Abstract
Current evidence supports the efficacy of placebo analgesia and illustrates that patients may be open to placebo use despite uncertainty regarding its mechanisms. Debate persists, however, concerning the ethics of placebo treatments. The purpose of the present web-based study was to expand upon the empirical literature on placebo analgesia ethics and acceptability. Participants (n = 100) provided their definition of a placebo and responded to 24 questions addressing placebo analgesia perceived knowledge, acceptability, effectiveness, and likelihood of placebo use among different healthcare providers. Results support previous research on the effects of placebo on negative mood and healthcare provider attributions, with findings illustrating that negative consequences of administration were largely mitigated by a beneficial treatment outcome. Results showed that participants conceptualized placebo as predominately “inert” and were mixed regarding interpretations of placebo effectiveness. Though acceptability ratings were dependent on the context of placebo administration, participants endorsing even moderate placebo acceptability were more open to placebo interventions and reported overall more positive treatment outcomes. Participants believed that placebos were used differentially among healthcare providers. Additional studies are needed to determine if placebo education can beneficially impact perceptions of placebo analgesia knowledge, acceptability, and treatment effectiveness.
Keywords: Placebo analgesia, placebo acceptability, placebo ethics, placebo knowledge, placebo treatment
INTRODUCTION
There has been extensive research elucidating the mechanisms underlying placebo effects, particularly for pain and its relief, but debate persists among ethicists, clinicians, and researchers concerning the clinical applications of placebo.13, 33 The primary issues are 1) dispute concerning placebo effectiveness/efficacy for reducing symptoms and 2) the ethics and feasibility of clinically administered placebo.29 Although several investigators have questioned the relevance of placebo effects based upon clinical trial meta-analyses 18, 19 others have shown that placebo mechanism studies, typically conducted within the context of pain reduction, systematically manipulate relevant placebo factors (e.g. expectation, classical conditioning) to elicit robust, clinically relevant reductions in pain.38, 39 Evidence from neuropharmacological and neuroimaging studies confirm that placebo analgesic effects are potent, psychoneurobiological events 1, 2 independent of response biases32 and often indistinguishable from the effects of known active agents.26, 40, 41 Studies have also demonstrated that placebo analgesic effects can occur in the absence of placebos8. Once paradoxically characterized as the effects of an ‘inert’ agent used to appease suffering patients,22 contemporary conceptualizations of placebo effects highlight the psychosocial context of an intervention, and how this context contributes to treatment efficacy; 21 thus, placebo effects likely play a role in virtually all active treatments and procedures.
Several authors have stated that placebo use is unethical due to violation of autonomy through deceptive administration and assumed negative consequences of deception, 30 such as psychological harm (e.g. depression, anxiety, and anger) and harmful sequelae secondary to violations of the physician-patient relationship.9 Contrary to these theoretical tenants, empirical evidence suggests that, despite lacking cogent understanding of placebo mechanisms, patients may be open to placebo use,6 particularly if a placebo may reduce pain.24 Findings from a open-label randomized controlled trial suggests that placebo can be used ethically and effectively to reduce symptoms in irritable bowel symptoms patients.23 As pain management is one of the primary reasons for seeking healthcare in the US,16 and with mounting evidence illustrating the frequency with which healthcare providers utilize and prescribe placebo treatments,12, 20, 28, 37 it is important to assess acceptance as well as knowledge of analgesic placebo use as a more sophisticated understanding of placebo mechanisms by patients and the general public may result in greater acceptance of placebo use.
Current findings illustrate that placebo effects may be effective for the reduction of clinical pain, and suggest that patients may be open to placebo use despite uncertainty regarding the mechanism underlying placebo effects. The purpose of the present study was to expand upon the empirical literature on placebo ethics and our past research on placebo analgesia acceptability7, 24 by examining placebo analgesia treatment perceived knowledge, acceptability, and perceived efficacy, as well as the impact of placebo on aspects of mood and patient-provider relations. Finally, we examined conceptualizations of placebo, and the degree to which these definitions reflect contemporary conceptualizations of the construct found in the empirical literature.
METHODS
Survey Development
The present survey was designed as a follow-up to the Placebo Attitudes survey, a vignette-based questionnaire assessing the sequelae of a physician administered placebo intervention under varying conditions of treatment deceptiveness, patient pain status, and treatment outcome.24 Our primary outcomes were lay individuals’ perceptions of placebo analgesia acceptability in regards to effects on aspects of patient negative mood and healthcare provider attributions. The present study represents a brief, non-vignette-based descriptive examination of placebo analgesia acceptability. In addition to investigating outcomes examined in our previous investigation (e.g. negative mood), new outcomes were added that we hypothesized would be relevant to the assessment of placebo analgesia ethics, including concepts of acceptability, perceived placebo knowledge and perceived treatment efficacy.
Participants
Study participants were 100 adults between the ages of 18 and 65 (68 females and 32 males; M age = 26.90, SD = 9.94). The majority of participants’ highest level of education was a college degree (48%), several participants had some college education (21%) or a graduate degree (18%). In regards to employment, most participants where either full-time employed (39%), students or not employed (31%), or were part-time employed (23%). The ethnic/racial distribution of the sample was as follows: Caucasian/white (51%); Hispanic (14%); Asian (14%); African American/black (13%) and Indian (8%). Demographic statistics are presented in Table 6.
Table 6.
Participant Demographics (n=100)
| n | |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Female | 68 |
| Male | 32 |
| Race/Ethnicity | |
| Caucasian/White | 51 |
| African American/Black | 13 |
| Hispanic | 14 |
| Asian | 14 |
| Indian | 8 |
| Highest level of Education | |
| High School | 2 |
| Some College Graduate degree | 21 |
| College Degree | 48 |
| Some college education | 11 |
| Graduate School Degree | 18 |
| Employment | |
| Unemployed | 7 |
| Part time employed | 23 |
| Full time Employed | 39 |
| Student, Disabled, not employed | 31 |
Procedure
The present study was approved by the University of Florida Institutional Review Board. The web-based study was advertized through flyers posted throughout the University of Florida campus. Interested participants were provided an online URL for the study in addition to a unique username and password necessary to log into the study. The Placebo Survey consisted of thirty-seven items assessing demographic characteristics and varying aspects of placebo analgesia perceived knowledge, acceptability, and perceived treatment efficacy. Select items were used for the present study. The Placebo Survey was completed online and informed consent was obtained from each participant. The survey took approximately 10–15 minutes to complete and all responses were anonymous. Upon study completion, participants provided a name and postal address to receive a $10 gift card in the mail.
Measures
Placebo Survey
The Placebo Survey consisted of Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) ratings of the following (Table 1): 1) perceived knowledge of placebo analgesia; 2) placebo analgesia treatment acceptability; 3) perceived placebo analgesia treatment effectiveness; 4) likelihood of analgesic placebo use among different healthcare providers; 5) the consequence of analgesic placebo use on aspects of negative mood, 6) positive mood, and 7) effects on healthcare provider attributions/trust; 8) willingness to participate in placebo controlled/randomized controlled involving a placebo for pain relief. Participants rated the likelihood of analgesic placebo use among 6 different health care providers: physicians, dentists, nurses, chiropractors, physician assistants, and physical therapists. Placebo analgesia treatment acceptability, one of our primary outcome measures, was evaluated through four questions spanning a variety of treatment contexts (e.g. acceptability when other standard treatment for pain exists; acceptability of using placebo as a diagnostic aid). Participants were also asked to define a placebo in their own words.
Table 1.
Placebo Survey measure descriptions, means, and test-retest reliability
| Placebo survey | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | Mean (SD) | Test-Retest (R) | VAS Anchors (0–100) |
| Knowledge | |||
| Rate your knowledge of placebo for pain relief | 41.47 (23.55) | .531 | “No knowledge of placebo for pain relief” to “Most knowledge of placebo for pain relief imaginable” |
| Acceptability | |||
| How acceptable would it be if you received a placebo treatment for pain? | 47.74 (34.45) | .824 | “Completely unacceptable” to “Completely acceptable” |
| A medical practitioner to treat pain with placebo for a condition for which there are other established treatments | 32.51 (29.32) | .751 | “Completely unacceptable” to “Completely acceptable” |
| A medical practitioner to treat pain with placebo for a condition for which there are no other established treatments? | 57.05 (35.65) | .861 | “Completely unacceptable” to “Completely acceptable” |
| Placebo to be used to determine if a patient’s symptoms are “real”? | 52.35 (35.45) | .815 | “Completely unacceptable” to “Completely acceptable” |
| Efficacy | |||
| How effective would placebo be for your pain? | 34.98 (22.05) | .522 | “Completely ineffective” to “Completely effective” |
| Likelihood of use among health care providers | 21.22 (14.77) | .577 | “Never” to “Always” |
| Level of Positive Mood if | |||
| You got a placebo that improved your pain | 66.90 (32.24) | .327 | “Neutral” to “most positive imaginable” |
| You got a placebo that had no effect on your pain | 19.96 (26.36) | .704 | “Neutral” to “most positive imaginable” |
| You got a placebo that made your pain worse? | 13.32 (27.26) | .178 | “Neutral” to “most positive imaginable” |
| Level of Negative Mood if | |||
| You got a placebo that improved your pain | 15.72 (23.52) | .175 | “Neutral” to “most negative imaginable” |
| You got a placebo that had no effect on your pain | 50.16 (30.73) | .210 | “Neutral” to “most negative imaginable” |
| You got a placebo that made your pain worse | 74.07 (32.87) | .117 | “Neutral” to “most negative imaginable” |
| Doctor Attributions/Trust if | |||
| You got a placebo that improved your pain | 55.00 (28.69) | .624 | “Least Trust” to “Most trust” |
| You got a placebo that had no effect on your pain | 29.07 (32.39) | .685 | “Least Trust” to “Most trust” |
| You got a placebo that made your pain worse | 12.36 (19.41) | .488 | “Least Trust” to “Most trust” |
| Willingness to participate in clinical trial involving placebo for pain relief | 62.99 (33.92) | .628 | “Completely unwilling” to “completely willing” |
Patients were also asked to rate their positive mood, negative mood, and trust in their physician across three treatment outcomes – when pain improved, worsened, or remained unchanged following placebo administration. A single negative mood construct was used, as opposed individual factors such as anxiety, depression and anger, as previous research in our lab has shown that pain-related negative emotions load highly on to a single latent negative mood factor.17, 24, 34 We choose to examine positive mood, a related but distinct construct from negative mood, 5, 42, 43 as to our knowledge no study has examined positive mood in relation to placebo acceptability.
Statistical Analyses
Analyses were performed using PASW for windows (Version 18). Means, standard deviations, and test retest reliability were computed for all continuous outcome measures (Table 1). Frequencies for demographic variables are provided above. Repeated Measures Analyses of Variance (ANOVA) were run to determine if there were 1) significant differences among perceived likelihood of placebo analgesic use among different healthcare providers, 2) differences in acceptability across distinct contexts of administration (e.g. when standard treatment for pain were available vs. not available), 3) determine if there were significant differences in negative mood, positive mood, and doctor attribution ratings for different placebo treatment outcomes; simple contrasts were used to compare differences between levels of the above mentioned constructs.
Principle axis factoring was used to reduce multicollinearity among select outcomes. Clutter analysis was used to empirically form subgroups of placebo acceptability. Qualitative analysis was used to determine the degree with which placebo definitions represented something ‘inert’ vs. ‘active’ and whether placebo effects were characterized as ‘effective’ vs. ‘ineffective’ for alleviating symptoms.
RESULTS
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics for survey VAS outcomes are summarized in Table 1. These variables were used as independent and dependent variables in subsequent ANOVA analyses.
Test-Retest Reliability
The first twenty-three study completers were asked to retake the survey within two weeks in order to calculate test-retest reliability. Correlations ranges of 0–.39, 0.4–0.69, and 0.7–1.0 were described as small, medium, and large effects, respectively. Overall, Survey VAS measures showed moderate to strong test-retest reliability (Table 1). Pearson Product Moment Correlations between likelihood of use by healthcare providers items ranged from .379–.725; reducing these variables to one factors (see principle axis factors below) yielded a correlation of .577. Placebo acceptability measures displayed strong reliability (.751 – .861). Correlations for placebo knowledge, healthcare provider trust, placebo efficacy, and willingness to participate in RCT were adequate and ranged between .488–.685. Reliability for positive and negative mood outcomes was generally low, ranging between .175–.704. Scatter plot inspection revealed that low reliability may be a function of range restriction (discussed in further detail in the discussion section). While acknowledging interpretive limitations of using mood scales with low reliability, these variables were included in subsequent analyses to provide an exploratory comparison between findings from previous placebo acceptability investigations.
Likelihood of Placebo Analgesic use by Healthcare Providers
Participants rated chiropractors as most likely to use analgesic placebos; dentists were rated least likely to use placebo for pain relief. Ratings showed that there were significant differences in perceived likelihood of analgesic placebo use for nearly all healthcare providers, with three exceptions: there were no significant differences in placebo use between chiropractors and physical therapists (F(1,99) = 2.96, p = .089 ηp2 = .029), nurses and physician assistants (F(1,99) = .131, p = .718 ηp2 = .001), and between physical therapists and physicians (F(1,99) = .797, p=.374 ηp2 = .008) (Table 2). Principle Axis Factoring (see Statistical Analyses) was used to reduce these 6 variables into one likelihood of placebo among healthcare providers variable to use in subsequent analyses (see section below).
Table 2.
Placebo Survey ANOVAs main effects and simple contrast analyses for differences between levels of Placebo Acceptability, Positive and Negative Mood, and Trust (VAS = 0–100; n=100)
| Main Effect/Contrasts | F | P | ES (ηp2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acceptability | F(2.70, 268.12) = 18.80 | p < .001** | .160 |
| Self tx > Standard tx | F(1,99) = 28.06 | p < .001** | .221 |
| Self tx < No Standard tx | F(1,99) = 9.72 | p = .002* | .089 |
| Self tx - Diagnostically | F(1,99) = 1.53 | p = .218 | .015 |
| Standard tx < No Standard tx | F(1,99) = 53.54 | p < .001** | .351 |
| Standard tx < Diagnostically | F(1,99) = 27.51 | p < .001** | .217 |
| Diagnostically - No Standard tx | F(1,99) = 1.41 | p = .237 | .014 |
| Likelihood of using placebo by health care providers | F(3.50, 346.39)= 11.24 | P < .001** | .102 |
| Chiropractors > Physicians | F(1,99) = 4.13 | P = .067 | .040 |
| Chiropractors > Dentists | F(1,99) = 27.54 | P < .001** | .218 |
| Chiropractors > Nurses | F(1,99) = 16.82 | P < .001** | .145 |
| Chiropractors – Physical therapists | F(1,99) = 2.96 | P = .089 | .029 |
| Chiropractors > Physician Assistants | F(1,99) = 16.58 | P < .001** | .143 |
| Dentists < Physicians | F(1,99) = 22.94 | P < .001** | .186 |
| Dentists < Nurses | F(1,99) = 6.05 | P = .016* | .058 |
| Dentists < Physical therapists | F(1,99) =21.33 | P < .001** | .177 |
| Dentists < Physician Assistants | F(1,99) = 7.39 | P = .008* | .069 |
| Nurses < Physicians | F(1,99) =4.94 | P = .029* | .048 |
| Nurses < Physical therapists | F(1,99) =7.65 | P = .007* | .072 |
| Nurses – Physician Assistants | F(1,99) =.131 | P = .718 | .001 |
| Physical Therapists – Physicians | F(1,99) = .797 | P = .374 | .008 |
| Physical Therapists > Physician Assistants | F(1,99) = 8.376 | P = .005* | .078 |
| Physician Assistants < Physicians | F(1,99) = 4.13 | P = .045* | .040 |
| Negative Mood | F(1.81,179.03) = 123.85 | p < .001** | .556 |
| Pain Improves < Pain Worsens | F(1,99) = 185.83 | p < .001** | .652 |
| Pain Improves < No change in Pain | F(1,99) = 95.04 | p < .001** | .490 |
| No Change in Pain < Pain Worsens | F(1,99) = 52.538 | p < .001** | .347 |
| Positive mood | F(1.57,155.71) = 116.70 | p < .001** | .541 |
| Pain Improves > Pain Worsens | F(1,99) = 139.32 | p < .001** | .585 |
| Pain Improves > No Change in Pain | F(1,99) = 140.27 | p < .001** | .586 |
| No change in pain > Pain Worsens | F(1,99) = 5.84 | p < .017* | .056 |
| Trust | F(1.53,151.44) = 125.34 | p < .001** | .559 |
| Pain Improves > Pain Worsens | F(1,99) = 169.98 | p < .001** | .632 |
| Pain Improves > No change in Pain | F(1,99) = 86.78 | p < .001** | .467 |
| No change in pain > Pain Worsens | F(1,99) = 76.44 | p < .001** | .436 |
Note: F, F Statistic; P, P value; ES, effect size; ηp2, partial eta squared;
Indicates significant difference (p < 0.05).
Indicates significant difference (p < 0.001).
Principle Axis Factoring
As we had no priori hypotheses concerning perceived likelihood of placebo analgesic use among different healthcare providers, and in an effort to reduce multicollinearity among our six VAS, we sought to reduce the number of variables used in subsequent analyses through Principle Axis Factoring. A Principle Axis Factoring (PAF) with oblique rotation was conducted for likelihood of placebo analgesic use for our six healthcare providers to determine if the measures loaded on to a single latent perceived likelihood of placebo use factor. The analysis yielded one latent factor with an eigenvalue of 3.946 accounting for 65.76% of the variance across the 6 measures. The likelihood of use among physicians, nurses, physical therapists, chiropractors, physician assistants, and dentists had loading of .787, .858, .710, .640, .891, and .708, respectively. The corresponding factor regression scores were used to create a single “perceived Likelihood of analgesic placebo use among health care providers” variable used in subsequent analyses.
Acceptability, Trust, and Mood
Participant’s rated placebo analgesic treatments most acceptable when no other established treatments for pain were available; placebo treatments were least acceptable when other standard treatments for pain were available. Participants reported that using placebo diagnostically to validate/invalidate a patient’s pain report was as acceptable as both using placebo to manage their pain (F(1,99) = 1.53, p =.218 ηp2 = .015) and use of this treatment modality in the presence of other established pain interventions (F(1,99) = 1.41, p =.237 ηp2 = .014).
There were significant differences in trust rating when comparing pain outcomes; highest trust ratings were found when placebo improved pain (M = 55.0, SD= 28.69) with lowest ratings when placebo make pain worse (M=12.36, SD= 19.41). Negative and positive mood ratings were inversely related across improved and worsening treatment outcomes. Our findings show that negative and positive mood ratings are differentially influenced by sub-optimal placebo treatment outcomes; positive mood ratings were nearly indistinguishable (Cohen’s d = .056) between outcomes where pain did not improve (i. e. pain unaffected by treatment, pain worsened by treatment) compared to moderate differences in negative mood ratings between these same outcomes (Cohen’s d = .347) (Table 2).
Cluster Analysis
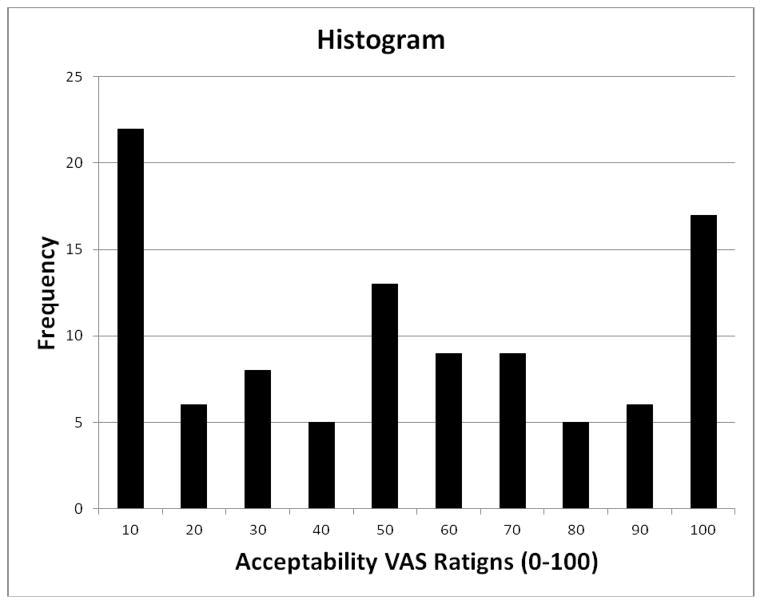
Graphical inspection (Figure 1) illustrates that the acceptability of treating one’s own pain with placebo was a trimodal distribution with peaks at the extremes and middle of the continuous variable. To more empirically form these subgroups, this variable was subjected to a Cluster Analysis. The agglomeration coefficients for Hierarchal Cluster Analysis yielded three distinct clusters characterized by: 1) low placebo acceptability, 2) moderate placebo acceptability, and 3) high placebo acceptability. A three level categorical variable was created to represent these three levels and ANOVA confirmed that all acceptability sub groups were significantly different from one another (P <.001).
Fig. 1.
Placebo Acceptability Histogram. Note: This graph depicts the trimodal distribution of placebo treatment acceptability.
Placebo Acceptability Sub-Group Analysis
Participants evaluated the acceptability of treating their pain with placebo. A cluster analysis empirically confirmed a trimodal distribution which supported three sub-groups: low, moderate, and high placebo acceptability. A three-level placebo “self-acceptability” independent variable was used for the following dependent variables in 10 ANOVA analyses (Table 3): two conditional placebo acceptability outcomes, willingness to participate in a placebo analgesia clinical trial, perceived placebo treatment effectiveness, and placebo treatment effects on mood and trust for pain improved and worsened outcomes. Post Hoc analyses with Bonferroni corrections were used to explore differences between the three levels of placebo acceptability for each variable. In comparing high vs. low placebo acceptability groups, participants endorsing high placebo acceptability were more willing to use a placebo analgesic intervention in the presence of other established (p <.001, Cohen’s d = 1.386) and non-established treatment for pain (p <.001, Cohen’s d= 1.343); these participants were also were more willing to participate in clinical trials of placebo analgesics (p =.017, Cohen’s d=.684) and believed that placebo was more effective for reducing pain (p <.001, Cohen’s d=1.03); high acceptability participants endorsed higher positive mood (p=.008, Cohen’s d=.750) and trust (p =.016, Cohen’s d = .682) for treatment outcomes in which placebo effectively reduced their pain. Comparable results were found when comparing participants endorsing moderate vs. low placebo acceptability.
Table 3.
Between-subjects “Acceptability Groups” ANOVA POST HOC analysis (VAS = 0–100; n=100)
| Main Effect/Post Hoc comparisons | F/Mean difference | p | ES (Cohen) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accept for Established Treatments | F(2,97)= 26.57 | P< .001** | f = .740 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 42.40 | P< .000** | d = 1.386 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 12.87 | P= .172 | d = .485 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 29.53 | P< .001** | d = 1.121 |
| Accept No Established treatments | F(2,97)= 26.69 | P< .001** | f =.742 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 53.74 | P<. 001** | d = 1.343 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 20.50 | P= .040* | d = .755 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 33.24 | P<.001** | d = .996 |
| Willingness to Participate in RCT | F(2,97)= 4.45 | P= .014* | f = .302 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 25.48 | P= .017 | d = .684 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 11.08 | P= .697 | d = .541 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 14.01 | P= .154 | d = .427 |
| Placebo Effectiveness | F(2,97)=19.74 | P< .001** | f = .638 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 23.30 | P< .001** | d = 1.030 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 0.82 | P= 1.00 | d = .045 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 24.11 | P< .001** | d = 1.106 |
| Negative mood improved pain | F(2,97)= 2.38 | P= .098 | f = .364 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 13.6 | P= .113 | d = .538 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 6.61 | P= .941 | d = .305 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 6.86 | P= .562 | d = .293 |
| Negative mood worsens pain | F(2,97)=2.318 | P= .104 | f = .220 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 18.29 | P= .130 | d = .515 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 17.16 | P= .188 | d = .523 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 1.14 | P= 1.00 | d = .037 |
| Positive mood improves pain | F(2,97)= 6.43 | P= .002* | f = .364 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 25.94 | P= .008* | d = .750 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 6.37 | P= 1.00 | d = .232 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 19.57 | P= .015* | d = .604 |
| Positive mood worsens pain | F(2,97)=1.97 | P= .145 | f = .220 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 10.86 | P= .443 | d = .350 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 0.05 | P= .100 | d = .002 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 10.80 | P= .226 | d = .377 |
| Trust improves pain Improves | F(2,97)= 10.24 | P< .001** | f = .459 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 32.14 | P<. 001** | d = 1.034 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 17.24 | P= .066 | d = .732 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 14.90 | P=. 038* | d = .517 |
| Trust worsens pain | F(2,97)= 4.083 | P= .020* | f = .291 |
| High Accept > Low Accept | 14.77 | P= .016* | d = .682 |
| High Accept > Mod Accept | 1.42 | P= .101 | d = .558 |
| Mod Accept > Low Accept | 3.35 | P= 1.00 | d = .204 |
Note: F, F Statistic; P, P value; ES, effect size; ηp2, partial eta squared; f, cohens F; d, cohen s d.
Indicates significant difference (p < 0.05).
Indicates significant difference (p < 0.001).
Qualitative Analysis of Placebo Knowledge
Two raters rated their agreement on placebo definitions based upon two dimensions: the degree to which the description of a placebo represented something traditionally considered ‘inert’ (e.g. sugar pill, sham treatment) or ‘active’ (e.g. medical intervention, drug), and the degree to which the description of placebo effects characterized ‘ineffectiveness’ (e.g. “placebo cannot help any ailments) or ‘effectiveness’ (e.g. “those who take placebo will experience significant relief from an ailment”) for alleviating or managing adverse symptoms. If the rater felt that the placebo definition did not fit into either category, they would designate “non-applicable” for the category. Cross - tabulations for inert vs. active and ineffective vs. effective are displayed in Tables 4 and 5, respectively. Raters agreed on 91/100 classifications of placebo inertness (Kappa = .555, p <.001). Of the 91 definitions, 93% were classified as inert, 4% were classified as active, and 2% could not be classified into either group. Raters agreed on 69/100 definitions of placebo effectiveness (Kappa = .526, p <.001). Of the 69 ratings, 24.6% found them ineffective, and 30.4% found placebos potentially effective for alleviating symptoms. Kappa coefficients indicated that we obtained moderate agreement between both raters for both categories. 25
Table 4.
Interrater consistency for characterizing placebo definitions as either “Inert” or “Active”
| Rater # 1 | Rater #2
|
Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n/a | Inert | Active | ||
| n/a | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Inert | 3 | 85 | 3 | 91 |
| Active | 0 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| Total | 5 | 87 | 8 | 100 |
Note: “Inert”, a placebo characterized as something traditionally inert (e.g. Sugar pill, sham treatment); “Active”, a placebo characterized as something traditionally considered active (medical intervention, drug); “n/a”, a placebo definition that does not fall into either the “Inert” or “Active” category.
Table 5.
Interrater consistency for characterizing placebo effects as either “Ineffective” or “Effective”
| Rater # 1 | Rater #2
|
Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n/a | Ineffective | Effective | ||
| n/a | 31 | 8 | 1 | 40 |
| Ineffective | 11 | 17 | 3 | 31 |
| Effective | 4 | 4 | 21 | 29 |
| Total | 48 | 29 | 25 | 100 |
Note: “Ineffective”, the degree to which the description of placebo characterizes something ineffective (e.g. “placebo cannot help any ailments); “Effective”, the degree to which the description of placebo characterizes something effective (e.g. “those who take placebo will experience significant relief from an ailment”); “n/a”, a placebo effects that does not fall into either the “ineffective” or “effective” category.
DISCUSSION
The present study investigated placebo analgesia acceptability, perceived knowledge, and perceived efficacy explicitly and exclusively for the alleviation of pain. While several placebo surveys have incorporated individual items related to pain reduction,6, 11, 14, 15 these items were often supplementary, as all studies also included items related to nonspecific disease symptoms, or explicit symptoms such as insomnia, substance abuse, and psychological factors. Our findings support and expand upon the empirical literature on placebo ethics, as well as expand upon research regarding placebo analgesia acceptability and knowledge.7, 24 While several studies have documented the frequency of placebo use among various healthcare providers across different settings 12, as well as patients’ attitudes towards placebo use,6, 10 to our knowledge this is the first study to assess the perceived likelihood of placebo analgesic use for different healthcare providers, with results showing that participants rated chiropractors the most likely, and dentists the least likely, to utilize placebo treatments for pain. Our findings support previous research on the effects of placebo on aspects of mood and healthcare provider attributions, with results illustrating that negative consequences of administration were largely mitigated by a beneficial treatment outcome. 7, 24 Our results support findings from previous investigations24, 27 that there are significant differences in placebo acceptability dependent on the context of administration, as placebo acceptability ratings, were highest in the absence of alternative established treatments for pain.
Placebo Definitions
The controversy surrounding placebo effects is in part due to how they are conceptualized, which is likely due to their association with randomized controlled trials.22 Research has demonstrated that there is not one, but many placebo effects, with different responses and mechanisms implicated for different conditions. Furthermore, there are different types of placebos, such as ‘pure’ placebos (e.g. sugar pills or saline injection) and ‘impure’ or placebos (e.g. antibiotics for a viral infection)12. Placebo effects can even occur without the explicit use of placebos.8 While some have advocated replacing the term ‘placebo’ with potentially more explicit language, such as “meaning and context effects,” 21 placebo terminology is likely too entrenched in the scientific literature to be replaced without an adequate substitute.13 One innovative aspect of our investigation was the qualitative assessment of placebo definitions. In a recent placebo survey meta analysis,12 the authors noted that that vast majority of placebo studies included explicit definitions of placebo, or bypassed definitional issues entirely. Directly assessing how participant’s characterized placebo is important in evaluating the extent to which empirical knowledge has disseminated to the general public. Our study found that, contrary to how placebo effects are frequently characterized in the scientific community (i.e. psychosocial context and its contribution to treatment efficacy), participants in our sample conceptualized placebo effects as predominately ‘inert’ and were mixed regarding their interpretations of placebo effectiveness for alleviating symptoms. Future studies are needed to disseminate contemporary placebo conceptualization to the lay public to evaluate whether empirically informed judgments will have a beneficial impact on conceptualizations of analgesic placebo acceptability.
Placebo Analgesia Acceptability
In regards to the acceptability of treating one’s own pain with placebo, the distribution of acceptability was tri-modal, and participants fell into three groups– low, moderate, and high acceptability. There were significant and large differences between these groups on ratings of acceptability across different treatment contexts, perceived treatment efficacy, and sequelae of placebo use. It is important to note that meaningful differences existed between even moderate and low acceptability subgroups for ratings of acceptability with and without the existence of other standard treatments for pain, ratings of placebo effectiveness, and for select positive mood and trust treatment outcomes. These findings suggest that even relatively minor alterations in placebo acceptability may have a meaningful impact on broad perceptions of placebo ethics. Future studies are needed to experimentally investigate the directionality of this relationship, and the degree to which manipulating acceptability and knowledge may beneficially alter treatment perceptions and outcomes.
Diagnostic use of Placebo for Pain
American Pain Society’s (APS) treatment guidelines caution against the “use of placebo to assess the nature of pain,” as “analgesic responses to placebo clearly should not be used to invalidate a patient’s pain complaint”.36 Our participant’s ratings of the acceptability of using placebo diagnostically for pain were variable (M =52.35, SD= 35.45) and generally correspond to the mixed findings among healthcare providers.12 While several studies have reported high acceptance of diagnostic placebo use,14 more recent studies suggest that among healthcare provider acceptability may be decreasing, with only 21–25% of general practitioners and primary care physicians deems diagnostic placebo use acceptable. 6, 11 Relatively few studies investigated the acceptability of diagnostic placebo use from patients or non-healthcare providers. A survey by Chen and Johnson6 found that 27% of patient’s deemed it appropriate to use placebo to determine whether a patients pain was organic or not. Given the wealth of literature highlighting both the physiological and psychological mechanisms underlying placebo effects for pain, it is imperative for future investigations to educate lay individuals and healthcare providers about the fallacy of adopting this viewpoint.
Implications
The findings from the present investigation represent important additions to the placebo ethics literature, though future studies are necessary to clarify the placebo acceptability debate. Placebo analgesia is currently the most well understood model of placebo effects, with numerous studies demonstrating clinically meaningful effect sizes, with studies showing that placebo analgesia responders on average experience a 5 point (on a 10 point Numerical Rating Scale) reduction in pain.3 There is now compelling evidence challenging popular longstanding perceptions regarding clinical placebo use, as research shows that placebos are potentially potent, biologically active agents, and that individuals are rather pragmatic in their determinations of placebo acceptability for pain. Although it is generally understood that deception is prima facie unacceptable from an ethical standpoint, there may be contexts in which deceptive placebo use may be tolerable. Thus, the onus on evaluating placebo ethic/acceptability lies largely on findings of placebo efficacy.
While the present investigation illustrated that there are individuals who consider placebo use at least moderately acceptable for the treatment of pain, the vast majority of our sample characterized placebo effects as inert and lacked a sophisticated understanding of placebo mechanisms. In order to clarify the placebo ethics debate, it is important to disseminate empirical evidence regarding placebo effects on various conditions, as well as frame placebo as a potentially active agent that contributes to the efficacy of all interventions. In order to make appropriate judgments regarding placebo ethics, individuals must understand the ubiquity of placebo effects and frequently with which placebos and placebo effects are being utilized in routine care. For example, several randomized controlled trials found that effects sizes for traditional acupuncture, an increasingly popular alternative treatment for pain, were clinically meaningful but indistinguishable from “sham” acupuncture, suggesting efficacy was largely due to placebo mechanisms. The benefits of placebo analgesia may extend beyond clinical pain management, as studies have shown that placebo induced reductions in pain are also associated with improved sport/physical performance.4, 31 To advance the debate, future studies are needed to evaluate four important areas: 1) the salience/duration of placebo analgesic effects over time; 2) whether it is possible elicit clinically meaningful analgesic effects non-deceptively; 3) the degree to which placebo knowledge affects acceptability and perceptions of treatment efficacy; 4) Finally, while placebo is often evaluated in the context of a standalone treatment, future studies should assesses acceptability and feasibility of utilizing placebo to augment existing treatments for pain .
There were limitations to the generalizability of this study. While participants were asked to respond to several questions as if they were patients, it is possible that ratings from a primary student sample may not have been representative of a pain patient population. However, it is important to note that these participants are and will be consumers of medical services for pain. Furthermore, as members of the voting public, their perspectives and opinions will be important in determining future policies regarding placebo use. Although rest-retest reliability was overall adequate, the low reliability of the mood constructs limits the confidence and likely the repeatability of findings using those ratings. Further inspection of scatter plot distributions of test vs. retest for negative and positive mood variables illustrated that low correlations were largely a function of skewed distributions, resulting in range restriction.35 Participants tended to endorse extreme values (0 or 100) for both test and retest, thus showing high reliability, but low correlations because of range restriction. This also explains why the mood ratings showed some validity (difference between conditions) despite low calculated reliability. Finally, this project was primarily exploratory and descriptive in nature, and further validation of the survey is necessary; however, we consider several of our analyses as the initial validation of this measure. We acknowledge our interpretive limitations, but suggest this design was necessary given the paucity of empirical data on specific variables, and we anticipate that this investigation will serve as rational for future hypothesis testing.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of the present study illustrate that lay individuals’ knowledge of placebo analgesia largely fails to reflect conceptualizations of placebo mechanisms found in the current empirical literature. Our findings support previous research showing that beneficial treatment outcomes may mitigate the negative consequences of placebo administration through moderating mood and augmenting trust. Evaluations of placebo analgesic acceptability are highly dependent on the context of administration. Although most participants evaluated placebo analgesic treatments as either acceptable or unacceptable, those endorsing even marginal acceptability overall rated treatment as more effective. Additional research is needed to determine if educational interventions reflecting current empirical evidence regarding placebo can beneficially impact perceptions of treatment acceptability and efficacy.
PERSPECTIVE.
This study presents an examination of analgesic placebo treatment perceived acceptability, efficacy, and knowledge among lay individuals. Our findings highlight the importance of assessing placebo conceptualizations and treatment perceptions in evaluating placebo ethics – a highly relevant finding that informs the clinical use of placebo components in managing pain.
Acknowledgments
This manuscript was supported by Grant 5R01AT001424-06 to Dr. Michael Robinson, from the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) of the NIH.
Footnotes
Disclosure Statement:
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errorsmaybe discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Amanzio M, Benedetti F. Neuropharmacological Dissection of Placebo Analgesia: Expectation-Activated Opioid Systems versus Conditioning-Activated Specific Subsystems. The Journal of Neuroscience. 1999;19:484–494. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-01-00484.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Amanzio M, Pollo A, Maggi G, Benedetti F. Response variability to analgesics: a role for non-specific activation of endogenous opioids. Pain. 2001;90:205–215. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00486-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Benedetti F. The opposite effects of the opiate antagonist naloxone and the cholecystokinin antagonist proglumide on placebo analgesia. PAIN. 1996;64:535–543. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(95)00179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Benedetti F, Pollo A, Colloca L. Opioid-mediated placebo responses boost pain endurance and physical performance: Is it doping in sport competitions? Journal of Neuroscience. 2007;27:11934–11939. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3330-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cacioppo JT, Berntson GG. Relationship between attitudes and evaluative space: A critical review, with emphasis on the separability of positive and negative substrates. Psychological Bulletin. 1994;115:401–423. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chen G-F, Johnson M. Patients’ attitudes to the use of placebos: results from a New Zealand survey. The New Zealand Medical Journal. 2009;122:11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chung SK, Price DD, Verne GN, Robinson ME. Revelation of a personal placebo response: its effects on mood, attitudes and future placebo responding. Pain. 2007;132:281–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.01.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Colloca L, Lopiano L, Lanotte M, Benedetti F. Overt versus covert treatment for pain, anxiety, and Parkinson’s disease. The Lancet Neurology. 2004;3:679–684. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00908-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cupples B, Myron G. The Investigator’s Duty Not to Deceive. IRB: Ethics and Human Research. 1985;7:1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fassler M, Gnadinger M, Rosemann T, Biller-Andorno N. Placebo interventions in practice: a questionnaire survey on the attitudes of patients and physicians. British Journal of General Practice. 2011;61:101–107. doi: 10.3399/bjgp11X556209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fassler M, Gnadinger M, Rosemann T, Biller-Andorno N. Use of placebo interventions among Swiss primary care providers. BMC Health Services Research. 2009;9:144. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-9-144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fassler M, Meissner K, Schneider A, Linde K. Frequency and circumstances of placebo use in clinical practice - a systematic review of empirical studies. BMC Medicine. 2010;8:15. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Finniss DG, Kaptchuk TJ, Miller F, Benedetti F. Biological, clinical, and ethical advances of placebo effects. The Lancet. 2010;375:686–695. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61706-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goodwin JS, Goodwin JM, Vogel AV. Knowledge and Use of Placebos by House Officers and Nurses. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1979;91:106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-1-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gray G, Flynn P. A survey of placebo use in a general hospital. General Hospital Psychiatry. 1981;3:199–203. doi: 10.1016/0163-8343(81)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hing E, Cherry DK, Woodwell DA. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2004 summary. Advance data. 2006:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hirsh AT, Waxenberg LB, Atchison JW, Gremillion HA, Robinson ME. Evidence for sex differences in the relationships of pain, mood, and disability. The Journal of Pain. 2006;7:592–601. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2006.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hróbjartsson A, Gøtzsche PC. Is the placebo powerless? Update of a systematic review with 52 new randomized trials comparing placebo with no treatment. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2004;256:91–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hróbjartsson A, Gøtzsche Peter C. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2010. Placebo interventions for all clinical conditions. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hrobjartsson A, Norup M. The Use of Placebo Interventions in Medical Practice--A National Questionnaire Survey of Danish Clinicians. Eval Health Prof. 2003;26:153–165. doi: 10.1177/0163278703026002002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jonas WB. Reframing placebo in research and practice. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2011;366:1896–1904. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kaptchuk TJ. Powerful placebo: The dark side of the randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 1998;351:1722. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)10111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kaptchuk TJ, Friedlander E, Kelley JM, Sanchez MN, Kokkotou E, Singer JP, Kowalczykowski M, Miller FG, Kirsch I, Lembo AJ. Placebos without Deception: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e15591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kisaalita NR, Roditi D, Robinson ME. Factors Affecting Placebo Acceptability: Deception, Outcome, and Disease Severity. The Journal of Pain. 2011;12:920–928. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2011.02.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Landis JR, Koch GG. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Levine JD, Gordon NC, Smith R, Fields HL. Analgesic responses to morphine and placebo in individuals with postoperative pain. PAIN. 1981;10:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(81)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lynöe N, Mattsson B, Sandlund M. The attitudes of patients and physicians towards placebo treatment – A comparative study. Social Science & Medicine. 1993;36:767–774. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(93)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Meissner K, Höfner L, Fässler M, Linde K. Widespread use of pure and impure placebo interventions by GPs in Germany. Family Practice. 2011 doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmr045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Miller FG, Colloca L. The Legitimacy of Placebo Treatments in Clinical Practice: Evidence and Ethics. American Journal of Bioethics. 2009;9:39–47. doi: 10.1080/15265160903316263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miller FG, Wendler D, Swartzman LC. Deception in Research on the Placebo Effect. PLoS Medicine. 2005;2:853–858. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pollo A, Carlino E, Benedetti F. The top-down influence of ergogenic placebos on muscle work and fatigue. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2008;28:379–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Price DD, Craggs J, Nicholas Verne G, Perlstein WM, Robinson ME. Placebo analgesia is accompanied by large reductions in pain-related brain activity in irritable bowel syndrome patients. Pain. 2007;127:63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2006.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Price DD, Finniss DG, Benedetti F. A Comprehensive Review of the Placebo Effect: Recent Advances and Current Thoughts. Annual Review of Psychology. 2008;59:2.1–2.26. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.59.113006.095941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Robinson ME, Riley JL, III, Gatchel RJ, Turk DC. The role of emotion in pain. New York, NY US: Guilford Press; 1999. pp. 74–88. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sackett PR, Laczo RM, Arvey RD. The effects of range restriction on estimates of criterion interrater reliability: Implications for validation research. Personnel Psychology. 2002;55:807–825. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sullivan M, Terman GW, Peck B, Correll DJ, Rich B, Clark WC, Latta K, Lebovits A, Gebhart G. APS position statement on the use of placebos in pain management. The Journal of Pain. 2005;6:215–217. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2005.01.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tilburt JC, Emanuel EJ, Kaptchuk TJ, Curlin FA, Miller FG. Prescribing placebo treatments: results of national survey of US internists and rheumatologists. BMJ. 2008;337 doi: 10.1136/bmj.a1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vase L, Petersen GT, Riley JL, Price D. Factors contributing to large analgesic effects in placebo mechanism studies conducted between 2002 and 2007. PAIN. 2009;145:36–44. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vase L, Riley JL, Price DD. A comparison of placebo effects in clinical analgesic trials versus studies of placebo analgesia. Pain. 2002;99:443–452. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3959(02)00205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vase L, Robinson ME, Verne GN, Price DD. The contributions of suggestion, desire, and expectation to placebo effects in irritable bowel syndrome patients: An empirical investigation. Pain. 2003;105:17–25. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(03)00073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Vase L, Robinson ME, Verne GN, Price DD. Increased placebo analgesia over time in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) patients is associated with desire and expectation but not endogenous opioid mechanisms. Pain. 2005;115:338–347. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Watson D, Clark LA. Measurement and Mismeasurement of Mood: Recurrent and Emergent issues. Journal of Personality Assessment. 1997;68:267–296. doi: 10.1207/s15327752jpa6802_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Watson D, Tellegen A. Toward a consensual structure of mood. Psychological Bulletin. 1985;98:219–235. doi: 10.1037//0033-2909.98.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]