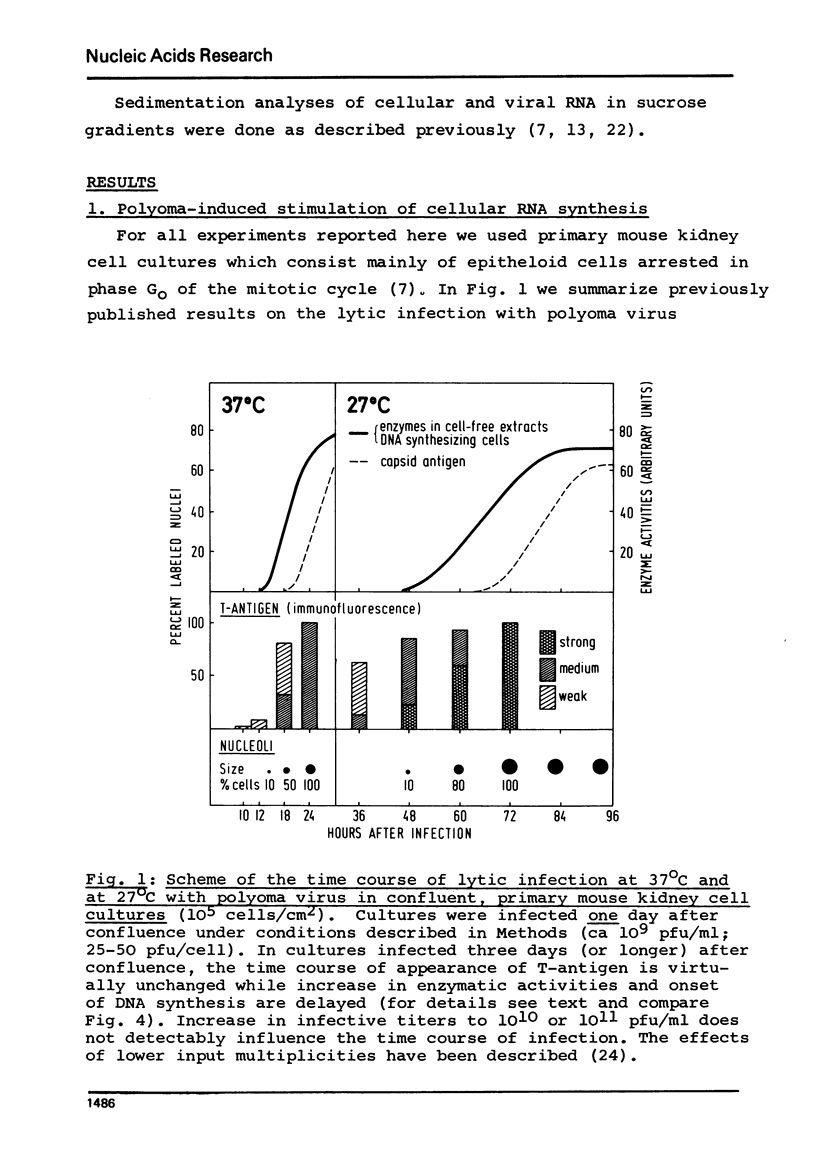
Abstract
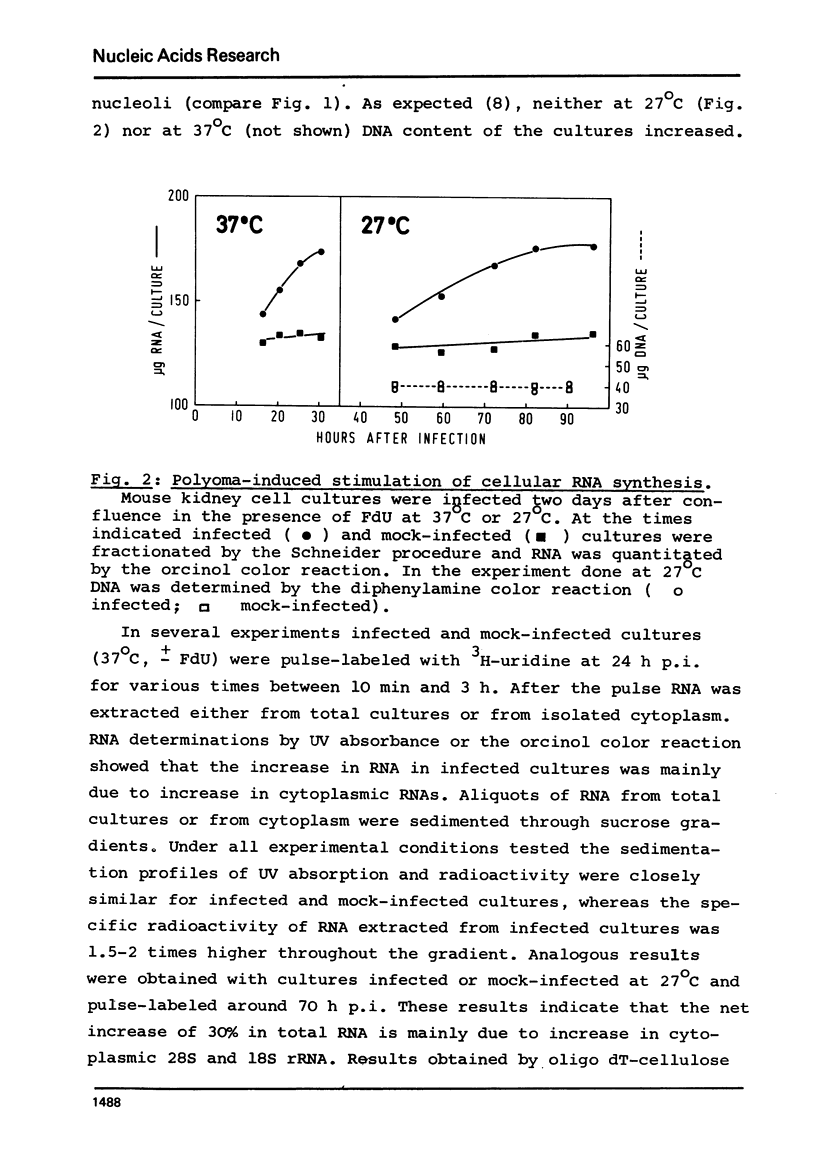
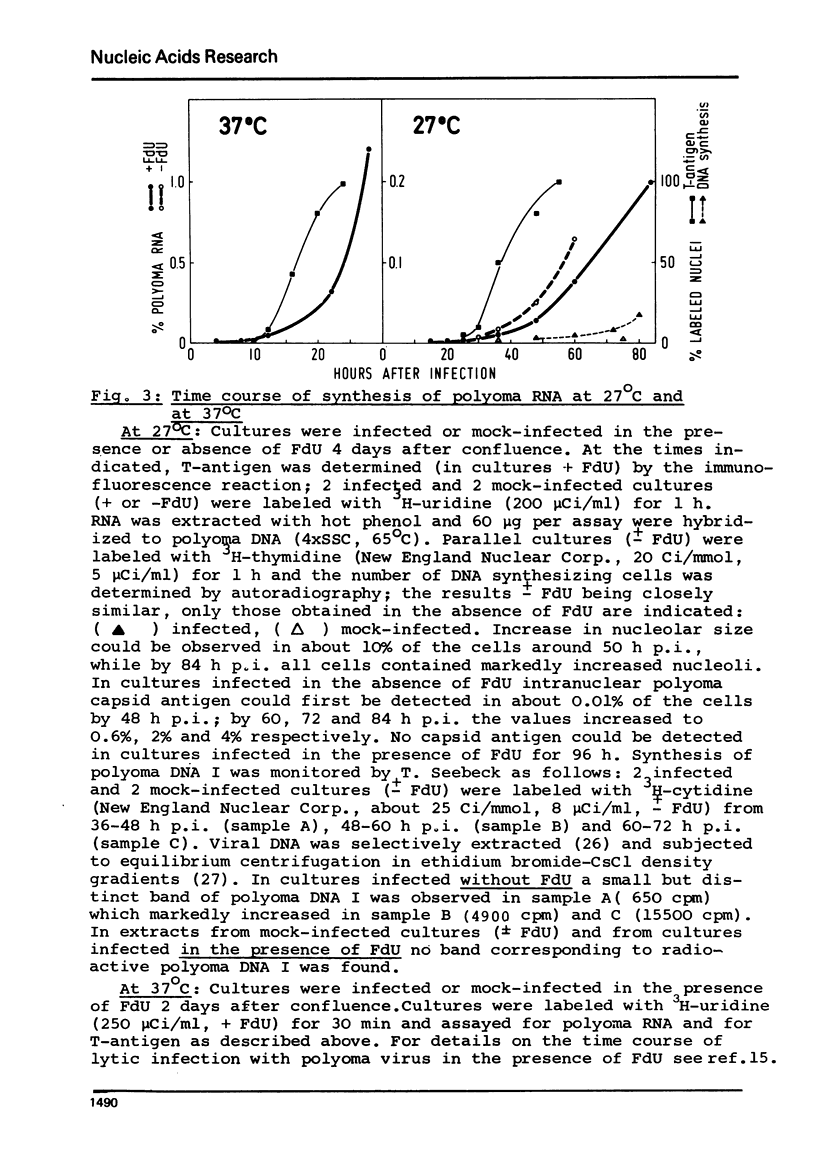
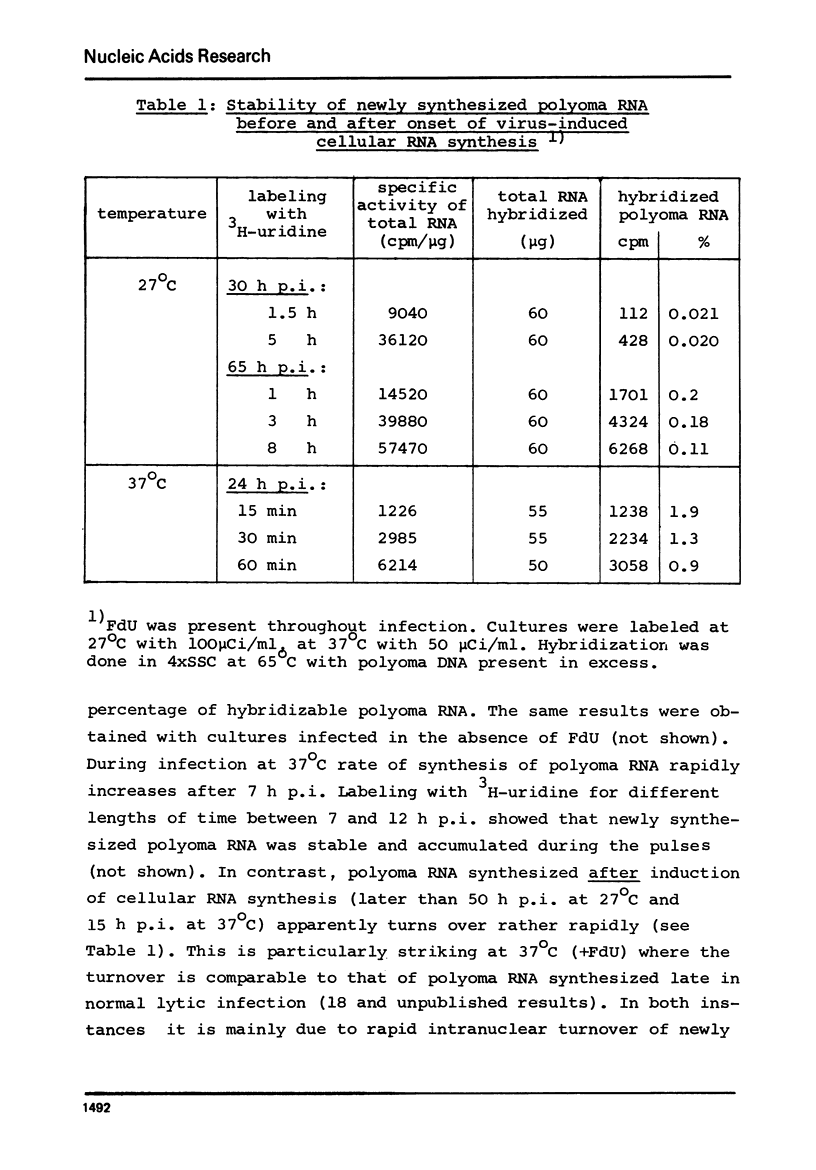
We studied synthesis of viral and cellular RNA in the presence and absence of 5-fluorodeoxyuridine (FdU, an inhibitor of DNA synthesis) during lytic infection with polyoma virus in confluent, primary mouse kidney cell cultures. In the presence of FdU, synthesis of early 19S polyoma mRNA and of polyoma tumor (T)-antigen, i.e. expression of the early viral gene, is rapidly followed by a mitogenic reaction of the host cell; it leads to an increase of 30 +/- 5% in cellular, mainly 28S and 18S rRNA, followed by activation of the cellular DNA-synthesizing apparatus. Polyoma-induced cellular RNA synthesis is paralleled by increased production of early 19S mRNA and begin of expression of the late viral genes, leading to synthesis of small amounts of late 19S and 16S mRNAs. Changed expression of the viral genome occurs in the absence of detectable synthesis of polyoma DNA I. Infection in the absence of FdU induces the same sequence of events; it is followed, however, by duplication of the mouse cell chromatin (S-phase) and production of progeny virus.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H., Buetti E., Scherrer K., Weil R. Transcription of the polyoma virus genome: synthesis and cleavage of giant late polyoma-specific RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2231–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad-Zadeh C., Allet B., Greenblatt J., Weil R. Two forms of simian-virus-40-specific T-antigen in abortive and lytic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1097–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Acheson N. H., Maxwell I. H. Strand-specific transcription of polyoma virus DNA-early in productive infection and in transformed cells. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.20-26.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E. Characterization of late polyoma mRNA. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):249–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.249-260.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. L., Gibson E. M. Control of synthesis and wastage of ribosomal ribonucleic acid in lymphocytes. II. The role of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5059–5066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C., Pignatti P. F., Croissant O., Yaniv M. Chromatin-like structures in polyoma virus and simian virus 10 lytic cycle. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.204-211.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. A., Hall M. R., Meinke W. Properties of nucleoprotein complexes containing replicating polyoma DNA. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):887–900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.887-900.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessman A. "Early" simian-virus-40-specific RNA contains information for tumor antigen formation and chromatin replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. F., Allet B., Weil R., Ahmad-Zadeh C. Synthesis of the tumour antigen and the major capsid protein of simian virus 40 in a cell-free system derived from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):361–379. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Fried M., Cowie A. Polyoma DNA: a physical map. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2077–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R., Weil R. Biochemical evidence for induction by polyoma virus of replication of the chromosomes of mouse kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1144–1150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Lindstrom D. M., Shure H., Old R. W. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):187–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Shure H. Topography of polyoma virus messenger RNA molecules. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):361–371. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kára J., Weil R. Specific activation of the DNA-synthesizing apparatus in contact-inhibited mouse kidney cells by polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):63–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. L., Consigli R. A. Early events in polyoma virus infection: attachment, penetration, and nuclear entry. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):620–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.620-636.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., May P., Weil R. "Early" virus-specific RNA may contain information necessary for chromosome replication and mitosis induced by Simian Virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1654–1658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétursson G., Weil R. A study on the mechanism of polyoma-induced activation of the cellular DNA-synthesizing apparatus. Synchronization by FUdR of virus-induced DNA synthesis. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;24(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01242898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal L. J. Isolation and characterization of poly(A)-containing polyoma "early" and "late" messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Mar;3(3):661–676. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal L. J., Salomon C., Weil R. Isolation and characterization of poly(A)-containing intranuclear polyoma-specific "giant" RNA'S. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 May;3(5):1167–1183. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.5.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seebeck T., Weil R. Polyoma viral DNA replicated as a nucleoprotein complex in close association with the host cell chromatin. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):567–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.567-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seehafer J. G., Weil R. Synthesis of polyoma virus structural polypeptides in mouse kidney cells. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Türler H., Salomon C., Allet B., Weil R. Mapping of the three species of polyoma mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1480–1484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL R., VINOGRAD J. THE CYCLIC HELIX AND CYCLIC COIL FORMS OF POLYOMA VIRAL DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:730–738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E. Purification of polyoma virus. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:158–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Kára J. Polyoma "tumor antigen": an activator of chromosome replication? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):1011–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Salomon E., May E., May P. A simplifying concept in tumor virology: virus-specific "pleiotropic effectors". Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):381–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Warnaar S. O., Winocour E. Isolation and characterization of simian virus 40 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.193-201.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Robbins E. Histone synthesis in polyoma- and SV40-infected cells. Virology. 1970 Feb;40(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger E., Wintersberger U. Induction of DNA polymerase in polyoma virus-infected mouse cells requires transcription and translation. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):291–295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.291-295.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



