Abstract
Background
Computational methods for structural gene annotation have propelled gene discovery but face certain drawbacks with regards to prokaryotic genome annotation. Identification of transcriptional start sites, demarcating overlapping gene boundaries, and identifying regulatory elements such as small RNA are not accurate using these approaches. In this study, we re-visit the structural annotation of Mannheimia haemolytica PHL213, a bovine respiratory disease pathogen. M. haemolytica is one of the causative agents of bovine respiratory disease that results in about $3 billion annual losses to the cattle industry. We used RNA-Seq and analyzed the data using freely-available computational methods and resources. The aim was to identify previously unannotated regions of the genome using RNA-Seq based expression profile to complement the existing annotation of this pathogen.
Results
Using the Illumina Genome Analyzer, we generated 9,055,826 reads (average length ~76 bp) and aligned them to the reference genome using Bowtie. The transcribed regions were analyzed using SAMTOOLS and custom Perl scripts in conjunction with BLAST searches and available gene annotation information. The single nucleotide resolution map enabled the identification of 14 novel protein coding regions as well as 44 potential novel sRNA. The basal transcription profile revealed that 2,506 of the 2,837 annotated regions were expressed in vitro, at 95.25% coverage, representing all broad functional gene categories in the genome. The expression profile also helped identify 518 potential operon structures involving 1,086 co-expressed pairs. We also identified 11 proteins with mutated/alternate start codons.
Conclusions
The application of RNA-Seq based transcriptome profiling to structural gene annotation helped correct existing annotation errors and identify potential novel protein coding regions and sRNA. We used computational tools to predict regulatory elements such as promoters and terminators associated with the novel expressed regions for further characterization of these novel functional elements. Our study complements the existing structural annotation of Mannheimia haemolytica PHL213 based on experimental evidence. Given the role of sRNA in virulence gene regulation and stress response, potential novel sRNA described in this study can form the framework for future studies to determine the role of sRNA, if any, in M. haemolytica pathogenesis.
Background
A systems-level understanding of organisms is not feasible by studying the functions of individual genes or proteins using reductionist approaches. It requires describing all molecular-level components that constitute building blocks of the system, identifying interactions among these components and determining regulatory modules to model emergent behavior [1]. As such, identifying all functional elements including genes, RNA, and proteins is a prerequisite to generating predictive models of biological response to biotic or abiotic perturbations. The genome sequence encodes all the necessary information required to decipher its functions. Therefore, genome sequencing, with concomitant structural annotation, i.e., identification of the functional elements within the genome, including genes, gene structures, open reading frames and regulatory motifs, is a critical step for conducting systems biology research. It is imperative that current and up-to-date knowledge of molecular level components exists for a genome sequence. Therefore, re-annotation is key to identifying these fundamental components of biological processes.
De novo assembly of a genome is followed by mapping of functional elements using computational methods. Computational methods for prokaryotic gene annotation such as Gene Locator and Interpolated Markov ModelER (GLIMMER) [2] and GeneMark.hmm [3] use hidden Markov models [4] based on a sequence similarity measure generated from previously annotated genomes. These algorithms do not accurately identify all genes in the genome and sometimes result in errors, especially in positioning of translational start codons [5] and in the identification of small protein coding genes. Another major problem with computational approaches is over-annotation, which arises from the failure to discriminate between random open reading frames and those that are translated. Computational prediction of small non-coding RNA (sRNA), which lack sequence conservation in closely related species, has limited accuracy since transcriptional signal prediction (promoter and rho-independent terminator prediction) is also not accurate. Therefore, sRNA that regulate many biological processes, including virulence in bacterial pathogens, cannot be identified by computational approaches alone.
Experimental identification of expressed regions in the genome can help overcome some of the drawbacks of computational methods and is a complementary approach to computational genome annotation methods. DNA microarrays, serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE) or high throughput transcriptome sequencing technologies such as RNA-Seq, can all be used to measure genome expression [6-9]. Of these methods, RNA-Seq, which generates a single nucleotide resolution map of the transcriptome, can help annotate mRNA, non-coding RNA and sRNA, transcriptional structure of genes, and post-transcriptional modifications induced by alternate splicing in eukaryotes [10-13].
In this study, we report re-annotation of M. haemolytica, a gram-negative bacterial pathogen and one of the causative agents of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) in cattle. BRD is responsible for over $3 billion in losses to the cattle industry every year [14]. M. haemolytica is most commonly isolated in field cases of BRD [15] and is considered to be the primary pathogen for this disease. Due to its importance for disease etiology, the genome of a bovine strain of M. haemolytica was sequenced in 2006. However, to date, the 2.6 Mb M. haemolytica PHL213 genome sequenced with an 8.4× coverage, is still in its draft phase. Despite being sequenced 6 years ago, the M. haemolytica genome sequence has not seen any improvement in its quality. Therefore, we chose to conduct RNA-Seq based re-annotation of M.haemolytica. The single nucleotide resolution map generated helped identify novel protein coding regions, sRNA, correct annotation errors, and operon structures.
Materials and methods
RNA isolation
M. haemolytica PHL213 was cultured in brain heart infusion (BHI) to mid-log phase (OD620 = 0.8). Cells from a single culture were treated with RNAprotect reagent (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) and stored at -80°C for subsequent RNA isolation. Total RNA from this single culture was extracted using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA), following manufacturer's protocols. It is to be noted that this kit allows for the extraction of transcripts that are at least 200 nucleotides and larger. RNA preparations were treated with RNase-free DNAse (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and the integrity of the RNA was determined using Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). RNA sample with RNA Integrity Number (RIN) of 8 was used for the RNA-Seq experiment. From total RNA, mRNA was enriched by removing the rRNAs using MICROBExpress™ kit (Ambion, Austin, TX). This enrichment step specifically removes large rRNAs; small RNAs (i.e., tRNA and 5S rRNA) are not removed. In the first step of the MICROBExpress™ kit procedure, total RNA was mixed with an optimized set of capture oligonucleotides that bind to the bacterial 16S and 23S rRNAs. Next, the rRNA hybrids were removed from the solution using derivatized magnetic microbeads. The mRNA remained in the supernatant and was recovered by ethanol precipitation and quantified by Bioanalyzer 2100. Our RNA preparation did not include entities < 200 nucleotides in length.
RNA-Seq
A cDNA library was constructed using the Illumina mRNA-Seq sample prep kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA) with 100 ng RNA enriched for mRNA isolated from a single in vitro culture, following manufacturer's instructions. mRNA was chemically fragmented and randomly primed for reverse transcription and second-strand synthesis. The resulting cDNA was end-repaired and 'A' overhangs were added. Illumina paired-end sequence adaptors were ligated to the cDNA fragments. Fragments of approximately 200 bp were isolated from a 2% agarose gel and amplified (18 cycles) according to the Illumina protocol. Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent) was used to quantify and confirm the fragment size of each library. 1 nM of mRNA-seq library sample prepared for sequencing on the Illumina GAII (San Diego, CA) was denatured and diluted to 6 pM for clustering (v2) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Single read sequencing of the clustered flow cell was performed using Illumina's SBS chemistry (v3) and SCS data analysis pipeline v2.4. Flow-cell image analysis and cluster intensity calculations were carried out by Illumina Real Time Analysis (RTA v1.4.15.0) software. Subsequent base-calling was performed using the Illumina GA Pipeline v1.5.1 software. The resulting Illumina reads were quality-filtered by removing reads containing Ns.
Alignment
The sequencing experiment produced 9,055,826 reads. FASTQ reads generated by Illumina were converted to Sanger FASTQ format using Perl scripts from the Mapping and Assembly with Qualities (MAQ) software package [16]. Reads (Sanger FASTQ format) were mapped to the 2.6 Mb M. haemolytica PHL213 [GenBank: AASA00000000] reference genome using Bowtie [17]. The parameters in Bowtie that control the speed and sensitivity were adjusted as follows: reads with no more than 2 mismatches per read (n = 2) were aligned, and any reads mapped to more than one location across the genome (ambiguous reads) were discarded (m = 1). Post alignment, a human-readable sequence alignment/map (.SAM) format file was converted to a "pileup" format file using SAMTools [18]. This pileup file contains the count of reads per base aligned to each location across the length of the genome. The SAM file was also converted into a binary alignment/map (.BAM) format. These BAM formatted files are necessary for visualization of read alignments in Artemis viewer. The Artemis browser enabled the visual/manual inspection of alignment results in the context of the existing genome annotation. The pileup file, in conjunction with the annotation information of M. haemolytica PHL213, was processed using in-house Perl [19] scripts. Data generated from the RNA-Seq experiment was submitted to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive [SRA049621.1] as reads in FASTQ format [SRR402063.1] and the .BAM alignment file [SRR402079.4] generated by aligning the reads to the reference genome.
Analysis of expressed intergenic regions
Identifying expressed regions within the genome that have not been previously annotated will improve the existing structural annotation of the M. haemolytica PHL213. Prior to the analysis of expressed regions in the genome, we determined the signal to noise ratio cutoff for background expression using the pileup file. Coverage depth (reads per base) greater than the lower tenth percentile of all reads was considered to be expressed and in this dataset, this corresponded to 7 reads/base [8,20]. Based on this read/base cutoff, expressed intergenic regions (EIRs) were identified by applying an additional length cutoff of 70 bp. Shorter regions (less than 70 bp) were discarded to reduce the number of false positives. Custom Perl scripts were written to parse the pileup file and the existing genome structural annotation to identify (i) expressed annotated regions, (ii) expressed regions previously not annotated and, (iii) regions that are annotated but are not expressed. All EIRs were further analyzed using BLASTX [21] searches to determine their protein coding potential. If an EIR was found to be a perfect match (~100% coverage) for a protein, it was classified as a putative novel protein coding region. All EIRs with partial BLASTX hits were evaluated for the presence of an alternate start site or mutation in the start or stop codon associated with the annotated region. If the BLASTX search revealed a frameshift mutation, the EIR and the gene associated with the frameshift mutation were classified as a frameshift. EIRs with poor BLASTX hits and without any association to genes containing annotation errors were excluded from further analysis. EIRs without BLASTX hits were considered to be potential small non-coding RNA.
The Prokaryotic Promoter Prediction (PPP) program [22] (from PePPER suite [23]) and Transterm HP [24] were used to predict promoters and rho-independent terminators, respectively, in the forward and reverse strands of the M. haemolytica PHL213 genome. The locations of promoters and terminators were organized into .GFF files. A Perl script was written to identify putative sRNA i.e. EIRs with promoters or terminators associated to their loci. EIRs with no computationally-predicted promoters or rho-independent terminators were searched against the Rfam database [25] to determine whether these sequences were annotated in Rfam. EIRs that could not be classified as sRNA by Rfam were excluded from further analysis.
Analysis of expressed annotated regions
Using the annotation information (gene loci) of M. haemolytica PHL213 and the pileup file, all annotated regions that were expressed above the background signal to noise ratio cutoff with at least 60% coverage were considered to be expressed, which accounts for uniform evaluation of varying gene lengths. Similar measures have been used in other transcriptome profiling studies [8,26,27]. Annotated regions below 60% coverage were considered as 'not expressed' under the current experimental conditions. After having identified expressed genes, operon structures within the genome were also defined. The first step towards identifying an operon was to identify co-expressed pairs of coding regions. Two regions were considered to be co-expressed when they were identified as expressed on the same strand (5' to 3' or 3' to 5') and the region between them was also expressed. After such co-expressed pairs were identified, they were extended to construct operons by including additional co-expressed pairs in the vicinity satisfying the same conditions for co-expression as described earlier. Operon structures identified by RNA-Seq were compared to the computationally-predicted operon structures described by the Database for prOkaryotic OpeRons (DOOR) [28] for cross validation.
Results
Read alignment to the M. haemolytica PHL213 genome
The M. haemolytica PHL213 is a 2.6 Mb draft genome containing 2,837 annotated regions of which 2,695 are protein coding with a 40% G+C content [29]. For structural annotation of M. haemolytica at the RNA level, the transcriptome of M. haemolytica PHL213 was sequenced using RNA-Seq. Sequencing-based analysis of the transcriptome overcomes the limitations of the hybridization-based microarray approach. Head-on comparison of RNA-Seq with microarrays has shown that RNA-Seq has negligible technical variability [30], making it possible to obtain a reliable estimate of gene expression without replicate analysis. Therefore, we applied RNA-Seq for re-annotation of M. haemolytica and conducted the analysis from a single in vitro experiment. Reads with an average length of 76 bp generated on the Illumina platform were mapped onto the reference genome using the Bowtie read alignment program. Bowtie is an ultrafast, memory efficient alignment program that uses the Burrows-Wheeler transform [31] with a novel quality backtracking algorithm that permits mismatches. Bowtie performs better than Short Oligonucleotide Analysis Package (SOAP) [32] and MAQ, and its sensitivity at aligning reads is as good as both SOAP and MAQ. Of the 9,055,826 reads generated by Illumina, 3,917,458 reads (43.26%) that mapped uniquely to the genome were used for downstream analysis. 2,989,603 reads (33.01%) failed to align due to mismatches. The remaining 2,148,765 reads (23.73%), which mapped to more than one location in the genome (ambiguous reads), were excluded from analysis. For annotation purposes, reads that map to unique locations alone are used [8,33-37]. The cutoff value for true-positive expression of a coding region of 7 reads/base was calculated from the expression (number of reads per base) in the tenth percentile of all reads [8,20], as we did earlier for RNA-Seq based re-annotation of another BRD pathogen Histophilus somni [8].
Expressed intergenic regions
We used the existing annotation of open reading frames in M.haemolytica PHL213 i.e., locus of each gene in the genome and reads identified as expressed by RNA-Seq, to identify expressed intergenic regions (EIRs). We identified 630 EIRs, previously un-annotated as expressed, of a minimum length of 70 bp. Each EIR was further characterized by adding computationally-predicted promoter and rho-independent terminators. Prokaryotic Promoter Prediction (PPP) identified 11,847 promoter regions and Transterm HP identified 1,204 rho-independent terminator regions, in forward and reverse strands of the genome. Identified EIRs, in conjunction with existing gene annotation information and loci of regulatory signals, were subjected to the analysis workflow described in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Data analysis flow-chart. RNA-Seq reads are aligned to the genome using Bowtie to generate a single nucleotide resolution map. Mapped reads analyzed in the context of existing annotation using SAMTools and Perl scripts generate expressed intergenic regions (EIRs). Homologs for EIRs, if present, are identified by BLASTX and are classified accordingly. An EIR with no BLASTX matches is subjected to computational search for regulatory elements (promoter/rho-independent terminator) in its vicinity. An EIR with a regulatory signal is classified as potential sRNA. EIR without BLASTX matches and predicted transcriptional signals are searched against Rfam database.
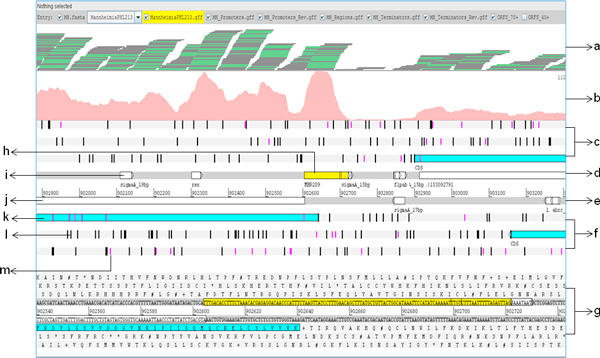
Artemis is a genome browser and annotation tool that allows visualization of sequence features, next generation sequencing data, and the results of the analyses within the context of the genome sequence [38]. The Artemis genome browser illustrates all the six reading frames of the genome sequence along with the translated amino acid sequences, start and stop codons, as well open readings frames across the length of genome (Figure 2). We visualized the alignment file generated by Bowtie, the gene annotation file, promoter and terminator loci, and EIRs in Artemis. Artemis generated a base coverage graph, giving a pictorial representation of the expression in various regions of the genome.
Figure 2.
Overview of Artemis genome browser. Description of the tracks used for data analysis in Artemis genome browser. (a) reads aligned to the genome (b) expression portrayed as coverage graph (c) reading frames 5'-3', (d) forward strand of the genome, (e) reverse strand of the genome, (f) reading frames 3'-5', (g) amino acid sequences corresponding to the 6 reading frames, (h) expressed intergenic region, (i) computationally predicted regulatory signal (promoter/rho-independent terminator), (j) annotated gene (white), based on M. haemolytica Genbank accession # AASA00000000, (k) ORFs (blue) of a specified minimum length, predicted by Artemis between two consecutive stop codons, (l) stop codons in all six reading frames (black) and, (m) start codons in all six reading frames (pink).
Novel protein coding regions
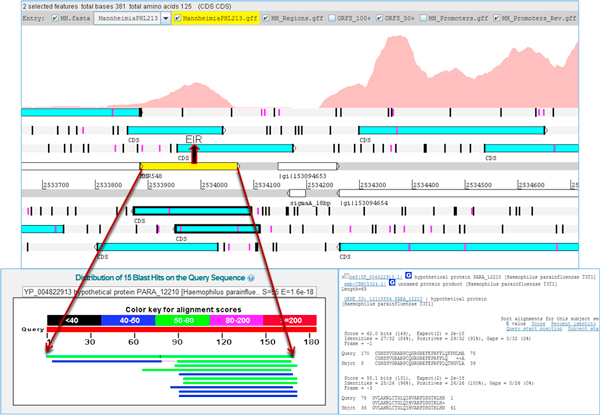
The protein coding potential of EIRs was determined by conducting BLASTX searches with the translated nucleotide sequence of EIRs, against the protein database containing all bacterial species. BLASTX results showed that 14 EIRs had full length matches to target sequences, indicating their potential for coding proteins. The Artemis browser was used to identify the boundaries of these 14 potential novel protein coding regions (Figure 3). These novel protein coding regions had an average G+C content of approximately 46%. The length of these regions was between 37 to 200 amino acids. While the RNA-Seq experiment itself was not strand specific, strand specificity of novel protein coding regions was inferred from the proteins identified as ~100% matches to these EIRs in BLASTX. EIR MHP4 aligned to PG1 protein of Lactobacillus crispatus ST1 while MHP12 aligned to serine acetyltransferase of Haemophilus influenzae NT127. The rest of the EIRs (Table 1) aligned to proteins classified as hypothetical.
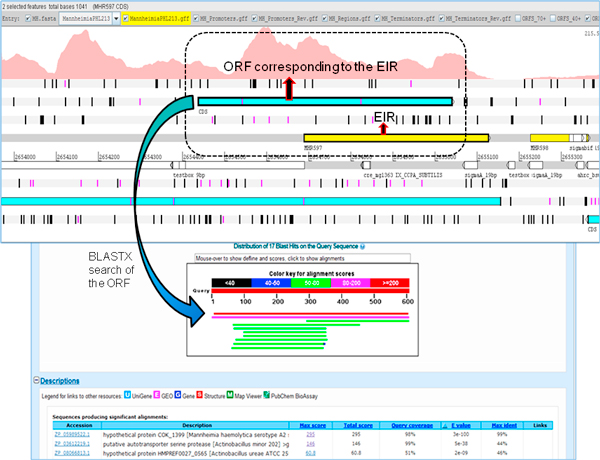
Figure 3.
A novel protein coding region. Identification of novel protein coding regions using expressed intergenic region (EIR, yellow) and its corresponding open reading frame (ORF, blue). A BLASTX search of the ORF identified a full length match to a protein with 98% coverage. The coverage graph for the region of interest is shown (dotted line).
Table 1.
Potential novel protein coding regions identified in M. haemolytica PHL213
| Protein ID | Protein Start | Protein End | Length | Strand | Protein description | Organism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHP1 | 5578 | 5898 | 107 | - | hypothetical protein HPS_04442 | Haemophilus parasuis 29755 |
| MHP2 | 532998 | 533216 | 73 | - | conserved hypothetical protein | Methylococcus capsulatus str. Bath |
| MHP3 | 608419 | 608553 | 45 | - | hypothetical protein COI_2717 | M. haemolytica serotype A2 str. OVINE |
| MHP4 | 740406 | 740837 | 144 | - | PG1 protein | Lactobacillus crispatus ST1 |
| MHP5 | 740634 | 740759 | 42 | + | hypothetical protein GG9_1745 | Haemophilus haemolyticus M19501 |
| MHP6 | 740709 | 740936 | 76 | - | hypothetical protein Csp_D29610 | Curvibacter putative symbiont of Hydra magnipapillata |
| MHP7 | 901072 | 901212 | 47 | + | hypothetical protein COK_2315 | M. haemolytica serotype A2 str. Bovine |
| MHP8 | 1168344 | 1168478 | 45 | - | hypothetical protein COI_2717 | M. haemolytica serotype A2 str. Ovine |
| MHP9 | 1256181 | 1256366 | 62 | + | hypothetical protein COI_1129 | M. haemolytica serotype A2 str. Ovine |
| MHP10 | 1460962 | 1461081 | 40 | - | hypothetical protein COK_1081 | M. haemolytica serotype A2 str. Bovine |
| MHP11 | 2531614 | 2531724 | 37 | - | hypothetical protein COK_2196 | M. haemolytica serotype A2 str. Bovine |
| MHP12 | 2605237 | 2605434 | 66 | - | serine acetyltransferase | Haemophilus influenzae NT127 |
| MHP13 | 2639084 | 2639221 | 46 | - | hypothetical protein COK_0003 | M. haemolytica serotype A2 str. Bovine |
| MHP14 | 2654438 | 2655037 | 200 | + | hypothetical protein COK_1399 | M. haemolytica serotype A2 str. Bovine |
Potential protein loci, length (aa), inferred strand direction, description of the corresponding BLASTX protein match.
Corrections made to the existing genome annotation
Artemis genome browser creates open reading frames (ORFs) of a desired minimum length. It identifies ORFs as regions between two consecutive stop codons with the specified minimum length. Thus ORFs corresponding to EIRs can be generated and visualized in this browser. RNA-Seq based expression in relation to the existing genome annotation, when visualized in Artemis, enabled the identification of the actual locus and length for some of the annotated proteins. We identified 4 genes with a mutated start codon. This anomaly could be the result of computational gene prediction programs identifying the next available "AUG" as the start codon (Figure 4). Our observation is substantiated by the consecutive expression of an identified EIR preceding the 5' region of these genes. 4 genes had a mutation that led to the replacement of start codon by a leucine (L).
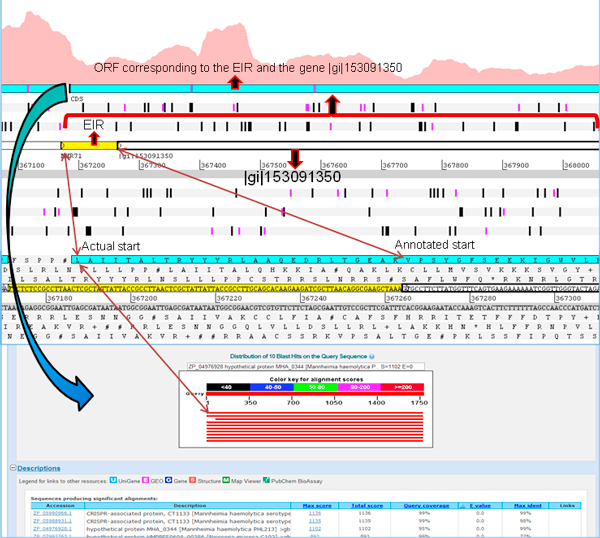
Figure 4.
Mutated start site. Visualization of a gene identified with a mutation in the start site in Artemis genome browser. RNA-Seq based coverage graph clearly shows expression upstream of the annotated start site of the gene |gi|153091350. When the ORF encompassing the gene |gi|153091350 and the expressed intergenic region (EIR, yellow) upstream of the gene, was used for conducting BLASTX searches, we identified a full length match suggesting that the actual start site is at 'leucine' (probably mutated), instead of 'valine' (based on existing annotation).
Since Artemis allows marking the start codons within an ORF, it is possible to identify alternate start sites, if any, for any ORF associated with an EIR. ORFs created from EIRs in Artemis revealed possible alternate starts sites for 7 genes. BLASTX searches of the EIR and its translated protein revealed that the actual start site varied with respect to previous annotation (Figure 5). Where there was a discrepancy between the existing annotation and the current transcriptome based identification of start site, the consensus of start site of similar proteins identified in BLASTX was used to determine the actual start site. The suggested revisions to existing annotation are in Table 2 (detailed results in Additional file 1). BLASTX searches of EIRs also revealed mutations that lead to disruption of a protein coding region, resulting in a frameshift (Figure 6). Two such EIRs which had BLASTX alignments revealed frameshifts which would otherwise be protein coding regions (Additional file 1).
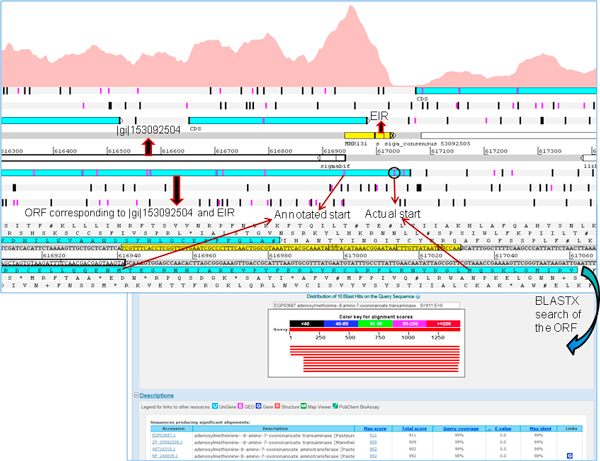
Figure 5.
Alternate start site. Artemis genome browser identified an alternate start site for the gene |gi|153092504. The coverage graph for this gene showed that the start codon based on expression is different from annotated start site. In the 5' upstream region of annotated start site, there are two methionines that could be potential start sites. BLASTX search identified a full length match, and confirmed one on these two methionines as the actual start site.
Table 2.
Suggested corrections made to the existing annotation of M. haemolytica PHL213
| Protein ID | Gene start | Gene end | Gene length | Protein length | Strand | Corrected start | Corrected end | Corrected gene length | Corrected protein length | Correction Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHA_0097 | 91433 | 92209 | 777 | 258 | - | 91433 | 92281 | 849 | 282 | Mutated Start (L) |
| MHA_0304 | 314414 | 316213 | 1800 | 599 | + | 314210 | 316213 | 2004 | 667 | Mutated Start (L) |
| MHA_0344 | 367264 | 368961 | 1698 | 565 | + | 367186 | 368961 | 1776 | 591 | Mutated Start (L) |
| MHA_0410 | 430731 | 431060 | 330 | 109 | + | 430650 | 431060 | 411 | 136 | Alternate Start |
| MHA_0591 | 615640 | 616941 | 1302 | 433 | - | 615640 | 617052 | 1413 | 470 | Alternate Start |
| MHA_0736 | 750172 | 751350 | 1179 | 392 | + | 750121 | 751350 | 1230 | 409 | Alternate Start |
| MHA_0819 | 821700 | 822038 | 339 | 112 | + | 821472 | 822038 | 567 | 188 | Mutated Start (L) |
| MHA_1225 | 1209899 | 1211335 | 1437 | 478 | + | 1209791 | 1211335 | 1545 | 514 | Alternate Start |
| MHA_1712 | 1697137 | 1698519 | 1383 | 460 | + | 1696987 | 1698519 | 1533 | 510 | Alternate Start |
| MHA_2666 | 2591266 | 2592276 | 1011 | 336 | - | 2591266 | 2592360 | 1095 | 364 | Alternate Start |
| MHA_2723 | 2659955 | 2660545 | 591 | 196 | - | 2659955 | 2660692 | 738 | 245 | Alternate Start |
Previously annotated gene locus, length and strand specificity. Observed locus based on RNA-Seq expression along with gene length (bp) and protein length (aa) and the description of the annotation error. In case of a mutated start, the amino acid start codon identified by RNA-Seq.
Figure 6.
Frameshift mutation. An expressed intergenic region (EIR, yellow) and its corresponding ORFs (highlighted) visualized in Artemis genome browser indicate a possible frameshift mutation. BLASTX search of the EIR identified a full length match, confirming the frameshift mutation.
Small RNA
Small RNA are known to have regulatory roles in Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholera and many other bacterial pathogens [39]. Genome-scale identification of sRNA using RNA-Seq is reported for E. coli [40] and Vibrio cholerae [41], among other pathogenic bacteria. The identification of the loci of sRNA in the genome is an important pre-requisite for understanding their role in modulating bacterial physiology and virulence [42]. sRNA are synthesized by RNA polymerase (RNAP) in a manner analogous to the synthesis of any RNA in bacteria (mRNA, rRNA, tRNA); sRNA promoters could be regulated by transcription factors or use of alternative sigma factors [43]. Therefore, the presence of promoters and terminators for potential sRNA [8,44] identified by experimental approaches like RNA-Seq, increases the confidence in their identification. Although the RNA extraction protocol used in this study does not facilitate extraction of smaller transcripts and strand specificity is lost during cDNA synthesis, we identified potential sRNA. EIRs with no protein coding potential, as observed via BLASTX searches, were considered to be candidate sRNA. It is possible that EIRs with no BLASTX matches are non-conserved ORFs; since there are no in silico methods to validate this assumption, we chose to consider all EIRs with no BLASTX as candidates for small RNA analysis. Candidate sRNA loci were searched for the presence of a promoter or terminator. For 44 EIRs that had no BLASTX matches, a promoter or a rho-independent terminator was identified either on the forward or the reverse strand (Figure 7) of their locus. Promoters/terminators were present in the transcriptional regulatory regions, i.e., a promoter was present in the -1 to -35 region or a terminator was present in the +1 to +20 position at the end of the EIR. Therefore, we classified the 44 candidate sRNA as potential novel small RNA in the M. haemolytica PHL213 genome (Table 3). The average length of the identified novel sRNA was approximately 100 bp and ranged between 70 to 253 bp. The average G+C content of sRNA was 34.35%, which is relatively lower than the G+C content of the genome. All identified sRNA had a promoter associated with their locus and sRNA MHS17 also had an associated terminator. When sequences of the identified sRNA were searched in the Rfam [25] database to identify their function, no matches were found.
Figure 7.
Identification of potential sRNA. (a) Criterion for identifying potential sRNA. If a promoter located upstream of the expressed intergenic region (EIR) or a rho-independent terminator located downstream of the EIR, either in the forward or the reverse strands of the genome is identified, then the EIR is classified as a potential sRNA. (b) & (c) a promoter was identified upstream of the EIR in both the cases and the EIRs were classified as sRNA.
Table 3.
Putative novel sRNA identified in M. haemolytica PHL213
| sRNA_ID | Start | End | Length(bp) | Flanking gene (left) | Flanking gene (right) | Promoter (Strand) | BLASTN match |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHS1 | 219874 | 219955 | 82 | MHA_0231|- | MHA_0232|lamB | Y(+) | |
| MHS2 | 309458 | 309563 | 106 | MHA_0300|- | MHA_0301|- | Y(+) | Haemophilus parasuis SH0165 |
| MHS3 | 319131 | 319229 | 99 | MHA_0307|era | MHA_0308|recO | Y(+) | Mannheimia granulomatis str. P1135/26 |
| MHS4 | 353514 | 353599 | 86 | MHA_0333|res | MHA_0334|gyrB | Y(+) | |
| MHS5 | 428735 | 428820 | 86 | MHA_0405|- | MHA_0406|- | Y(+) | Bacteriophage phi-MhaA1-BAA410 |
| MHS6 | 601909 | 601989 | 81 | MHA_0568|- | MHA_0569|- | Y(+) | Haemophilus parasuis SH0165 |
| MHS7 | 694168 | 694238 | 71 | MHA_0694|uppS | MHA_0695|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS8 | 728194 | 728446 | 253 | MHA_0724|- | MHA_0725|hemL | Y(+) | |
| MHS9 | 760853 | 760946 | 94 | MHA_0748|dnaA | MHA_0749|ccmA | Y(+) | |
| MHS10 | 809903 | 810012 | 110 | MHA_0806|- | MHA_0807|rluC | Y(+) | |
| MHS11 | 849372 | 849453 | 82 | MHA_0843|pstC | MHA_0844|pstS | Y(+) | |
| MHS12 | 962811 | 962887 | 77 | MHA_0957|- | MHA_0958|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS13 | 1004733 | 1004837 | 105 | MHA_1000|crp | MHA_1001|murB | Y(+) | |
| MHS14 | 1006880 | 1006950 | 71 | MHA_1003|- | MHA_1004|hxuA | Y(+) | |
| MHS15 | 1111723 | 1111820 | 98 | MHA_1103|- | MHA_1104|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS16 | 1164081 | 1164188 | 108 | MHA_1167|- | MHA_1168|- | Y(+) | Histophilus somni 2336 |
| MHS17 | 1422454 | 1422537 | 84 | MHA_1444|- | MHA_1445|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS18 | 1427285 | 1427368 | 84 | MHA_1449|- | MHA_1450|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS19 | 1544002 | 1544093 | 92 | MHA_1562|- | MHA_1563|dapA | Y(+) | |
| MHS20 | 1576948 | 1577051 | 104 | MHA_1597|- | MHA_1598|rpmE | Y(+) | |
| MHS21 | 1580406 | 1580478 | 73 | MHA_1601|- | MHA_1602|lon | Y(+) | |
| MHS22 | 1590485 | 1590566 | 82 | MHA_1610|- | MHA_1611|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS23 | 1674686 | 1674757 | 72 | MHA_1690|leuA | MHA_1691|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS24 | 1705600 | 1705693 | 94 | MHA_1719|- | MHA_1720|uspA | Y(+) | |
| MHS25 | 1784761 | 1784848 | 88 | MHA_1796|- | MHA_1797|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS26 | 1842730 | 1842833 | 104 | MHA_1864|rpoZ | MHA_1865|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS27 | 1861740 | 1861815 | 76 | MHA_1884|- | MHA_1885|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS28 | 1872042 | 1872162 | 121 | MHA_1892|- | MHA_1893|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS29 | 1902920 | 1903001 | 82 | MHA_1926|aroE | MHA_1927|uvrD | Y(+,-) | |
| MHS30 | 1977320 | 1977411 | 92 | MHA_2021|- | MHA_2022|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS31 | 2054477 | 2054562 | 86 | MHA_2099|ansB | MHA_2100|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS32 | 2087705 | 2087940 | 236 | MHA_2131|- | MHA_2132|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS33 | 2135304 | 2135406 | 103 | MHA_2171|mtlD | MHA_2172|- | Y(+) | Haemophilus ducreyi strain 35000 HP |
| MHS34 | 2141830 | 2141953 | 124 | MHA_2185|tolQ | MHA_2186|tolR | Y(+) | |
| MHS35 | 2233877 | 2234009 | 133 | MHA_2261|hmbR2 | MHA_2262|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS36 | 2245148 | 2245226 | 79 | MHA_2272|- | MHA_2273|purM | Y(+) | |
| MHS37 | 2333531 | 2333628 | 98 | MHA_2360|- | MHA_2361|gntK | Y(+) | |
| MHS38 | 2438972 | 2439053 | 82 | MHA_2487|nagB | MHA_2488|nagA | Y(+) | |
| MHS39 | 2623678 | 2623787 | 110 | MHA_2696|dinJ | MHA_2697|- | Y(+) | |
| MHS40 | 2624952 | 2625021 | 70 | MHA_2698|miaA | MHA_2699|hfq | Y(+) | |
| MHS41 | 2646708 | 2646793 | 86 | MHA_2712|- | MHA_2713|tpx | Y(+) | |
| MHS42 | 2691938 | 2692007 | 70 | MHA_2762|ansB | MHA_2763|pyrG | Y(+,-) | |
| MHS43 | 2703602 | 2703676 | 75 | MHA_2776|- | MHA_2777|trmU | Y(+) | Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serovar 3 str. JL03 |
| MHS44 | 2755982 | 2756108 | 127 | MHA_2824|mgsA | MHA_2825|thrC | Y(+) |
Identified potential sRNA, their locus, length (bp), flanking genes, predicted promoter and its strand specificity, top BLASTN hit (if any).
EIRs with no BLASTX matches, predicted promoter, or a rho-independent terminator, were searched against the Rfam database to identify potential matches with any of the known conserved RNA families in the database. Five EIRs mapped to five different functional categories within Rfam, shown in Table 4. MHS45 was classified as bacterial signal recognition particle RNA, a conserved ribonulceoprotein that directs movement of proteins within the cell and aids their secretion. MHS46 was classified as MOCO RNA motif which is presumed to be a riboswitch that binds to molybdenum cofactor or related tungsten cofactor. MHS47 was classified as a thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) riboswitch that binds directly to thiamine pyrophosphate to regulate gene expression. MHS48 was classified as an alpha operon ribosome binding site that binds to ribosomal protein S4 which acts as a translational repressor. MHS49 was annotated by Rfam as a gcvB RNA that encodes small non-coding RNA involved in the regulation of amino acid transport systems and amino acid biosynthetic genes. All predicted functions will need to be validated by further experimentation.
Table 4.
Putative sRNA identified in identified in M. haemolytica PHL213 using the Rfam database
| sRNA_ID | Start | End | strand | rfam-id | rfam accession | G+C content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHS45 | 698093 | 698190 | - | Bacteria_small_SRP | RF00169 | 49 |
| MHS46 | 902602 | 902713 | - | MOCO_RNA_motif | RF01055 | 33 |
| MHS47 | 2002337 | 2002433 | + | TPP | RF00059 | 51 |
| MHS48 | 2339489 | 2339566 | - | Alpha_RBS | RF00140 | 32 |
| MHS49 | 2687066 | 2687209 | - | GcvB | RF00022 | 34 |
EIRs that do not have either a BLASTX hits or predicted promoter or rho-independent terminator, but with matches in Rfam database. sRNA locus, strand specificity and description based on Rfam.
Gene expression and operons
The M. haemolytica PHL213 genome consists of 2,837 annotated genes, 2,695 of which code for proteins. Genes were considered to be expressed if 60% of the gene length had at least 7 reads aligned/nucleotide. Based on this criteria, 2,506 of all annotated regions in the genome (87.63%) were identified as expressed with 95.25% coverage i.e. approximately 95% of the sequence of the annotated region had at least 7 reads aligned/nucleotide. Expressed annotated genes and their coverage are documented in Additional file 2.
Functional analysis of the expressed annotated regions was based on the existing annotation of M. haemolytica genome available at NCBI. It is interesting to note that genes that are described as virulence factors are also expressed under normal culture conditions. For example, genes related to leukotoxin (MHA_0253, MHA_0254, MHA_0255 and MHA_0266), an important virulence factor, were all expressed. Also, the 12 capsule forming genes whose role in virulence includes adherence to host and resistance to serum-mediated killing and phagocytosis [45,46] were all found to be expressed. In addition to these, we also found that 40 genes associated with lipopolysaccharide or lipoproteins and contribute to virulence by initiating an inflammatory cytokine response [45,47] to be expressed. Genes responsible for forming the type IV pilus associated with M. haemolytica that is responsible for DNA uptake, adhesion, and motility [48] were expressed. Filamentous hemagglutinin genes of M. haemolytica (MHA_0866, MHA_0867), responsible for adhesion to host mucosa [49], were expressed. Adhesins play an important role in virulence, and all annotated genes related to this function, such as MHA_2262, MHA_0708, MHA_2492, MHA_2701, MHA_1367, MHA_0563 and MHA_2800, among others, were all identified as expressed in our experiment. Genes responsible for resistance towards antibiotics such as β-lactams, tetracycline, streptomycin, and sulfonamides [45] in M. haemolytica were also expressed. Annotated regions that were not expressed had coverage of only 30%. Of the 331 annotated regions that were not expressed 236 were annotated as "hypothetical proteins" and 26 were "hypothetical bacteriophage proteins."
Using expression patterns of coding regions, we identified paired gene expression and operon structures. RNA-Seq based operon structures were compared to the computationally predicted structures using DOOR [28]. We identified 1,086 co-expressed pairs of genes that could be organized into 518 potential operons. DOOR predicted 1,295 co-expressed pairs forming 599 operons (Additional file 3). The overlap between RNA-Seq based and DOOR-based co-expressed pairs was 854. Our study identified relatively fewer co-expressed pairs as compared to DOOR. This could be due to the fact that 331 of the 2,837 annotated regions were not expressed in our dataset. Furthermore, this method cannot detect genes whose expression is suppressed by polar mutations. The single nucleotide resolution map enabled the identification of co-expressed pairs and definition of operon structures and regulatory patterns. Availability of operon structures will facilitate understanding the coordinated regulation of genes in M. haemolytica to moderate metabolic pathways under different environmental conditions.
Discussion
Identification of all functional elements of the genome is fundamental to understanding the dynamics of biological processes that occur within any living organism. Gene models are available for sequenced genomes that are based on computational approaches. However, a number of recent studies highlight the need for genome re-annotation, prior to conducting holistic systems biology analyses. Experimental approaches, at times, shed light on regions of the genome where computational methods of structural annotation fail. Re-annotation studies of several species including disease causing pathogens have revealed numerous genes, regulatory regions and complex metabolic pathways that remained undetected based on the initial annotation [8,50-55]. In this study, we applied a combinatorial approach i.e. RNA-Seq based transcriptome analysis in conjunction with computational resources, to structurally annotate a bacterial genome at the RNA level. For the first time, we report RNA-Seq based annotation of the genome of M. haemolytica PHL213, one of the primary pathogens of Bovine Respiratory Disease in cattle [56]. Its genome was sequenced with 8.4× coverage, and is in draft phase since 2006.
We have recently re-annotated Histophilus somni 2336, another BRD pathogen belonging to Pasteurellaceae like M. haemolytica. RNA-Seq based transcriptome analysis identified 38 novel protein coding regions and 82 sRNA in H. somni [8]. Compared to the draft genome for M. haemolytica, H. somni has a complete genome sequence. Yet, re-annotation of this genome identified a number of functional elements missed in the initial annotation. The relatively poor quality of the existing structural annotation of M. haemolytica can be enhanced by re-annotation, and this was the motivation behind the current study.
Re-annotation enabled us to fix errors in existing annotation. A mutation that might have occurred during replication could alter the structure of the gene in its vicinity. Computational methods, when predicting a gene, seek to identify an ORF and its putative start and stop codons to define gene boundaries. Mutations in the sequence between the start or stop codon of a gene might not actually affect gene prediction or may sometimes result in a frameshift. If the mutation is to occur in the start or stop codon itself, algorithms would seek to identify the next available start or stop codon. This would lead to alteration in gene locus and a subsequent gene annotation error. Such annotation errors cannot be detected without experimental validations. The single nucleotide resolution transcription map generated by RNA-Seq is one of the most efficient ways to detect such annotation errors. As described in our workflow (Figure 1), once EIRs overlapping a certain gene were identified, BLASTX searches of these regions helped in defining the actual boundaries and correct annotation errors, if any. Mutations leading to a frameshift can result in a gene being completely disrupted. Such frameshifts remain undetected by automated approaches, but can be identified by experimental approaches such as RNA-Seq used in this study. Genome-wide studies using experimental methods can help validate these predictions and improve the quality of annotation across genomes and eliminate errors from being transferred from one genome to another during annotation of novel assemblies.
Understanding coordinated regulation of gene expression in bacteria requires the description of operon structures in the genome. Prior to this study, operon structures were unavailable for M. haemolytica. Since computationally-predicted operon structures were unavailable, we first generated a set of computationally-predicted operons using DOOR (Additional file 3). RNA-Seq enabled us to identify expressed gene pairs that could be expanded into potential operons. Comparison of DOOR predicted operons with RNA-Seq based operons in M. haemolytica showed a major overlap and cross-validated the findings in both approaches. Thus re-annotation helped validate 599 operons predicted by DOOR. We also identified 233 co-expressed pairs that were not identified by DOOR. Since the strand specificity of expression is lost in RNA-Seq experiment described here, at best the operons identified in this study should be considered 'potential operons' that will require experimental validation in future studies. Furthermore, this experiment-based identification of co-expression will not be able to identify genes that are expressed in a polar fashion within the operon. Analysis of the functions of genes identified as expressed by RNA-Seq resulted in an interesting finding. Genes that are annotated as being virulence factors were identified as expressed under normal culture conditions. These results are consistent with our findings in H. somni. Our results indicate that the expectation of 'virulence factor' being expressed only during pathogenesis may not be accurate. It is possible that there is a basal pervasive level of expression of these factors and that it is the difference in the expression level that actually corresponds to virulence.
Computational methods for identification of sRNA are not accurate, and transcriptome profiling using deep sequencing methods can help identify novel sRNA. sRNA play a crucial role in adaptive response to stress by directly or indirectly regulating virulence genes [39], as shown in Staphylococcus aureus [57], Pseudomonas aeruginosa [58] and Vibrio cholerae [59,60]. However, a comprehensive understanding of sRNA regulatory roles during adaptive responses and pathogenesis is only possible after their identification. Despite the drawbacks in sample preparation and lack of strand specificity, we identified 44 potential novel sRNA. The identified novel sRNA were searched for homology in the sRNA database (sRNAdb) against other bacterial sRNA identified through similar transcriptomics studies and/or computational approaches [61]. Only 15 sRNA had partial alignments of 20-30 nucleotides and the remaining had very poor sequence conservation across the database (Additional file 4). We also compared the 44 sRNA identified in the M. haemolytica genome with 82 H. somni sRNA using 'BLAST 2 sequences' megablast [21]. No similarity was found, indicating poor consensus among non-coding RNA. These results suggest that regulation of sRNA is probably as diverse and as complex as gene or protein regulation.
The inherent limitations of our experimental setup i.e. lack of enrichment specifically for sRNA, lack of strand specificity information and lack of biological replicates, isolation of RNA at different stages of in vitro growth, etc, did not allow comprehensive identification of sRNA. Due to the same limitations, the identified gene co-expression also needs further validation work in future. However, as the results indicate, application of RNA-Seq enhanced the existing annotation of M. haemolytica. RNA-Seq based annotation is not the 'final' and conclusive step in identifying functional elements in this important bacterial pathogen. In fact, this work is part of the continuum in a typical systems biology work flow.
Conclusion
The RNA-Seq based transcriptome map of M. haemolytica PHL213 validated annotated open reading frames and led to the discovery of potential novel protein coding regions. We identified operon structures and were able to fix exiting annotation errors by correcting gene boundaries. The availability of experimentally validated open reading frames, potential novel sRNA, potential protein coding regions, and operon structures form the basis for future investigations to determine the role of these elements during BRD pathogenesis. This study also demonstrates the utility of free and easy to bioinformatics tools for RNA-Seq data analysis workflow.
List of abbreviations used
BAM: Binary Alignment/Map; BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool; BRD: Bovine Respiratory Disease; BHI: Brain Heart Infusion; DOOR: Database for prOkaryotic OpeRons; EIR: Expressed Intergenic Region; GLIMMER: Gene Locator and Interpolated Markov ModelER; MAQ: Mapping and Assembly with Qualities; ORF: Open Reading Frame; PPP: Prokaryotic Promoter Prediction; Rfam: RNA families; RNAP: RNA Polymerase; SAGE: Serial Analysis of Gene Expression; SAM: Sequence Alignment/Map; SOAP: Short Oligonucleotide Analysis Package; sRNA: small RNA; sRNAdb: small non-coding RNA database.
Competing interests
One of the authors, James M Watt, is currently employed with Eagle Applied Science. Since the research work for this manuscript was performed when he was an employee at College of Veterinary Medicine, Mississippi State, Mississippi, it does not alter the authors' adherence to all the BMC Bioinformatics policies on sharing data and materials. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
JSR developed the analysis workflow with RK and BN, wrote all scripts required for analysis, carried out data analysis, and wrote the initial draft of this manuscript. JMW prepared the RNA for conducting RNA-Seq. SCB, MLL, and BN conceived and designed this collaborative study, and helped with data analysis and interpretation. BN helped draft the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Complete description of suggested corrections to existing annotation, and identified frameshift mutations. Sheet 1 labeled 'Annotation Errors' contains corrections to annotated genes in M. haemolytica PHL213, previously annotated gene locus and length, suggested correction to its locus. RNA-Seq expression based observed gene and protein length along with description of the exception in the genome that led to the annotation error; in case of mutated start, the mutated amino acid; BLASTX hit used to correct the annotation and its description. Sheet 2 labeled 'Frameshift' contains the two frameshift mutations identified, their frame locus and the BLASTX hit used to identify the frameshift.
RNA-Seq based expression profile of annotated genes. The sheet labeled as 'MH_Expressed' consists of annotated genes identified as expressed in the RNA-Seq experiment, the observed coverage, average reads per base for each gene and the description of the gene, Sheet 2 labeled as 'MH_NotExpressed' contains annotated genes identified as not expressed in RNA-Seq experiment, the observed coverage, average reads per base for each gene and the description of the gene.
Comparison of co-expressed gene pairs identified by RNA-Seq and operons predicted by DOOR. Sheet 1 labeled 'MH_DOOR' has a list of operons predicted by DOOR. Sheet 2 labeled 'MH_DOOR_Pairwise' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs predicted by DOOR. Sheet 3 labeled 'MH_JR' contains a list of operons identified in our RNA-Seq experiment. Sheet 4 labeled 'MH_JR_Pairs' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs identified by RNA-Seq. Sheet 6 labeled 'MH_Pairwise_Common' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs common to both DOOR and RNA-Seq. Sheet 7 labeled 'MH_DOOR_Unique' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs unique to DOOR. Sheet 8 labeled 'MH_JR_Unique' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs unique to our RNA-Seq experiment.
Results of M. haemolytica PHL213 sRNA searched against sRNAdb. Putative sRNA identified by RNA-Seq were searched against other bacterial sRNA in small non-coding RNA database (sRNAdb) by conducting BLASTN searches.
Contributor Information
Joseph S Reddy, Email: jreddy@cvm.msstate.edu.
Ranjit Kumar, Email: rkumar@uab.edu.
James M Watt, Email: james.watt@eagle-apt-sci.com.
Mark L Lawrence, Email: lawrence@cvm.msstate.edu.
Shane C Burgess, Email: sburgess@cals.arizona.edu.
Bindu Nanduri, Email: bnanduri@cvm.msstate.edu.
Acknowledgements
This project was partially supported by the Institute for Genomics, Biocomputing and Biotechnology, and the National Science Foundation (Mississippi EPSCoR-0903787), and Mississippi INBRE funded by grants from the National Center for Research Resources (5P20RR016476-11) and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (8 P20 GM103476-11) from the National Institutes of Health.
This article has been published as part of BMC Bioinformatics Volume 13 Supplement 15, 2012: Proceedings of the Ninth Annual MCBIOS Conference. Dealing with the Omics Data Deluge. The full contents of the supplement are available online at http://www.biomedcentral.com/bmcbioinformatics/supplements/13/S15
References
- Oltvai ZN, Barabasi AL. Systems Biology. Life's Complexity Pyramid. Science. 2002;298(5594):763–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1078563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcher AL, Harmon D, Kasif S, White O, Salzberg SL. Improved Microbial Gene Identification with Glimmer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27(23):4636–41. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.23.4636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukashin AV, Borodovsky M. Genemark.Hmm: New Solutions for Gene Finding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26(4):1107–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.4.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy SR. What Is a Hidden Markov Model? Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22(10):1315–6. doi: 10.1038/nbt1004-1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathe C, Sagot MF, Schiex T, Rouze P. Current Methods of Gene Prediction, Their Strengths and Weaknesses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(19):4103–17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker DD, Schadt EE, Armour CD, He YD, Garrett-Engele P, McDonagh PD, Loerch PM, Leonardson A, Lum PY, Cavet G. et al. Experimental Annotation of the Human Genome Using Microarray Technology. Nature. 2001;409(6822):922–7. doi: 10.1038/35057141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers M, Carninci P. Tag-Based Approaches for Transcriptome Research and Genome Annotation. Nat Methods. 2005;2(7):495–502. doi: 10.1038/nmeth768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R, Lawrence ML, Watt J, Cooksey AM, Burgess SC, Nanduri B. Rna-Seq Based Transcriptional Map of Bovine Respiratory Disease Pathogen "Histophilus Somni 2336". PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorek R, Cossart P. Prokaryotic Transcriptomics: A New View on Regulation, Physiology and Pathogenicity. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(1):9–16. doi: 10.1038/nrg2695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L. Transcript Assembly and Quantification by Rna-Seq Reveals Unannotated Transcripts and Isoform Switching During Cell Differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(5):511–5. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho BK, Zengler K, Qiu Y, Park YS, Knight EM, Barrett CL, Gao Y, Palsson BO. The Transcription Unit Architecture of the Escherichia Coli Genome. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27(11):1043–9. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandlik A, Livny J, Robins WP, Ritchie JM, Mekalanos JJ, Waldor MK. Rna-Seq-Based Monitoring of Infection-Linked Changes in Vibrio Cholerae Gene Expression. Cell Host Microbe. 2011;10(2):165–74. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma CM, Hoffmann S, Darfeuille F, Reignier J, Findeiss S, Sittka A, Chabas S, Reiche K, Hackermuller J, Reinhardt R. et al. The Primary Transcriptome of the Major Human Pathogen Helicobacter Pylori. Nature. 2010;464(7286):250–5. doi: 10.1038/nature08756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. Economic Impact Associated with Respiratory Disease in Beef Cattle. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1997;13(3):367–77. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0720(15)30302-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank GH, Tabatabai LB. Neuraminidase Activity of Pasteurella Haemolytica Isolates. Infect Immun. 1981;32(3):1119–22. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1119-1122.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Ruan J, Durbin R. Mapping Short DNA Sequencing Reads and Calling Variants Using Mapping Quality Scores. Genome Res. 2008;18(11):1851–8. doi: 10.1101/gr.078212.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL. Ultrafast and Memory-Efficient Alignment of Short DNA Sequences to the Human Genome. Genome Biol. 2009;10(3):R25. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-3-r25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and Samtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(16):2078–9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L, Christiansen T, Orwant J. Programming Perl. 3. Beijing; Cambridge, Mass.: O'Reilly; 2000. p. 1067. xxxiii. [Google Scholar]
- Wurtzel O, Sapra R, Chen F, Zhu Y, Simmons BA, Sorek R. A Single-Base Resolution Map of an Archaeal Transcriptome. Genome Res. 2010;20(1):133–41. doi: 10.1101/gr.100396.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ. Gapped Blast and Psi-Blast: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25(17):3389–402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokaryote Promoter Prediction. http://pepper.molgenrug.nl/index.php/pepper-tools/promoter-predictie-tool
- Pepper: A Web Based Regulon, Tf and Tfbs Mining System. http://pepper.molgenrug.nl
- Kingsford CL, Ayanbule K, Salzberg SL. Rapid, Accurate, Computational Discovery of Rho-Independent Transcription Terminators Illuminates Their Relationship to DNA Uptake. Genome Biol. 2007;8(2):R22. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-2-r22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner PP, Daub J, Tate J, Moore BL, Osuch IH, Griffiths-Jones S, Finn RD, Nawrocki EP, Kolbe DL, Eddy SR. et al. Rfam: Wikipedia, Clans and The "Decimal" Release. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:D141–5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R, Burgess SC, Lawrence ML, Nanduri B. Taapp: Tiling Array Analysis Pipeline for Prokaryotes. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2011;9(1-2):56–62. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(11)60008-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David L, Huber W, Granovskaia M, Toedling J, Palm CJ, Bofkin L, Jones T, Davis RW, Steinmetz LM. A High-Resolution Map of Transcription in the Yeast Genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(14):5320–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601091103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao F, Dam P, Chou J, Olman V, Xu Y. Door: A Database for Prokaryotic Operons. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:D459–63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioia J, Qin X, Jiang H, Clinkenbeard K, Lo R, Liu Y, Fox GE, Yerrapragada S, McLeod MP, McNeill TZ. et al. The Genome Sequence of Mannheimia Haemolytica A1: Insights into Virulence, Natural Competence, and Pasteurellaceae Phylogeny. J Bacteriol. 2006;188(20):7257–66. doi: 10.1128/JB.00675-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marioni JC, Mason CE, Mane SM, Stephens M, Gilad Y. Rna-Seq: An Assessment of Technical Reproducibility and Comparison with Gene Expression Arrays. Genome Res. 2008;18(9):1509–17. doi: 10.1101/gr.079558.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Durbin R. Fast and Accurate Long-Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(5):589–95. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R, Li Y, Kristiansen K, Wang J. Soap: Short Oligonucleotide Alignment Program. Bioinformatics. 2008;24(5):713–4. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S, Klockgether J, Hagendorf P, Geffers R, Schock U, Pohl T, Davenport CF, Tummler B. Pseudomonas Putida Kt2440 Genome Update by Cdna Sequencing and Microarray Transcriptomics. Environ Microbiol. 2011;13(5):1309–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins TT, Kingsley RA, Fookes MC, Gardner PP, James KD, Yu L, Assefa SA, He M, Croucher NJ, Pickard DJ. et al. A Strand-Specific Rna-Seq Analysis of the Transcriptome of the Typhoid Bacillus Salmonella Typhi. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(7):e1000569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croucher NJ, Fookes MC, Perkins TT, Turner DJ, Marguerat SB, Keane T, Quail MA, He M, Assefa S, Bahler J. et al. A Simple Method for Directional Transcriptome Sequencing Using Illumina Technology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(22):e148. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez D, Francois P, Farinelli L, Osteras M, Schrenzel J. De Novo Bacterial Genome Sequencing: Millions of Very Short Reads Assembled on a Desktop Computer. Genome Res. 2008;18(5):802–9. doi: 10.1101/gr.072033.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagalakshmi U, Wang Z, Waern K, Shou C, Raha D, Gerstein M, Snyder M. The Transcriptional Landscape of the Yeast Genome Defined by Rna Sequencing. Science. 2008;320(5881):1344–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1158441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford K, Parkhill J, Crook J, Horsnell T, Rice P, Rajandream MA, Barrell B. Artemis: Sequence Visualization and Annotation. Bioinformatics. 2000;16(10):944–5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/16.10.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romby P, Vandenesch F, Wagner EG. The Role of Rnas in the Regulation of Virulence-Gene Expression. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006;9(2):229–36. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan R, Groisman EA, Ochman H. Genome-Wide Detection of Novel Regulatory Rnas in E. Coli. Genome Res. 2011;21(9):1487–97. doi: 10.1101/gr.119370.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu JM, Livny J, Lawrence MS, Kimball MD, Waldor MK, Camilli A. Experimental Discovery of Srnas in Vibrio Cholerae by Direct Cloning, 5s/Trna Depletion and Parallel Sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(6):e46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repoila F, Darfeuille F. Small Regulatory Non-Coding Rnas in Bacteria: Physiology and Mechanistic Aspects. Biol Cell. 2009;101(2):117–31. doi: 10.1042/BC20070137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman KM. 6s Rna: A Small Rna Regulator of Transcription. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007;10(2):164–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argaman L, Hershberg R, Vogel J, Bejerano G, Wagner EG, Margalit H, Altuvia S. Novel Small Rna-Encoding Genes in the Intergenic Regions of Escherichia Coli. Curr Biol. 2001;11(12):941–50. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highlander SK. Molecular Genetic Analysis of Virulence in Mannheimia (Pasteurella) Haemolytica. Front Biosci. 2001;6:D1128–50. doi: 10.2741/Highland. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo RY, McKerral LJ, Hills TL, Kostrzynska M. Analysis of the Capsule Biosynthetic Locus of Mannheimia (Pasteurella) Haemolytica A1 and Proposal of a Nomenclature System. Infect Immun. 2001;69(7):4458–64. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4458-4464.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leite F, Gyles S, Atapattu D, Maheswaran SK, Czuprynski CJ. Prior Exposure to Mannheimia Haemolytica Leukotoxin or Lps Enhances Beta(2)-Integrin Expression by Bovine Neutrophils and Augments Lkt Cytotoxicity. Microb Pathog. 2003;34(6):267–75. doi: 10.1016/S0882-4010(03)00060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakaletz LO, Baker BD, Jurcisek JA, Harrison A, Novotny LA, Bookwalter JE, Mungur R, Munson RS Jr. Demonstration of Type Iv Pilus Expression and a Twitching Phenotype by Haemophilus Influenzae. Infect Immun. 2005;73(3):1635–43. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.3.1635-1643.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutte L, Alonso S, Reveneau N, Willery E, Quatannens B, Locht C, Jacob-Dubuisson F. Role of Adhesin Release for Mucosal Colonization by a Bacterial Pathogen. J Exp Med. 2003;197(6):735–42. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashid Y, Kamran Azim M. Structural Bioinformatics of Neisseria Meningitidis Ld-Carboxypeptidase: Implications for Substrate Binding and Specificity. Protein J. 2011;30(8):558–65. doi: 10.1007/s10930-011-9364-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du MZ, Guo FB, Chen YY. Gene Re-Annotation in Genome of the Extremophile Pyrobaculum Aerophilum by Using Bioinformatics Methods. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2011;29(2):391–401. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2011.10507393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood V, Rutherford KM, Ivens A, Rajandream MA, Barrell B. A Re-Annotation of the Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Genome. Comp Funct Genomics. 2001;2(3):143–54. doi: 10.1002/cfg.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundogdu O, Bentley SD, Holden MT, Parkhill J, Dorrell N, Wren BW. Re-Annotation and Re-Analysis of the Campylobacter Jejuni Nctc11168 Genome Sequence. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:162. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen LL, Ma BG, Gao N. Reannotation of Hypothetical Orfs in Plant Pathogen Erwinia Carotovora Subsp. Atroseptica Scri1043. FEBS J. 2008;275(1):198–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus JC, Pryor MJ, Medigue C, Cole ST. Re-Annotation of the Genome Sequence of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis H37rv. Microbiology. 2002;148(Pt 10):2967–73. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-10-2967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm CG, Love BC, Krehbiel CR, Johnson NJ, Step DL. Comparison of Antemortem Antimicrobial Treatment Regimens to Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of Postmortem Lung Isolates from Feedlot Cattle with Bronchopneumonia. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012;24(2):277–82. doi: 10.1177/1040638711428149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichon C, Felden B. Small Rna Genes Expressed from Staphylococcus Aureus Genomic and Pathogenicity Islands with Specific Expression among Pathogenic Strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(40):14249–54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503838102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilderman PJ, Sowa NA, FitzGerald DJ, FitzGerald PC, Gottesman S, Ochsner UA, Vasil ML. Identification of Tandem Duplicate Regulatory Small Rnas in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Involved in Iron Homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101(26):9792–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403423101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz DH, Mok KC, Lilley BN, Kulkarni RV, Wingreen NS, Bassler BL. The Small Rna Chaperone Hfq and Multiple Small Rnas Control Quorum Sensing in Vibrio Harveyi and Vibrio Cholerae. Cell. 2004;118(1):69–82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz DH, Miller MB, Zhu J, Kulkarni RV, Bassler BL. Csra and Three Redundant Small Rnas Regulate Quorum Sensing in Vibrio Cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 2005;58(4):1186–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small Non-Coding Regulatory Rna Database. http://bioinfo.mikrobio.med.uni-giessen.de/sRNAdb/Blast
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Complete description of suggested corrections to existing annotation, and identified frameshift mutations. Sheet 1 labeled 'Annotation Errors' contains corrections to annotated genes in M. haemolytica PHL213, previously annotated gene locus and length, suggested correction to its locus. RNA-Seq expression based observed gene and protein length along with description of the exception in the genome that led to the annotation error; in case of mutated start, the mutated amino acid; BLASTX hit used to correct the annotation and its description. Sheet 2 labeled 'Frameshift' contains the two frameshift mutations identified, their frame locus and the BLASTX hit used to identify the frameshift.
RNA-Seq based expression profile of annotated genes. The sheet labeled as 'MH_Expressed' consists of annotated genes identified as expressed in the RNA-Seq experiment, the observed coverage, average reads per base for each gene and the description of the gene, Sheet 2 labeled as 'MH_NotExpressed' contains annotated genes identified as not expressed in RNA-Seq experiment, the observed coverage, average reads per base for each gene and the description of the gene.
Comparison of co-expressed gene pairs identified by RNA-Seq and operons predicted by DOOR. Sheet 1 labeled 'MH_DOOR' has a list of operons predicted by DOOR. Sheet 2 labeled 'MH_DOOR_Pairwise' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs predicted by DOOR. Sheet 3 labeled 'MH_JR' contains a list of operons identified in our RNA-Seq experiment. Sheet 4 labeled 'MH_JR_Pairs' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs identified by RNA-Seq. Sheet 6 labeled 'MH_Pairwise_Common' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs common to both DOOR and RNA-Seq. Sheet 7 labeled 'MH_DOOR_Unique' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs unique to DOOR. Sheet 8 labeled 'MH_JR_Unique' contains a list of co-expressed gene pairs unique to our RNA-Seq experiment.
Results of M. haemolytica PHL213 sRNA searched against sRNAdb. Putative sRNA identified by RNA-Seq were searched against other bacterial sRNA in small non-coding RNA database (sRNAdb) by conducting BLASTN searches.