Abstract
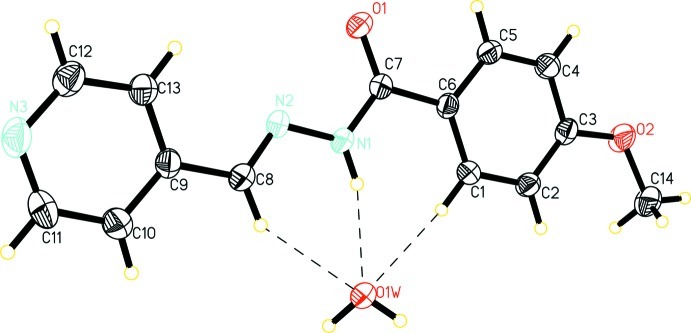
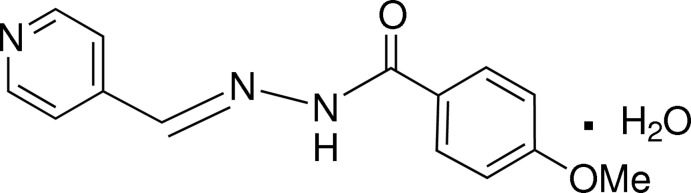
In the title compound, C14H13N3O2·H2O, the azomethine double bond adopts an E conformation and the N—N=C—C torsion angle is 178.37 (19)°. The dihedral angle between the benzene and pyridine rings is 5.58 (12)° and the C atom of the methoxy group is roughly coplanar with its attached ring [deviation = 0.157 (3) Å]. In the crystal, the components are linked by O—H⋯O, O—H⋯N, N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming (001) sheets. The water O atom accepts one N—H⋯O and two C—H⋯O interactions from the adjacent organic molecule.
Related literature
For the biological activity of benzohydraazides, see: Bayrak et al. (2009 ▶). For the crystal structures of related benzohydrazides, see: Taha et al. (2012) ▶; Fun et al. (2011 ▶); Lu et al. (2009 ▶); Zhang (2009a
▶,b
▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H13N3O2·H2O
M r = 273.29
Monoclinic,
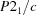
a = 6.6878 (5) Å
b = 7.0420 (5) Å
c = 29.249 (2) Å
β = 94.233 (2)°
V = 1373.74 (17) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 273 K
0.20 × 0.17 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.981, T max = 0.991
7767 measured reflections
2560 independent reflections
1548 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.038
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.047
wR(F 2) = 0.146
S = 1.03
2560 reflections
182 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL, PARST (Nardelli, 1995 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812034988/hb6930sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812034988/hb6930Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812034988/hb6930Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1W—H1⋯O1i | 0.84 | 2.00 | 2.811 (2) | 162 |
| O1W—H2⋯N3ii | 0.91 | 2.11 | 2.956 (3) | 154 |
| N1—H1A⋯O1W | 0.86 | 2.08 | 2.911 (2) | 161 |
| C1—H1B⋯O1W | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.440 (3) | 162 |
| C8—H8A⋯O1W | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.272 (3) | 143 |
| C11—H11A⋯O2iii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.375 (3) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 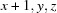 ; (ii)
; (ii) 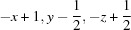 ; (iii)
; (iii) 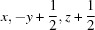 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
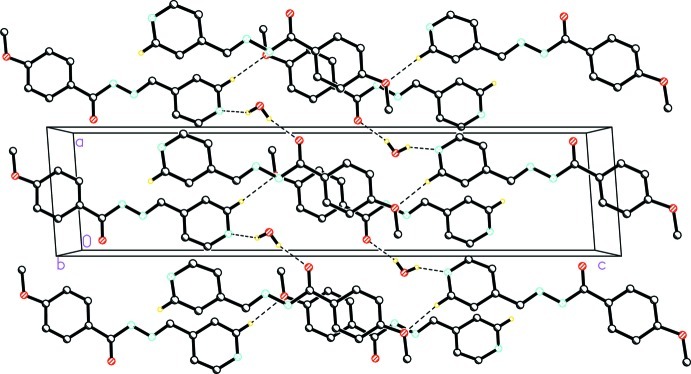
The diverse structural features and wide range of biological activities make Benzohydrazides as an importent class of organic compounds. The title compound is an structure analogue of Benzohydrazide, synthesize as a part of our ongoing research to study their varoius biological activities. The structure of title compound (Fig. 1) is similar to that of our recently published benzohydrazide derivative (E)-N'-(3,4-Dimethoxybenzylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide (Taha et al., 2012, Pv2573) with the difference that 3,4-dimethoxy phenyl ring is replaced by pyridine ring (N3/C9–C13). The azomethine (C=N,1.269 (3) Å) double bond adopt an E conformation (Fig. 1) with the torsion angle of 178.3 (19)° (N1–N2–C8–C9). Phenyl and pyridine rings (C1–C6 and N3/C9–C13) have a dihedral angle of 5.58 (12)° between them and maximum deviation of 0.006 (3) Å for C13 atoms from the root mean square plane. The bond lengths and angle were found to be similar as in structurally realted compounds (Fun et al., 2011, Lu et al., 2009, Zhang et al., 2009). In the crystal structure molecules are consolidated by C11—H11A···O2 intermolecular hydrogen bonds (Fig.2) and extended to form a two-dimensional-network due to O1W—H1···O1 and O1W—H2···N3 (symmetry codes as in Table 2) intermolecular linkages made by water solvates (Fig. 2).
Experimental
A mixture of 2 mmol of 4-methoxybenzohydrazide (0.332 g), 2 mmol isonicotinaldehyde (0.214 g) and catalytical amount of acetic acid was refluxed in methanol (20 ml) for 3 h. The progress of reaction was monitored by TLC. After completion of the reaction, the solvent was evaporated by vacuum to afford the crude product, which was dissolved and recrystallized from methanol to obtain colourless blocks (0.418 g in 82% yield).
Refinement
H atoms on Methyl, phenyl, methine, nitrogen and water were positioned geometrically with C—H = 0.95 Å, CH3 = 0.93 Å, NH = 0.86 Å and O–H = 0.83–0.90 Å and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with Uiso(H)= 1.5Ueq(CH3, OH) and 1.2Ueq(CH, NH). A rotating group model was applied to the methyl group.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) with displacement ellipsoids drawn at 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound I. Only hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding are shown.
Crystal data
| C14H13N3O2·H2O | F(000) = 576 |
| Mr = 273.29 | Dx = 1.321 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.6878 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 1112 reflections |
| b = 7.0420 (5) Å | θ = 2.8–22.8° |
| c = 29.249 (2) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 94.233 (2)° | T = 273 K |
| V = 1373.74 (17) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.20 × 0.17 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 2560 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1548 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.038 |
| ω scan | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 1.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.981, Tmax = 0.991 | k = −7→8 |
| 7767 measured reflections | l = −35→35 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.047 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.146 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.070P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2560 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 182 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.0974 (2) | 0.3345 (3) | 0.05572 (5) | 0.0607 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.6325 (2) | 0.1818 (3) | −0.10876 (5) | 0.0590 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.3945 (3) | 0.3260 (3) | 0.09758 (6) | 0.0446 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.5220 | 0.3083 | 0.0985 | 0.053* | |
| N2 | 0.3018 (3) | 0.3646 (3) | 0.13646 (6) | 0.0436 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.1587 (4) | 0.5223 (4) | 0.29858 (7) | 0.0662 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.5874 (3) | 0.2320 (3) | 0.01504 (7) | 0.0413 (6) | |
| H1B | 0.6640 | 0.2206 | 0.0428 | 0.050* | |
| C2 | 0.6754 (3) | 0.1988 (3) | −0.02547 (7) | 0.0424 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.8102 | 0.1659 | −0.0250 | 0.051* | |
| C3 | 0.5623 (3) | 0.2146 (3) | −0.06665 (7) | 0.0424 (6) | |
| C4 | 0.3619 (3) | 0.2658 (4) | −0.06705 (8) | 0.0513 (7) | |
| H4A | 0.2858 | 0.2773 | −0.0948 | 0.062* | |
| C5 | 0.2756 (3) | 0.2993 (3) | −0.02691 (8) | 0.0462 (6) | |
| H5A | 0.1412 | 0.3340 | −0.0277 | 0.055* | |
| C6 | 0.3867 (3) | 0.2821 (3) | 0.01516 (7) | 0.0380 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.2800 (3) | 0.3160 (3) | 0.05702 (7) | 0.0411 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.4126 (4) | 0.3827 (4) | 0.17334 (7) | 0.0469 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.5506 | 0.3663 | 0.1732 | 0.056* | |
| C9 | 0.3230 (3) | 0.4292 (3) | 0.21603 (7) | 0.0429 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.4319 (4) | 0.4088 (4) | 0.25789 (8) | 0.0544 (7) | |
| H10A | 0.5630 | 0.3639 | 0.2592 | 0.065* | |
| C11 | 0.3438 (5) | 0.4556 (4) | 0.29754 (9) | 0.0650 (8) | |
| H11A | 0.4189 | 0.4395 | 0.3253 | 0.078* | |
| C12 | 0.0554 (4) | 0.5413 (4) | 0.25821 (9) | 0.0580 (7) | |
| H12A | −0.0747 | 0.5880 | 0.2580 | 0.070* | |
| C13 | 0.1279 (4) | 0.4965 (4) | 0.21676 (8) | 0.0499 (6) | |
| H13A | 0.0476 | 0.5110 | 0.1896 | 0.060* | |
| C14 | 0.8422 (4) | 0.1550 (5) | −0.11117 (9) | 0.0640 (8) | |
| H14A | 0.8706 | 0.1333 | −0.1424 | 0.096* | |
| H14B | 0.8852 | 0.0473 | −0.0929 | 0.096* | |
| H14C | 0.9124 | 0.2663 | −0.0998 | 0.096* | |
| O1W | 0.8218 (2) | 0.2877 (3) | 0.12291 (5) | 0.0657 (6) | |
| H1 | 0.9224 | 0.2994 | 0.1078 | 0.098* | |
| H2 | 0.8700 | 0.2103 | 0.1461 | 0.098* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0361 (10) | 0.1027 (16) | 0.0440 (10) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0085 (7) | 0.0049 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0496 (10) | 0.0914 (15) | 0.0373 (9) | −0.0042 (10) | 0.0115 (8) | −0.0133 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0347 (10) | 0.0645 (15) | 0.0357 (11) | 0.0026 (10) | 0.0104 (8) | 0.0015 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0415 (11) | 0.0552 (13) | 0.0352 (11) | 0.0018 (10) | 0.0111 (9) | 0.0016 (9) |
| N3 | 0.0749 (17) | 0.0805 (18) | 0.0450 (14) | −0.0011 (14) | 0.0167 (12) | −0.0098 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0384 (13) | 0.0493 (15) | 0.0358 (12) | 0.0007 (11) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0032 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0360 (13) | 0.0508 (16) | 0.0410 (13) | 0.0012 (11) | 0.0057 (10) | −0.0028 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0419 (13) | 0.0485 (15) | 0.0378 (13) | −0.0085 (11) | 0.0102 (10) | −0.0054 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0428 (14) | 0.075 (2) | 0.0359 (14) | −0.0049 (13) | −0.0009 (10) | −0.0017 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0340 (13) | 0.0624 (18) | 0.0424 (14) | −0.0034 (12) | 0.0034 (10) | 0.0007 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0378 (12) | 0.0403 (14) | 0.0366 (12) | −0.0053 (11) | 0.0068 (9) | 0.0025 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0370 (13) | 0.0488 (16) | 0.0379 (13) | −0.0027 (11) | 0.0057 (10) | 0.0049 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0394 (13) | 0.0605 (17) | 0.0416 (14) | 0.0046 (12) | 0.0084 (11) | 0.0005 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0454 (14) | 0.0469 (16) | 0.0370 (13) | −0.0016 (12) | 0.0074 (10) | 0.0001 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0537 (15) | 0.0636 (19) | 0.0456 (15) | 0.0042 (14) | 0.0016 (11) | −0.0006 (13) |
| C11 | 0.081 (2) | 0.077 (2) | 0.0368 (15) | 0.0004 (17) | 0.0010 (13) | −0.0006 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0553 (16) | 0.0642 (19) | 0.0560 (17) | −0.0004 (14) | 0.0137 (13) | −0.0108 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0504 (15) | 0.0574 (17) | 0.0423 (14) | 0.0025 (13) | 0.0059 (11) | −0.0048 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0565 (17) | 0.087 (2) | 0.0516 (16) | 0.0062 (16) | 0.0226 (13) | −0.0059 (14) |
| O1W | 0.0371 (9) | 0.1143 (17) | 0.0465 (10) | 0.0079 (10) | 0.0095 (7) | 0.0166 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C7 | 1.226 (2) | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C3 | 1.370 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.481 (3) |
| O2—C14 | 1.422 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.462 (3) |
| N1—N2 | 1.362 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.365 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.385 (3) |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C9—C13 | 1.390 (3) |
| N2—C8 | 1.269 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.379 (3) |
| N3—C11 | 1.326 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9300 |
| N3—C12 | 1.330 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.375 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.388 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9300 | C13—H13A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.379 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.387 (3) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.367 (3) | O1W—H1 | 0.8361 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | O1W—H2 | 0.9098 |
| C5—C6 | 1.395 (3) | ||
| C3—O2—C14 | 118.14 (18) | N1—C7—C6 | 116.9 (2) |
| N2—N1—C7 | 118.33 (18) | N2—C8—C9 | 119.9 (2) |
| N2—N1—H1A | 120.8 | N2—C8—H8A | 120.1 |
| C7—N1—H1A | 120.8 | C9—C8—H8A | 120.1 |
| C8—N2—N1 | 117.12 (19) | C10—C9—C13 | 117.0 (2) |
| C11—N3—C12 | 116.1 (2) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.7 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.2 (2) | C13—C9—C8 | 122.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 119.4 | C11—C10—C9 | 119.3 (2) |
| C6—C1—H1B | 119.4 | C11—C10—H10A | 120.3 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.6 (2) | C9—C10—H10A | 120.3 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.2 | N3—C11—C10 | 124.1 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.2 | N3—C11—H11A | 117.9 |
| O2—C3—C2 | 124.7 (2) | C10—C11—H11A | 117.9 |
| O2—C3—C4 | 115.6 (2) | N3—C12—C13 | 124.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.7 (2) | N3—C12—H12A | 117.8 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.5 (2) | C13—C12—H12A | 117.8 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.8 | C12—C13—C9 | 119.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.8 | C12—C13—H13A | 120.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.8 (2) | C9—C13—H13A | 120.5 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.6 | O2—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.6 | O2—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.2 (2) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 124.6 (2) | O2—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.2 (2) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 121.0 (2) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 122.1 (2) | H1—O1W—H2 | 101.5 |
| C7—N1—N2—C8 | −176.5 (2) | C1—C6—C7—O1 | −169.8 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.3 (3) | C5—C6—C7—O1 | 9.2 (3) |
| C14—O2—C3—C2 | −9.1 (3) | C1—C6—C7—N1 | 10.1 (3) |
| C14—O2—C3—C4 | 171.4 (2) | C5—C6—C7—N1 | −170.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—O2 | −178.8 (2) | N1—N2—C8—C9 | 178.37 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.7 (4) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | 165.7 (2) |
| O2—C3—C4—C5 | 179.1 (2) | N2—C8—C9—C13 | −14.8 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.4 (4) | C13—C9—C10—C11 | −0.2 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.3 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 179.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.4 (3) | C12—N3—C11—C10 | 0.8 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 178.6 (2) | C9—C10—C11—N3 | −0.7 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.7 (4) | C11—N3—C12—C13 | 0.1 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.4 (2) | N3—C12—C13—C9 | −1.0 (4) |
| N2—N1—C7—O1 | −2.6 (3) | C10—C9—C13—C12 | 1.0 (4) |
| N2—N1—C7—C6 | 177.42 (18) | C8—C9—C13—C12 | −178.5 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1W—H1···O1i | 0.84 | 2.00 | 2.811 (2) | 162 |
| O1W—H2···N3ii | 0.91 | 2.11 | 2.956 (3) | 154 |
| N1—H1A···O1W | 0.86 | 2.08 | 2.911 (2) | 161 |
| C1—H1B···O1W | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.440 (3) | 162 |
| C8—H8A···O1W | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.272 (3) | 143 |
| C11—H11A···O2iii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.375 (3) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB6930).
References
- Bayrak, H., Demirbas, N. & Karaoglu, S. A. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 4362–4366. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2000). SADABS, SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Fun, H.-K., Promdet, P., Chantrapromma, S., Horkaew, J. & Karalai, C. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o3370–o3371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.-F., Min, S.-T., Ge, H.-G. & Ji, X.-H. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Taha, M., Naz, H., Rahman, A. A., Ismail, N. H. & Sammer, Y. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X. (2009a). Acta Cryst. E65, o1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X. (2009b). Acta Cryst. E65, o2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812034988/hb6930sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812034988/hb6930Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812034988/hb6930Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report