Abstract
The title compound, C17H15Br2NO6S2·C2H5OH, is the esterification reaction product of 2-(8,10-dibromo-2,6-dioxo-3,5,5a,11b-tetrahydro-2H,6H-chromeno[4′,3′:4,5]thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazol-5a-yl)acetic acid. Cleavage of the lactone ring and formation of ethoxycarbonyl and hydroxy groups from its structural elements were observed. On the other hand, the carboxymethyl group was not esterified. The H atom and carboxymethyl group, both at stereogenic centres, show a cis conformation. The six-membered dihydrothiopyran ring adopts a half-chair conformation. All NH and OH groups participate in the three-dimensional hydrogen-bond network, which is additionally strengthened by C—H⋯O and C—H⋯S interactions. Intramolecular O—H⋯Br and C—H⋯O interactions also occur.
Related literature
For the biological activity of 4-thiazolidinone and thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazole-2-one derivatives, see: Lesyk & Zimenkovsky (2004 ▶); Lesyk et al. (2011 ▶); Kaminskyy et al. (2011 ▶); Matiychuk et al. (2008 ▶); Lesyk et al. (2006 ▶); Atamanyuk et al. (2008 ▶). For ring conformation analysis, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).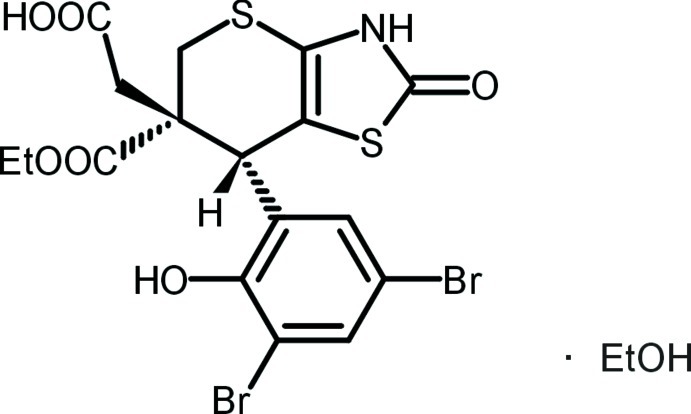
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H15Br2NO6S2·C2H6O
M r = 599.31
Monoclinic,
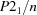
a = 16.8176 (9) Å
b = 8.1654 (4) Å
c = 18.3841 (9) Å
β = 113.303 (6)°
V = 2318.6 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.72 mm−1
T = 130 K
0.45 × 0.40 × 0.25 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Atlas diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.761, T max = 1.000
15312 measured reflections
5539 independent reflections
4500 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.022
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.027
wR(F 2) = 0.073
S = 1.09
5539 reflections
298 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 1.08 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.87 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812035325/bt5997sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812035325/bt5997Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O26—H26⋯Br1 | 0.98 (3) | 2.55 (3) | 3.1181 (15) | 117 (2) |
| C6—H6A⋯O13 | 0.97 | 2.44 | 3.033 (2) | 119 |
| N3—H3⋯O27i | 0.89 (2) | 1.83 (2) | 2.713 (2) | 171 (3) |
| O14—H14⋯O13ii | 0.85 (3) | 1.80 (3) | 2.645 (2) | 171 (3) |
| O26—H26⋯O16iii | 0.98 (3) | 1.96 (3) | 2.7800 (19) | 139 (2) |
| O27—H27⋯O10 | 0.87 (3) | 1.86 (3) | 2.724 (2) | 174 (2) |
| C6—H6A⋯S1iv | 0.97 | 2.75 | 3.5659 (17) | 142 |
| C23—H23⋯O10v | 0.93 | 2.36 | 3.253 (2) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 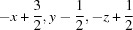 ; (ii)
; (ii) 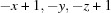 ; (iii)
; (iii) 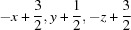 ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v) 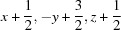 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The prominent success in thiazolidinone field is related to 4-thiazolidinone derivatives. Anticonvulsant, sedative, antidepressant, anti-inflammatory, antihypertensive, antihistaminic and anticancer activities are a few among many other biological responses shown by this scaffold (Lesyk & Zimenkovsky, 2004; Lesyk et al., 2011). Among mentioned heterocycles fused heterocyclic systems, particularly thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazole-2-ones possess a special interest as cyclic isosteric mimics of their synthetic precursors namely 4-thiazolidones without Michael accepting functionalities (Kaminskyy et al., 2011; Matiychuk et al., 2008). Fixation of highly active 5-arylidene-4-thiazolidinone in thiopyranothiazole system usually allows save the activity vector and opens up new possibilities of obtained derivatives optimization. Following the fact of anticancer activity discovery for various thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazole-2-ones (Lesyk et al., 2006; Atamanyuk et al., 2008) the introduction of exocyclic carboxylic group into the mentioned heterocycles can be considered as on the way of lead-structures optimization. This prompted us to synthesize title compound, (I).
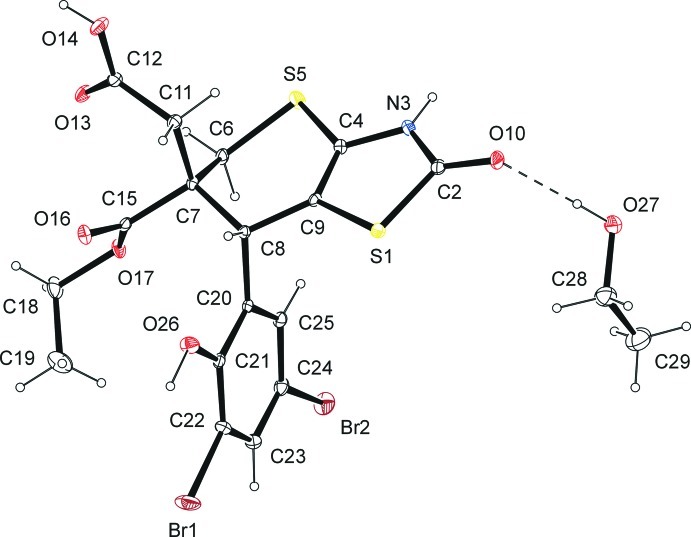
The molecular structure of compound (I) and the atom-labelling scheme is illustrated in Fig. 1.
The X-ray analysis showed that the crystal exists as ethanolic solvate. The asymmetric part of the unit cell contains one molecule of the compound (I) (solute) and one molecule of ethanol (solvent).
The studies on the structure of (I) showed that refluxing of 2-(8,10-dibromo-2,6-dioxo-3,5,5a,11b-tetrahydro-2H,6H-chromeno[4',3':4,5]thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazol-5a-yl)acetic acid for three hours in ethanol resulted in the cleavage of the lactone ring and formation of an ethoxycarbonyl moiety from its structural elements. On the other hand, the carboxymethyl group was not esterified under these conditions.
Investigations of the geometry of dihydrothiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazol-2-one showed that the six-membered dihydrothiopyran ring has a half-chair conformation [Cremer & Pople (1975) puckering parameters: Q = 0.5136 (19) Å, Θ = 49.7 (2)°, φ = 268.5 (2)°].
The C4═C9 bond length of 1.342 (2) Å confirmed the presence of a double bond between these carbons.
The C2—N3 interatomic distance of 1.356 (3) Å in the thiazol-2-one moiety is lengthened of about 7σ relative to the normal (O═ )C—NH bond length [1.331 (2) Å] of secondary amide group of γ-lactam (Allen et al., 1987).
The carboxymethyl and ethoxycarbonyl groups at C7 atom of dihydrothiopyran ring are in an axial and equatorial positions, respectively, while the 3,4-dibromo-2-hydroxyphenyl substituent at C8 atom is in a pseudoaxial position.
The carboxymethyl and ethoxycarbonyl groups are trans and cis, respectively, relative to the 3,4-dibromo-2-hydroxyphenyl substituent. The torsion angles C11—C7—C8—C20 and C15—C7—C8—C20 are 159.65 (15) and 45.32 (19)°, respectively.
The planar carboxymethyl and phenyl groups are approximately perpendicular to the least squares plane of the dihydrothiopyran ring; the dihedral angles are 83.10 (6) and 86.47 (6)°, respectively. The C12═O13 carbonyl group of the carboxymethyl substituent is synperiplanar (+sp) relative to the C7—C11 bond [torsion angle C7—C11—C12—O13: 2.3 (2)°]. On the other hand, the C11—C12 bond is antiperiplanar (-ap) in relation to the C7—C8 bond [torsion angle: C8—C7—C11—C12: -168.91 (14)°]. The C21 atom of the 3,4-dibromo-2-hydroxyphenyl substituent, at which the hydroxy group is attached, is anticlinal relative to the C7—C8 bond (-ac) [torsion angle C7—C8—C20—C21: -108.48 (18)°].
The flat fragment of the ethoxycarbonyl group, consisted of C15,O16,O17, and C18 atoms, forms a 55.18 (6)° dihedral angle with the best plane of dihydrothiopyran ring. The remaining C19 atom of the ethoxycarbonyl group, projected away of 1.367 (4) Å from the above atoms plane, is synclinal relative to the C15—O17 bond [torsion angle C15—O17—C18—C19: -81.1 (2)°]. Moreover, the C15═O16 carbonyl group is synclinal in relation to the C7—C8 bond [torsion angle C8—C7—C15—O16: 76.5 (2)°]. However, the torsion angles C15—O17—C18—C19 and C8—C7—C15—O16 are of different signs.
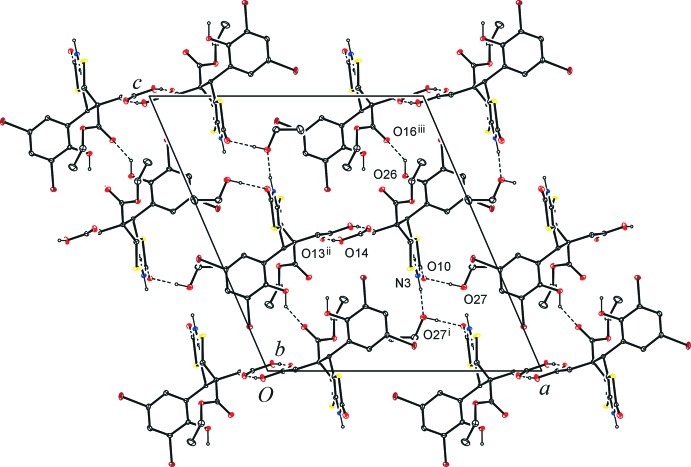
The molecules of (I) are interconnected with a screw axis and are linked by hydrogen bonds O26—H26···O16iii in chains (Table 1, Fig. 2). The neighbouring chains exist in antiparallel arrangement and are connected by hydrogen bonds O14—H14···.O13ii in layers growing parallel to the (-101) plane (Table 1, Fig. 2). The ethanol molecules form hydrogen bonding O27—H27···O10 and N3—H3···O27i (Table 1, Fig. 2) being both proton donors and acceptors. They link the molecules from neighbouring layers that results in formation of a three-dimensional lattice of hydrogen bonds in the crystal.
Experimental
An equimolar mixture of 5-(2-hydroxy-3,5-dibromobenzylidene)-4-thioxo-2-thiazolidinone, itaconic anhydride and pinch of hydroquinone (2–3 mg, for preventing of polymerization) in acetic acid was refluxed for 2 hrs. The product formed was filtered, washed, dried and re-crystallized from mixture DMF–AcOH. Obtained 2-(8,10-dibromo-2,6-dioxo-3,5,5a,11b-tetrahydro-2H,6H-chromeno[4',3':4,5]thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazol-5a-yl)acetic acid was refluxed in ethanol for 3 hrs. The product formed was filtered, washed, dried and recrystallized from ethanol.
Refinement
Except for the amide and hydroxy H atoms which were refined freely the remaining H atoms were positioned into the idealized positions and were refined within the riding model approximation: Cmethyl—H = 0.96 Å, Cmethylene—H = 0.97 Å, Cmethine—H = 0.98 Å, C(sp2)—H = 0.93 Å; Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H. The methyl groups were refined as rigid groups which were allowed to rotate. The largest peaks and holes in the ΔF Fourier map are within 1.0 Å of the Br1 and Br2 atom sites.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing the atomic labelling scheme. Non-H atoms are drawn as 30% probability displacement ellipsoids; H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
The hydrogen bonding in the title crystal structure. Symmetry codes: (i) 1.5–x, -1/2+y, 0.5–z; (ii) 1–x, –y, 1–z; (iii) 1.5–x, 1/2+y, 1.5–z. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds have been ommitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C17H15Br2NO6S2·C2H6O | F(000) = 1200 |
| Mr = 599.31 | Dx = 1.717 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Melting point = 510–512 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 16.8176 (9) Å | Cell parameters from 6534 reflections |
| b = 8.1654 (4) Å | θ = 2.4–29.1° |
| c = 18.3841 (9) Å | µ = 3.72 mm−1 |
| β = 113.303 (6)° | T = 130 K |
| V = 2318.6 (2) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.45 × 0.40 × 0.25 mm |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Atlas diffractometer | 5539 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 4500 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.022 |
| ω scans | θmax = 29.1°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009) | h = −22→22 |
| Tmin = 0.761, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −10→11 |
| 15312 measured reflections | l = −24→24 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.027 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.073 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.044P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5539 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 298 parameters | Δρmax = 1.08 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.87 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.996319 (13) | 0.62878 (3) | 0.839566 (12) | 0.03491 (8) | |
| Br2 | 1.074501 (12) | 0.35750 (3) | 0.592151 (13) | 0.02712 (7) | |
| S1 | 0.75077 (3) | 0.80961 (6) | 0.48078 (3) | 0.01618 (11) | |
| C2 | 0.71841 (11) | 0.8163 (2) | 0.37660 (11) | 0.0157 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.69780 (10) | 0.66259 (19) | 0.34724 (9) | 0.0148 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.6864 (14) | 0.639 (3) | 0.2971 (14) | 0.017 (6)* | |
| C4 | 0.70683 (11) | 0.5421 (2) | 0.40400 (10) | 0.0126 (4) | |
| S5 | 0.68259 (3) | 0.33898 (6) | 0.37237 (3) | 0.01932 (11) | |
| C6 | 0.72417 (12) | 0.2434 (2) | 0.46983 (11) | 0.0144 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.7010 | 0.1332 | 0.4647 | 0.017* | |
| H6B | 0.7866 | 0.2345 | 0.4884 | 0.017* | |
| C7 | 0.70239 (11) | 0.3352 (2) | 0.53289 (10) | 0.0115 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.74732 (10) | 0.5062 (2) | 0.55304 (10) | 0.0104 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.7183 | 0.5682 | 0.5812 | 0.013* | |
| C9 | 0.73311 (11) | 0.5980 (2) | 0.47848 (10) | 0.0115 (4) | |
| O10 | 0.71500 (8) | 0.94164 (17) | 0.33849 (8) | 0.0213 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.60359 (11) | 0.3610 (2) | 0.50519 (11) | 0.0140 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.5927 | 0.4331 | 0.5422 | 0.017* | |
| H11B | 0.5816 | 0.4140 | 0.4538 | 0.017* | |
| C12 | 0.55580 (11) | 0.2028 (2) | 0.49939 (11) | 0.0156 (4) | |
| O13 | 0.59224 (8) | 0.07109 (16) | 0.51734 (8) | 0.0178 (3) | |
| O14 | 0.47090 (8) | 0.22172 (18) | 0.47434 (9) | 0.0224 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.4454 (16) | 0.132 (3) | 0.4748 (16) | 0.037 (8)* | |
| C15 | 0.73196 (11) | 0.2392 (2) | 0.61104 (11) | 0.0132 (4) | |
| O16 | 0.70277 (8) | 0.26568 (16) | 0.66029 (7) | 0.0182 (3) | |
| O17 | 0.79311 (8) | 0.12991 (15) | 0.61807 (8) | 0.0171 (3) | |
| C18 | 0.82447 (13) | 0.0290 (3) | 0.69041 (12) | 0.0246 (5) | |
| H18A | 0.8501 | −0.0706 | 0.6807 | 0.030* | |
| H18B | 0.7759 | −0.0016 | 0.7033 | 0.030* | |
| C19 | 0.89052 (17) | 0.1187 (3) | 0.75959 (15) | 0.0419 (7) | |
| H19A | 0.8633 | 0.2095 | 0.7738 | 0.063* | |
| H19B | 0.9361 | 0.1583 | 0.7452 | 0.063* | |
| H19C | 0.9143 | 0.0455 | 0.8038 | 0.063* | |
| C20 | 0.84402 (11) | 0.4998 (2) | 0.60762 (10) | 0.0112 (3) | |
| C21 | 0.87065 (11) | 0.5535 (2) | 0.68594 (10) | 0.0133 (4) | |
| C22 | 0.95879 (12) | 0.5481 (3) | 0.73445 (10) | 0.0186 (4) | |
| C23 | 1.02008 (11) | 0.4888 (3) | 0.70848 (11) | 0.0202 (4) | |
| H23 | 1.0783 | 0.4837 | 0.7423 | 0.024* | |
| C24 | 0.99208 (12) | 0.4375 (2) | 0.63082 (12) | 0.0173 (4) | |
| C25 | 0.90546 (11) | 0.4444 (2) | 0.58003 (11) | 0.0143 (4) | |
| H25 | 0.8883 | 0.4122 | 0.5275 | 0.017* | |
| O26 | 0.80868 (9) | 0.61034 (17) | 0.70964 (8) | 0.0207 (3) | |
| H26 | 0.8325 (17) | 0.644 (3) | 0.7654 (17) | 0.046 (8)* | |
| O27 | 0.84716 (10) | 1.0647 (2) | 0.30489 (9) | 0.0325 (4) | |
| H27 | 0.8036 (16) | 1.032 (3) | 0.3155 (15) | 0.041 (7)* | |
| C28 | 0.91066 (14) | 1.1225 (3) | 0.37811 (13) | 0.0307 (5) | |
| H28A | 0.9057 | 1.0634 | 0.4219 | 0.037* | |
| H28B | 0.9016 | 1.2380 | 0.3845 | 0.037* | |
| C29 | 0.99888 (15) | 1.0965 (3) | 0.37809 (17) | 0.0432 (7) | |
| H29A | 1.0085 | 0.9815 | 0.3744 | 0.065* | |
| H29B | 1.0419 | 1.1392 | 0.4262 | 0.065* | |
| H29C | 1.0027 | 1.1523 | 0.3336 | 0.065* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.01994 (11) | 0.0685 (2) | 0.01402 (10) | −0.00743 (10) | 0.00428 (8) | −0.01027 (10) |
| Br2 | 0.01891 (11) | 0.03218 (14) | 0.03580 (13) | 0.00589 (9) | 0.01672 (9) | 0.00288 (10) |
| S1 | 0.0194 (2) | 0.0091 (2) | 0.0160 (2) | −0.00223 (18) | 0.00270 (18) | 0.00152 (18) |
| C2 | 0.0100 (8) | 0.0176 (10) | 0.0185 (9) | 0.0012 (7) | 0.0047 (7) | 0.0051 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0157 (8) | 0.0126 (7) | 0.0013 (6) | 0.0059 (6) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0135 (8) | 0.0123 (9) | 0.0132 (8) | 0.0003 (7) | 0.0064 (7) | 0.0008 (7) |
| S5 | 0.0323 (3) | 0.0126 (2) | 0.0124 (2) | −0.0027 (2) | 0.00818 (19) | −0.00275 (18) |
| C6 | 0.0185 (9) | 0.0100 (9) | 0.0158 (8) | −0.0028 (7) | 0.0079 (7) | −0.0002 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0128 (8) | 0.0092 (8) | 0.0132 (8) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0057 (7) | 0.0013 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0116 (8) | 0.0093 (9) | 0.0109 (8) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0051 (6) | −0.0008 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0108 (8) | 0.0076 (8) | 0.0153 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0045 (7) | 0.0007 (7) |
| O10 | 0.0198 (7) | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0241 (7) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0058 (6) | 0.0102 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0137 (8) | 0.0120 (9) | 0.0165 (9) | −0.0002 (7) | 0.0062 (7) | 0.0002 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0138 (8) | 0.0191 (10) | 0.0140 (8) | −0.0025 (8) | 0.0057 (7) | −0.0006 (8) |
| O13 | 0.0160 (6) | 0.0110 (7) | 0.0258 (7) | −0.0024 (5) | 0.0076 (5) | 0.0003 (6) |
| O14 | 0.0144 (7) | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0340 (8) | −0.0040 (6) | 0.0064 (6) | 0.0028 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0130 (8) | 0.0094 (9) | 0.0164 (8) | −0.0032 (7) | 0.0050 (7) | 0.0008 (7) |
| O16 | 0.0245 (7) | 0.0170 (7) | 0.0161 (6) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0114 (6) | 0.0035 (5) |
| O17 | 0.0189 (6) | 0.0149 (7) | 0.0186 (7) | 0.0055 (5) | 0.0087 (5) | 0.0077 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0277 (11) | 0.0191 (11) | 0.0273 (11) | 0.0066 (9) | 0.0112 (9) | 0.0122 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0368 (13) | 0.0460 (16) | 0.0305 (13) | 0.0038 (11) | 0.0001 (11) | 0.0122 (11) |
| C20 | 0.0132 (8) | 0.0084 (8) | 0.0120 (8) | −0.0019 (7) | 0.0051 (7) | 0.0016 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0147 (8) | 0.0132 (9) | 0.0139 (8) | −0.0030 (7) | 0.0075 (7) | 0.0007 (7) |
| C22 | 0.0176 (9) | 0.0250 (11) | 0.0104 (8) | −0.0043 (8) | 0.0024 (7) | −0.0002 (8) |
| C23 | 0.0123 (9) | 0.0271 (11) | 0.0183 (9) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0028 (7) | 0.0053 (8) |
| C24 | 0.0141 (8) | 0.0182 (10) | 0.0227 (9) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0106 (7) | 0.0036 (8) |
| C25 | 0.0158 (9) | 0.0120 (9) | 0.0160 (8) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0072 (7) | 0.0000 (7) |
| O26 | 0.0204 (7) | 0.0289 (8) | 0.0149 (7) | −0.0018 (6) | 0.0091 (6) | −0.0064 (6) |
| O27 | 0.0262 (8) | 0.0515 (11) | 0.0188 (7) | −0.0123 (8) | 0.0079 (6) | 0.0049 (7) |
| C28 | 0.0312 (12) | 0.0357 (14) | 0.0252 (11) | −0.0081 (10) | 0.0111 (9) | −0.0066 (10) |
| C29 | 0.0270 (12) | 0.0459 (16) | 0.0511 (16) | −0.0037 (11) | 0.0094 (11) | 0.0067 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C22 | 1.8980 (18) | C15—O17 | 1.329 (2) |
| Br2—C24 | 1.9061 (19) | O17—C18 | 1.473 (2) |
| S1—C9 | 1.7510 (18) | C18—C19 | 1.507 (3) |
| S1—C2 | 1.773 (2) | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C2—O10 | 1.229 (2) | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C2—N3 | 1.356 (3) | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| N3—C4 | 1.398 (2) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| N3—H3 | 0.88 (2) | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C9 | 1.342 (2) | C20—C25 | 1.394 (3) |
| C4—S5 | 1.7515 (19) | C20—C21 | 1.398 (2) |
| S5—C6 | 1.8212 (19) | C21—O26 | 1.361 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.541 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.396 (2) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9700 | C22—C23 | 1.383 (3) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9700 | C23—C24 | 1.380 (3) |
| C7—C15 | 1.536 (2) | C23—H23 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C11 | 1.548 (2) | C24—C25 | 1.386 (2) |
| C7—C8 | 1.561 (2) | C25—H25 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.496 (2) | O26—H26 | 0.98 (3) |
| C8—C20 | 1.537 (2) | O27—C28 | 1.427 (3) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9800 | O27—H27 | 0.87 (3) |
| C11—C12 | 1.503 (3) | C28—C29 | 1.499 (3) |
| C11—H11A | 0.9700 | C28—H28A | 0.9700 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9700 | C28—H28B | 0.9700 |
| C12—O13 | 1.217 (2) | C29—H29A | 0.9600 |
| C12—O14 | 1.325 (2) | C29—H29B | 0.9600 |
| O14—H14 | 0.85 (3) | C29—H29C | 0.9600 |
| C15—O16 | 1.208 (2) | ||
| C9—S1—C2 | 91.59 (9) | C15—O17—C18 | 116.76 (15) |
| O10—C2—N3 | 126.65 (18) | O17—C18—C19 | 111.79 (18) |
| O10—C2—S1 | 124.54 (16) | O17—C18—H18A | 109.3 |
| N3—C2—S1 | 108.81 (14) | C19—C18—H18A | 109.3 |
| C2—N3—C4 | 114.77 (16) | O17—C18—H18B | 109.3 |
| C2—N3—H3 | 122.1 (14) | C19—C18—H18B | 109.3 |
| C4—N3—H3 | 122.6 (14) | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.9 |
| C9—C4—N3 | 114.66 (17) | C18—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C9—C4—S5 | 126.90 (15) | C18—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| N3—C4—S5 | 118.44 (13) | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C4—S5—C6 | 97.51 (8) | C18—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—S5 | 114.75 (12) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 108.6 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| S5—C6—H6A | 108.6 | C25—C20—C21 | 119.64 (15) |
| C7—C6—H6B | 108.6 | C25—C20—C8 | 121.24 (15) |
| S5—C6—H6B | 108.6 | C21—C20—C8 | 119.12 (15) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 107.6 | O26—C21—C22 | 124.10 (16) |
| C15—C7—C6 | 111.71 (14) | O26—C21—C20 | 117.57 (15) |
| C15—C7—C11 | 106.57 (14) | C22—C21—C20 | 118.33 (16) |
| C6—C7—C11 | 111.24 (14) | C23—C22—C21 | 122.58 (17) |
| C15—C7—C8 | 106.69 (13) | C23—C22—Br1 | 118.67 (13) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 112.13 (14) | C21—C22—Br1 | 118.74 (14) |
| C11—C7—C8 | 108.21 (14) | C24—C23—C22 | 117.86 (16) |
| C9—C8—C20 | 111.07 (14) | C24—C23—H23 | 121.1 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 110.11 (14) | C22—C23—H23 | 121.1 |
| C20—C8—C7 | 114.34 (13) | C23—C24—C25 | 121.48 (18) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 107.0 | C23—C24—Br2 | 119.28 (14) |
| C20—C8—H8 | 107.0 | C25—C24—Br2 | 119.23 (15) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 107.0 | C24—C25—C20 | 120.06 (17) |
| C4—C9—C8 | 129.31 (16) | C24—C25—H25 | 120.0 |
| C4—C9—S1 | 110.15 (14) | C20—C25—H25 | 120.0 |
| C8—C9—S1 | 120.54 (13) | C21—O26—H26 | 112.4 (16) |
| C12—C11—C7 | 112.39 (15) | C28—O27—H27 | 105.8 (17) |
| C12—C11—H11A | 109.1 | O27—C28—C29 | 108.9 (2) |
| C7—C11—H11A | 109.1 | O27—C28—H28A | 109.9 |
| C12—C11—H11B | 109.1 | C29—C28—H28A | 109.9 |
| C7—C11—H11B | 109.1 | O27—C28—H28B | 109.9 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 | C29—C28—H28B | 109.9 |
| O13—C12—O14 | 123.74 (17) | H28A—C28—H28B | 108.3 |
| O13—C12—C11 | 122.87 (16) | C28—C29—H29A | 109.5 |
| O14—C12—C11 | 113.39 (16) | C28—C29—H29B | 109.5 |
| C12—O14—H14 | 112.1 (17) | H29A—C29—H29B | 109.5 |
| O16—C15—O17 | 125.14 (17) | C28—C29—H29C | 109.5 |
| O16—C15—C7 | 122.17 (16) | H29A—C29—H29C | 109.5 |
| O17—C15—C7 | 112.67 (15) | H29B—C29—H29C | 109.5 |
| C9—S1—C2—O10 | 178.68 (17) | C7—C11—C12—O13 | 2.3 (3) |
| C9—S1—C2—N3 | −0.71 (14) | C7—C11—C12—O14 | −178.81 (15) |
| O10—C2—N3—C4 | −179.39 (17) | C6—C7—C15—O16 | −160.59 (16) |
| S1—C2—N3—C4 | −0.01 (19) | C11—C7—C15—O16 | −38.9 (2) |
| C2—N3—C4—C9 | 1.0 (2) | C8—C7—C15—O16 | 76.5 (2) |
| C2—N3—C4—S5 | −179.55 (13) | C6—C7—C15—O17 | 20.9 (2) |
| C9—C4—S5—C6 | −10.25 (18) | C11—C7—C15—O17 | 142.56 (15) |
| N3—C4—S5—C6 | 170.43 (14) | C8—C7—C15—O17 | −102.00 (16) |
| C4—S5—C6—C7 | 41.76 (14) | O16—C15—O17—C18 | 2.8 (3) |
| S5—C6—C7—C15 | 174.57 (12) | C7—C15—O17—C18 | −178.74 (15) |
| S5—C6—C7—C11 | 55.62 (17) | C15—O17—C18—C19 | −81.1 (2) |
| S5—C6—C7—C8 | −65.71 (16) | C9—C8—C20—C25 | −52.6 (2) |
| C15—C7—C8—C9 | 171.17 (14) | C7—C8—C20—C25 | 72.8 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 48.57 (19) | C9—C8—C20—C21 | 126.18 (18) |
| C11—C7—C8—C9 | −74.49 (18) | C7—C8—C20—C21 | −108.48 (18) |
| C15—C7—C8—C20 | 45.32 (19) | C25—C20—C21—O26 | 178.33 (16) |
| C6—C7—C8—C20 | −77.29 (18) | C8—C20—C21—O26 | −0.5 (2) |
| C11—C7—C8—C20 | 159.65 (15) | C25—C20—C21—C22 | −0.7 (3) |
| N3—C4—C9—C8 | 178.26 (16) | C8—C20—C21—C22 | −179.45 (16) |
| S5—C4—C9—C8 | −1.1 (3) | O26—C21—C22—C23 | 179.74 (18) |
| N3—C4—C9—S1 | −1.5 (2) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | −1.3 (3) |
| S5—C4—C9—S1 | 179.11 (11) | O26—C21—C22—Br1 | −1.4 (3) |
| C20—C8—C9—C4 | 111.4 (2) | C20—C21—C22—Br1 | 177.50 (14) |
| C7—C8—C9—C4 | −16.3 (3) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | 1.7 (3) |
| C20—C8—C9—S1 | −68.83 (18) | Br1—C22—C23—C24 | −177.11 (15) |
| C7—C8—C9—S1 | 163.48 (12) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | −0.1 (3) |
| C2—S1—C9—C4 | 1.28 (14) | C22—C23—C24—Br2 | 179.24 (15) |
| C2—S1—C9—C8 | −178.54 (14) | C23—C24—C25—C20 | −1.8 (3) |
| C15—C7—C11—C12 | −54.49 (19) | Br2—C24—C25—C20 | 178.81 (14) |
| C6—C7—C11—C12 | 67.49 (19) | C21—C20—C25—C24 | 2.2 (3) |
| C8—C7—C11—C12 | −168.91 (14) | C8—C20—C25—C24 | −179.02 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O26—H26···Br1 | 0.98 (3) | 2.55 (3) | 3.1181 (15) | 117 (2) |
| C6—H6A···O13 | 0.97 | 2.44 | 3.033 (2) | 119 |
| N3—H3···O27i | 0.89 (2) | 1.83 (2) | 2.713 (2) | 171 (3) |
| O14—H14···O13ii | 0.85 (3) | 1.80 (3) | 2.645 (2) | 171 (3) |
| O26—H26···O16iii | 0.98 (3) | 1.96 (3) | 2.7800 (19) | 139 (2) |
| O27—H27···O10 | 0.87 (3) | 1.86 (3) | 2.724 (2) | 174 (2) |
| C6—H6A···S1iv | 0.97 | 2.75 | 3.5659 (17) | 142 |
| C23—H23···O10v | 0.93 | 2.36 | 3.253 (2) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (iii) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (iv) x, y−1, z; (v) x+1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5997).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Atamanyuk, D., Zimenkovsky, B. & Lesyk, R. (2008). J. Sulfur Chem. 29, 151–162.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Kaminskyy, D., Vasylenko, O., Atamanyuk, D., Gzella, A. & Lesyk, R. (2011). Synlett, 10, 1385–1388.
- Lesyk, R. B. & Zimenkovsky, B. S. (2004). Curr. Org. Chem. 8, 1547–1577.
- Lesyk, R., Zimenkovsky, B., Atamanyuk, D., Jensen, F., Kieć-Kononowicz, K. & Gzella, A. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14, 5230–5240. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lesyk, R. B., Zimenkovsky, B. S., Kaminskyy, D. V., Kryshchyshyn, A. P., Havrylyuk, D. Ya., Atamanyuk, D. V., Subtel’na, I. Yu. & Khyluk, D. V. (2011). Biopolym. Cell, 27, 107–117.
- Matiychuk, V., Lesyk, R., Obushak, M., Gzella, A., Atamanyuk, D., Ostapiuk, Yu. & Kryshchyshyn, A. (2008). Tetrahedron Lett. 49, 4648–4651.
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis PRO Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812035325/bt5997sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812035325/bt5997Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report