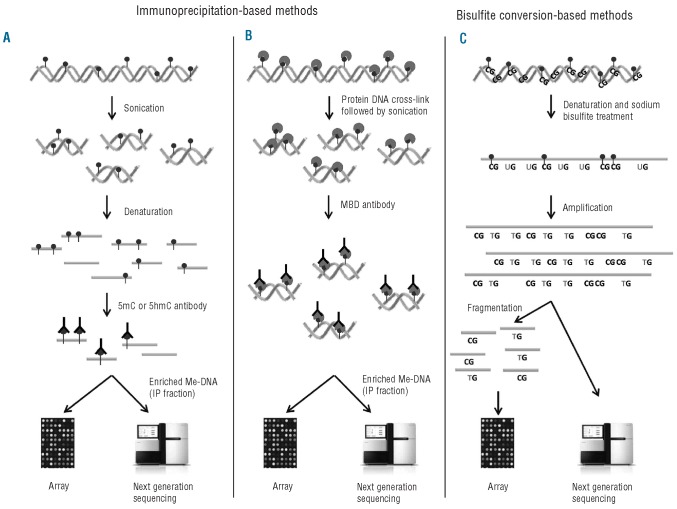
Figure 1.
Methods to detect global DNA methylation. (A) Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP). DNA is sonicated and subsequently denatured. Single stranded DNA is incubated with antibodies against either methylated (5mC) or hydroxymethylated (5hmC) cytosines followed by IP. The IP fraction (enriched for either methylated DNA or hydroxymethylated DNA) can either be labeled and hybridized to whole-genome tiling arrays or analyzed using next generation sequencing (NGS). (B) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) of methylated DNA. DNA and protein are cross-linked by formalin followed by sonication. DNA is incubated with antibodies or proteins that bind MBDs and precipitated. The enriched fraction can be analyzed by the same methods as for MeDIP. (C) The DNA is denatured and treated with sodium bisulfite. Unmethylated cytosine, ‘C’, is converted to uracil, ‘U’, while 5mC or 5hmC are unchanged. In the subsequent amplification, ‘U’ is amplified as thymine, ‘T’, while the unconverted 5mC or 5hmC are amplified as ‘C’. The amplification products are fragmented and hybridized to bead-based arrays or analyzed by NGS.