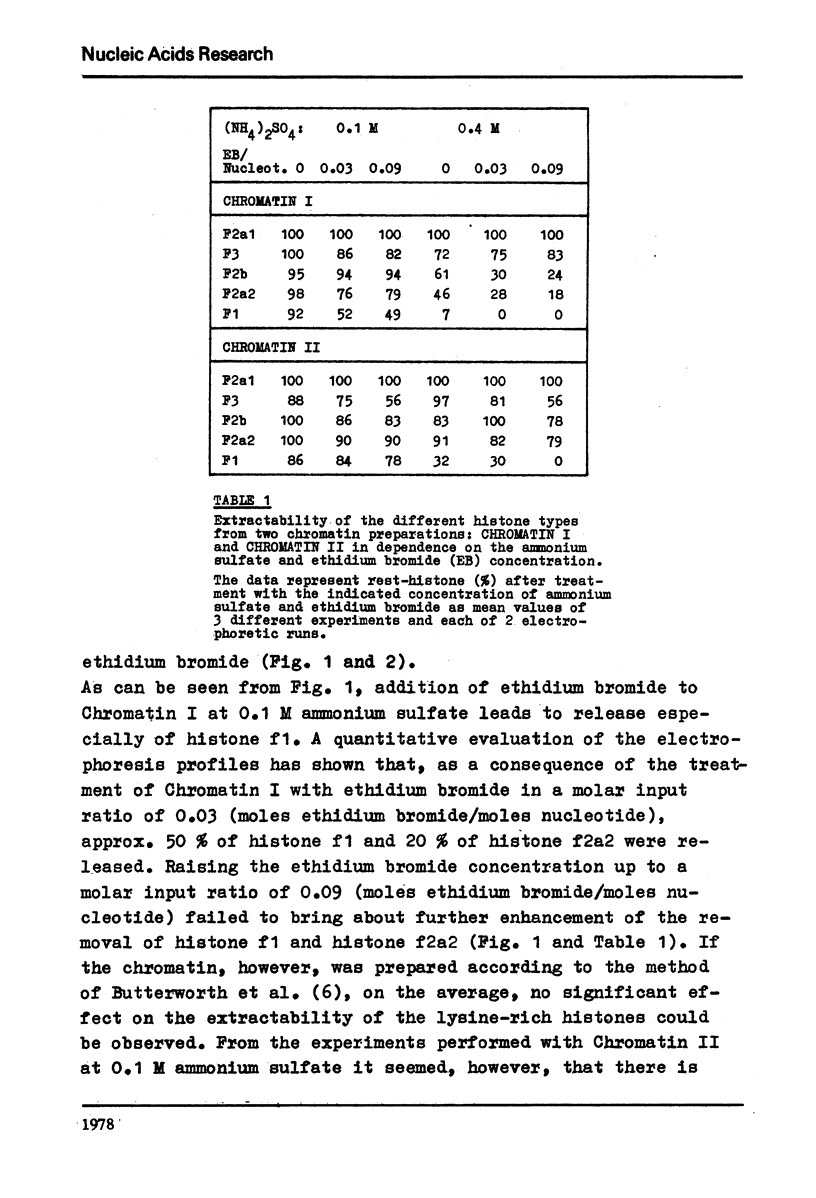
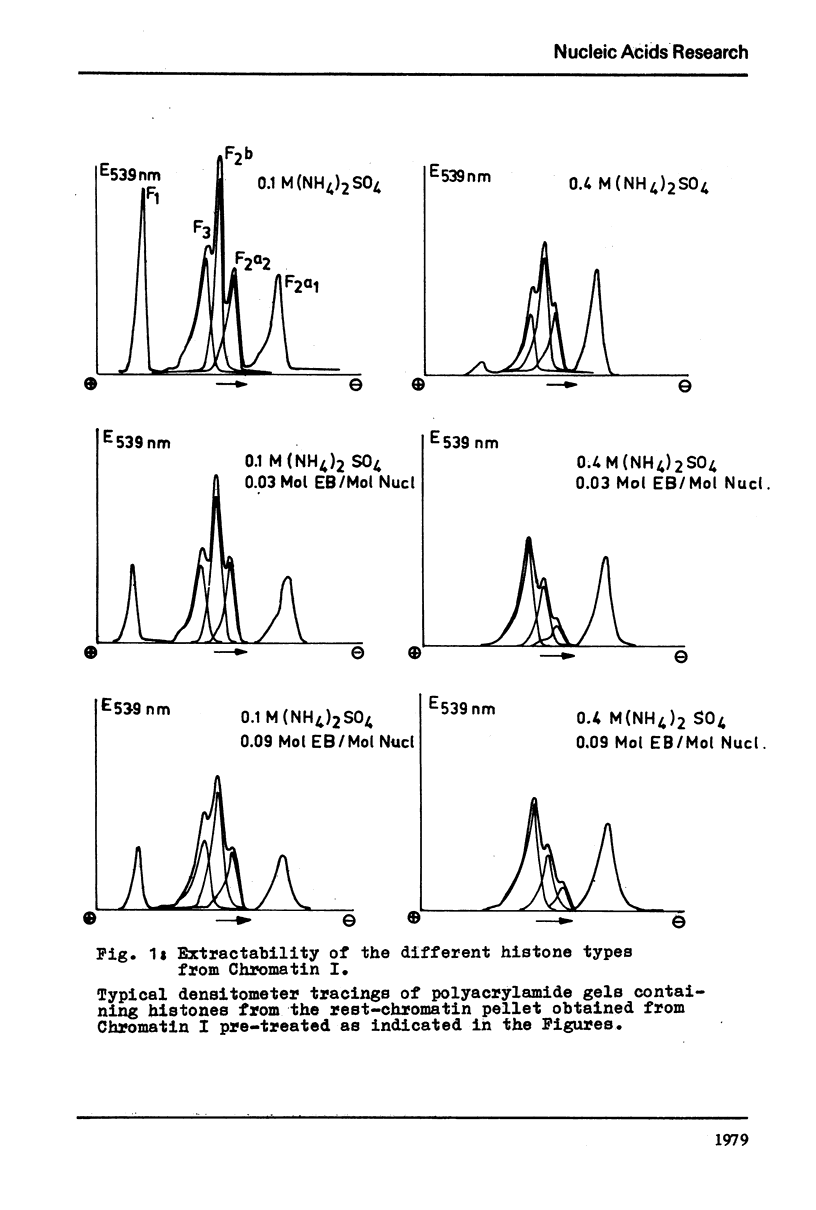
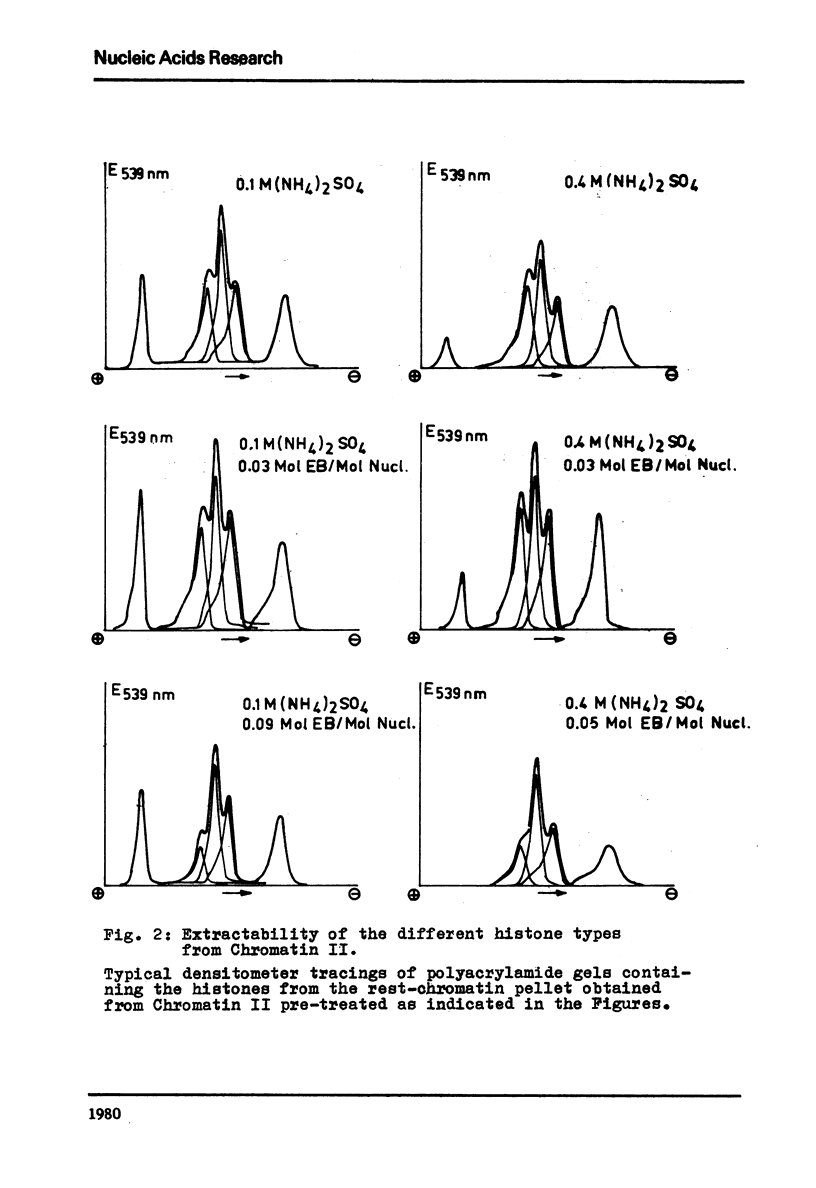
It is shown that the release of the slightly lysine-rich histones f2a2 and f2b by 0.4 M ammonium sulfate from conventionally isolated chromatin is diminished in comparison to the lysed nuclei. The change in extractability is further demonstrated by the application of ethidium bromide. At a molar input ratio of 0.09 (moles ethidium bromide/moles nucleotide) and 0.4 M ammonium sulfate the slightly lysine-rich histones are released from the chromatin to 70 - 80% if the lysed nuclei are used. At 0.1 M ammonium sulfate ethidium bromide effected also a release of 50 % of histone f1. Comparable effects could not be observed with chromatin prepared in a conventional way but instead a tendency towards loss of histone f3 in the presence of ethidium bromide was observed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradbury E. M., Carpenter B. G., Rattle H. W. Magnetic resonance studies of deoxyribonucleoprotein. Nature. 1973 Jan 12;241(5385):123–126. doi: 10.1038/241123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth P. H., Cox R. F., Chesterton C. J. Transcription of mammalian chromatin by mammalian DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(2):229–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenske H., Eichhorn I., Lindigkeit R. On extractability of histone f1 varying with the procedure used for chromatin isolation. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1975;34(2):303–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure; oligomers of the histones. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):865–868. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindigkeit R., Bellmann K., Fenske H., Böttger M., Holtzhauer M., Eichhorn I. Effect of removal of f1-histone on the conformation of nuclear chromatin and on the transcription process. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):146–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80713-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. Preparation of native chromatin and damage caused by shearing. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Spheroid chromatin units (v bodies). Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A. W., Debuysere M. S., Lewis E. A. Soluble nucleohistone of compact configuration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 15;361(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinert K. E. DNA stiffening and elongation caused by the binding of ethidium bromide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 24;319(2):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Van Holde K. E. The effect of trypsin on nuclease-resistant chromatin fragments. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


