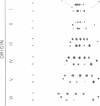
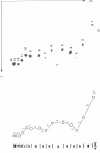
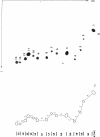
Abstract
Several electrophoretic and chromatographic systems have been investigated and compared for sequence analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Three systems were found to be useful for the separation of a series of sequential degradation products resulting from a labeled oligonucleotide: (I) 2-D electrophoresis†; (II) 2-D PEI-cellulose; and (III) 2-D homochromatography. System (III) proved generally most informative regardless of base composition and sequence. Furthermore, only in this system will the omission of an oligonucleotide in a series of oligonucleotides be self-evident from the two-dimensional map. The sequence of up to fifteen nucleotides can be determined solely by the characteristic mobility shifts of its sequential degradation products distributed on the two-dimensional map. With this method, ten nucleotides from the double-stranded region adjacent to the left-hand 3′-terminus and seven from the right-hand 3′-terminus of bacteriophage λ DNA have been sequenced. Similarly, nine nucleotides from the double-stranded region adjacent to the left-hand 3′-terminus and five nucleotides from the right-hand terminus of bacteriophage φ80 DNA have also been sequenced. The advantages and disadvantages of each separation system with respect to sequence analysis are discussed.
Full text
PDF








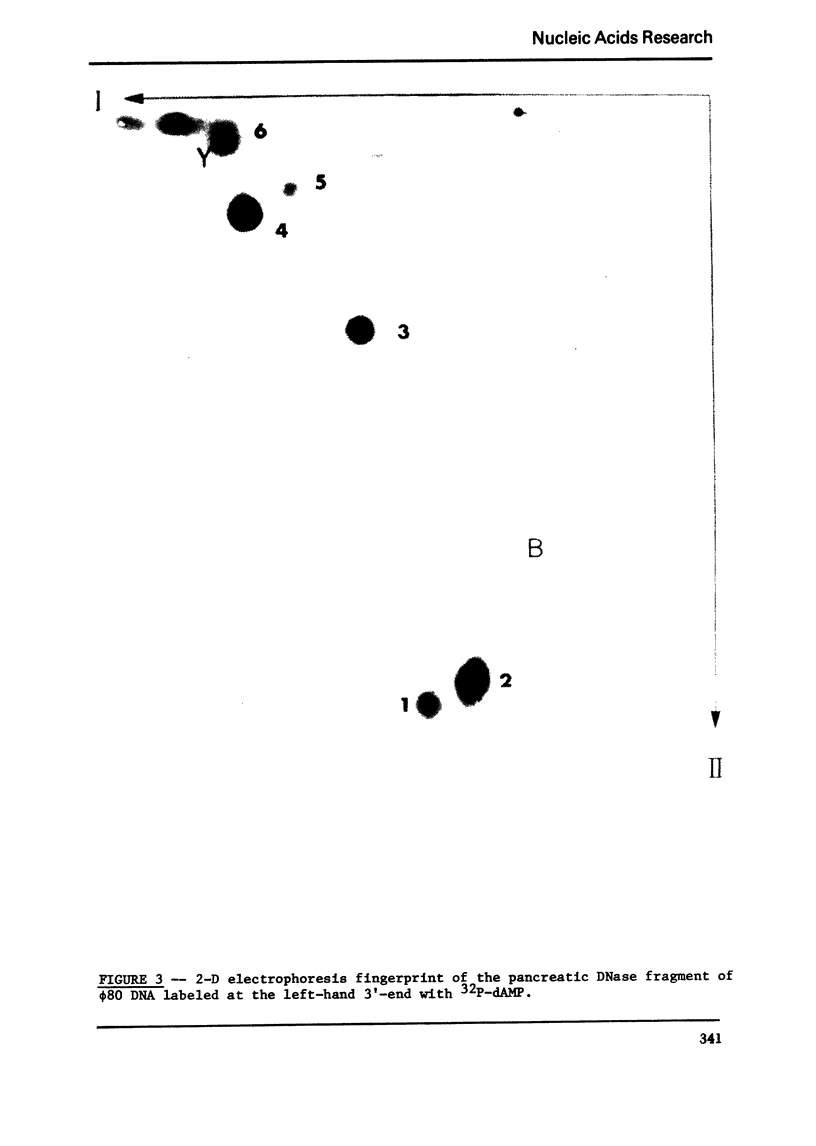
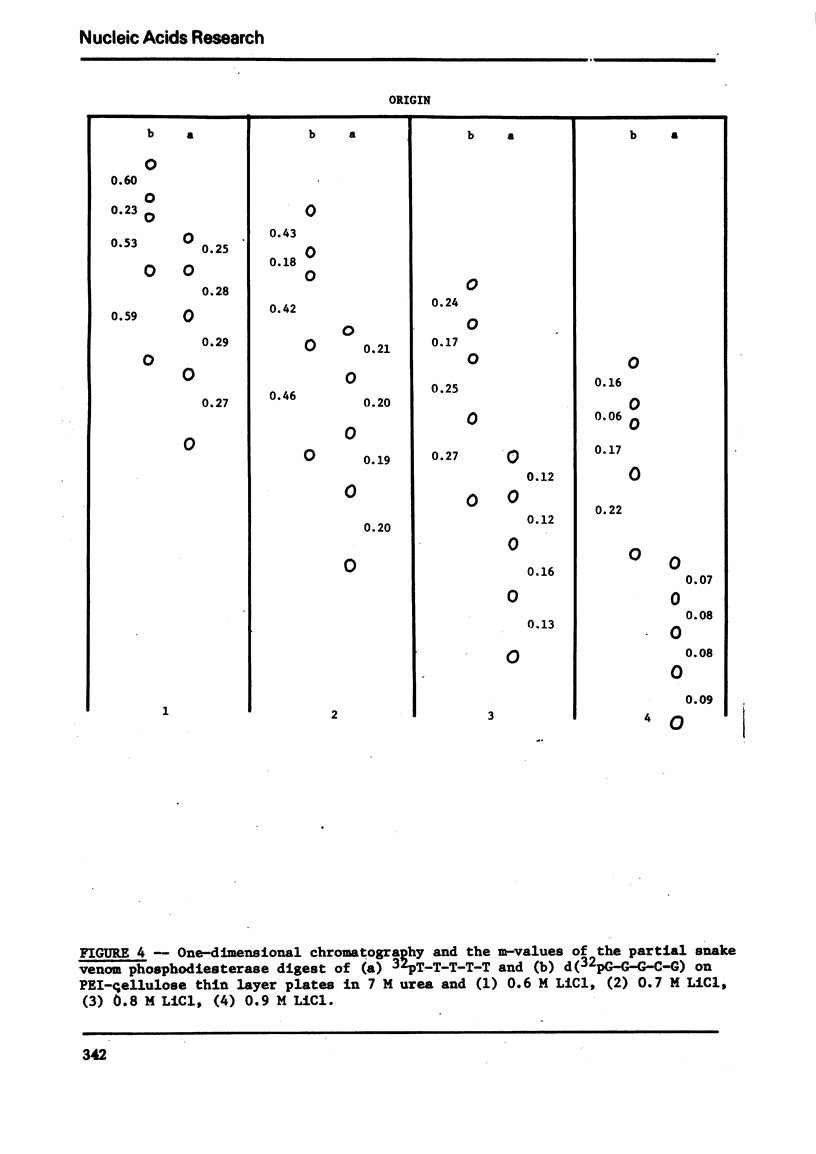
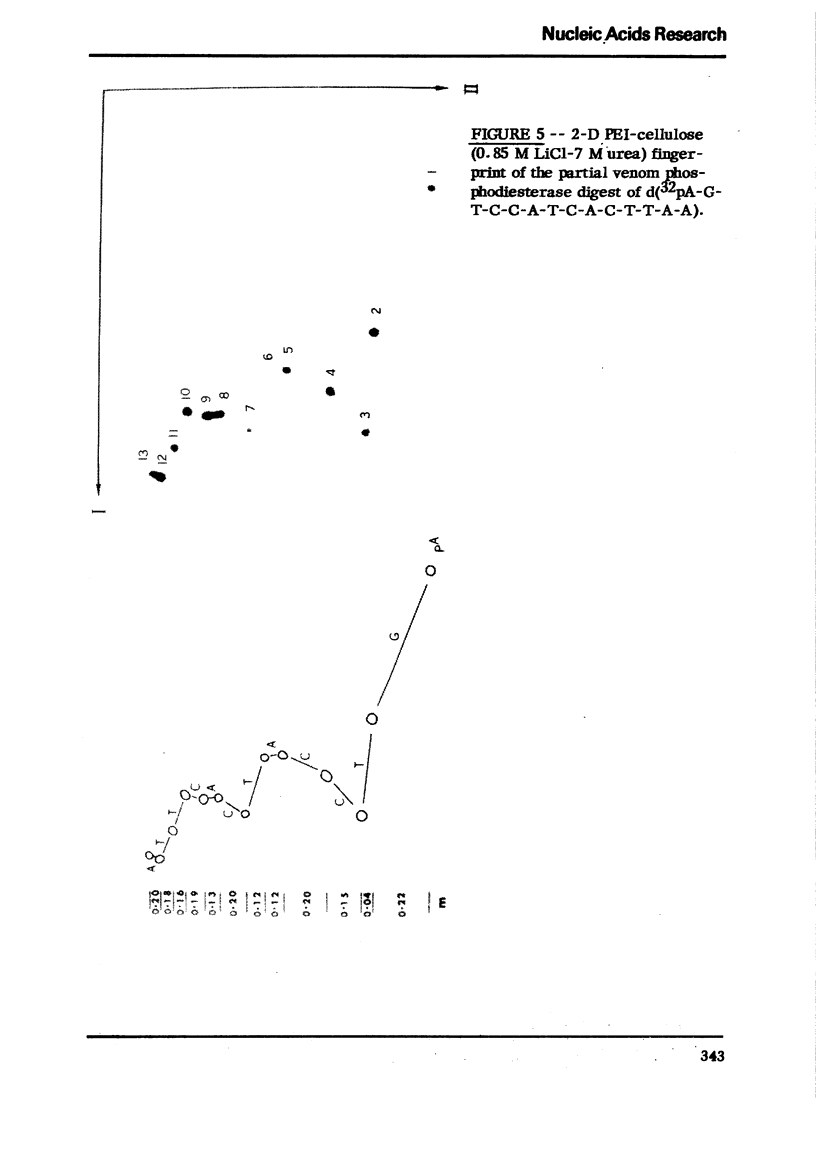
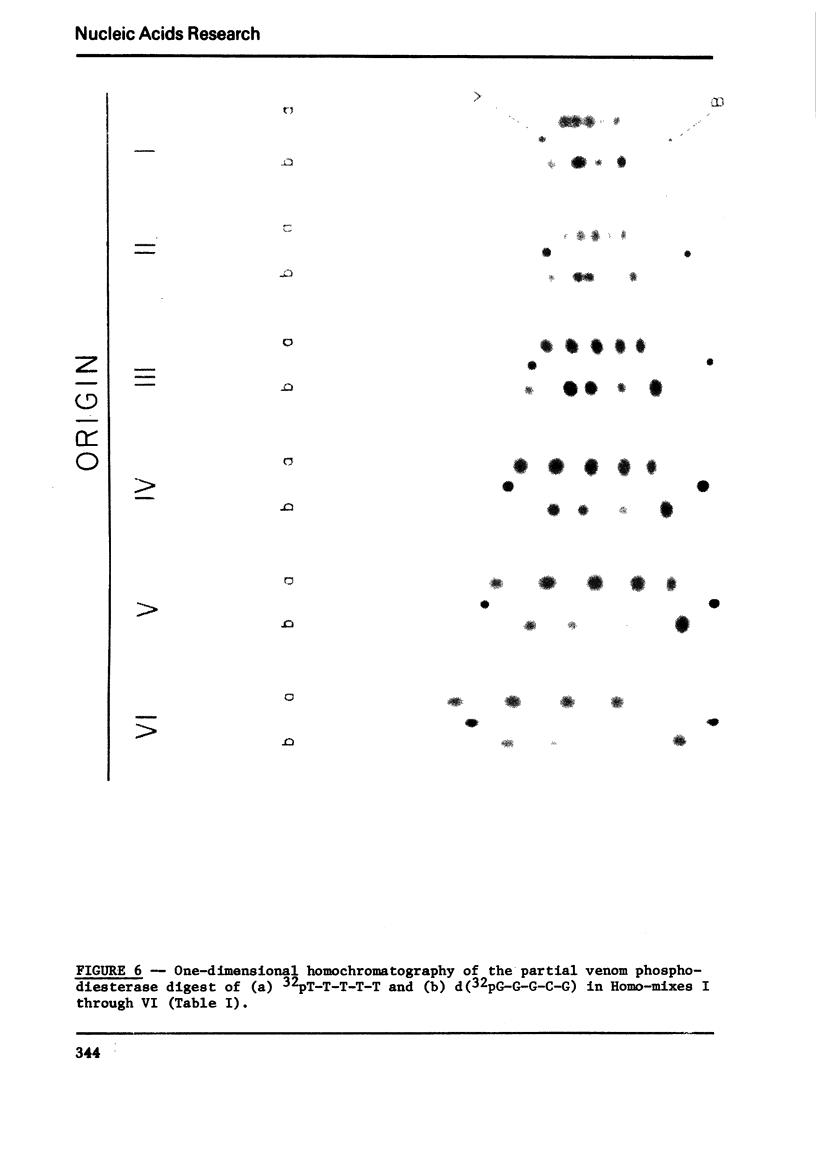

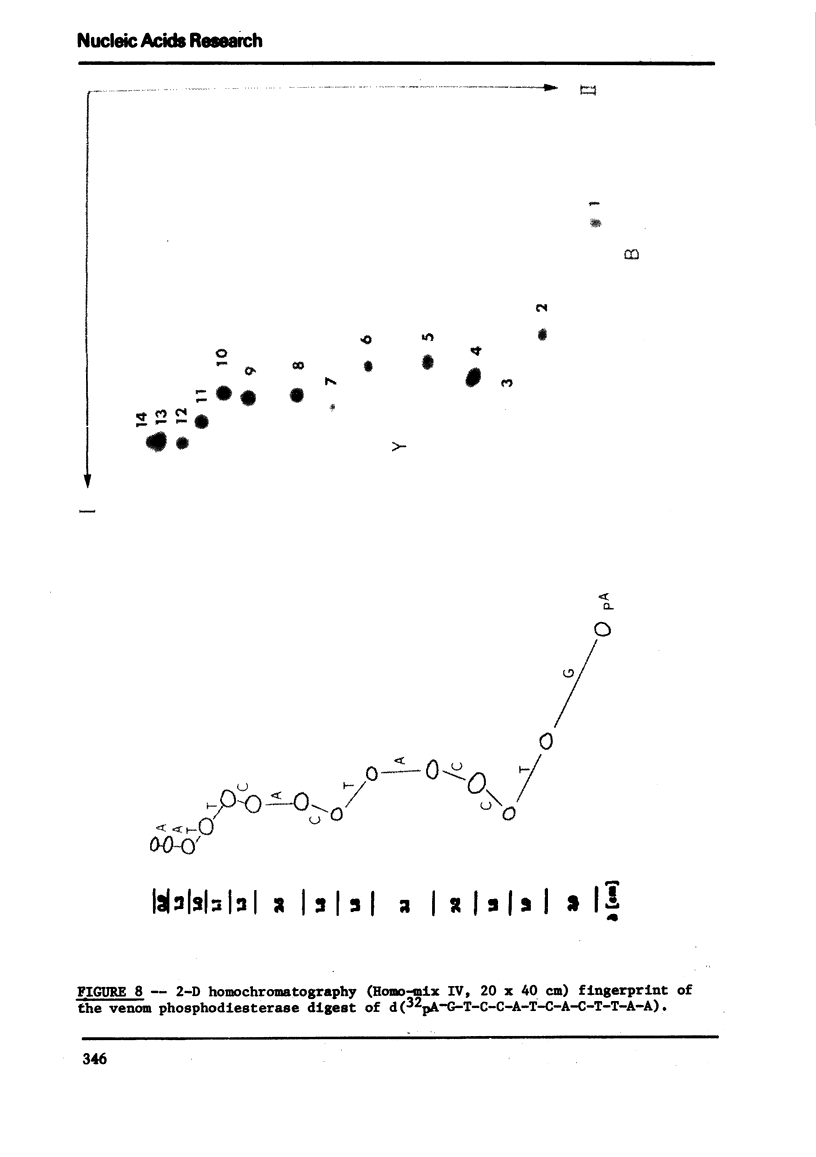
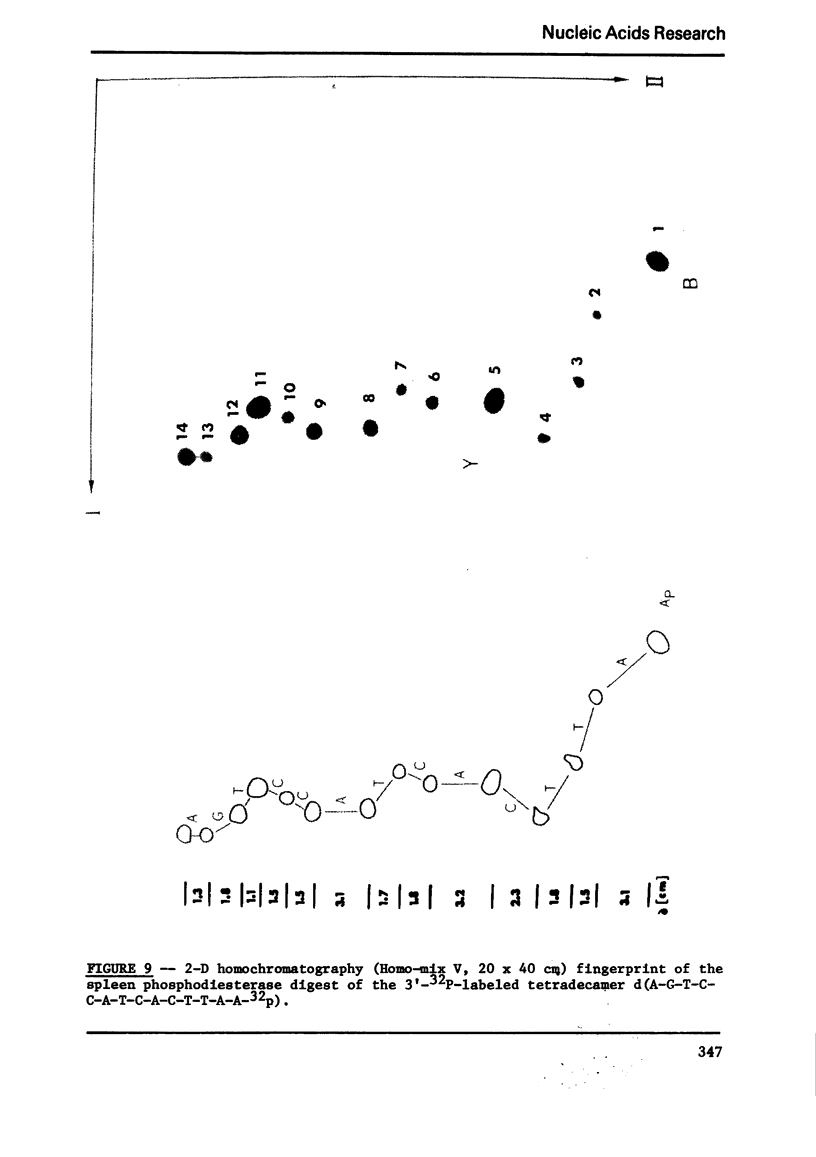
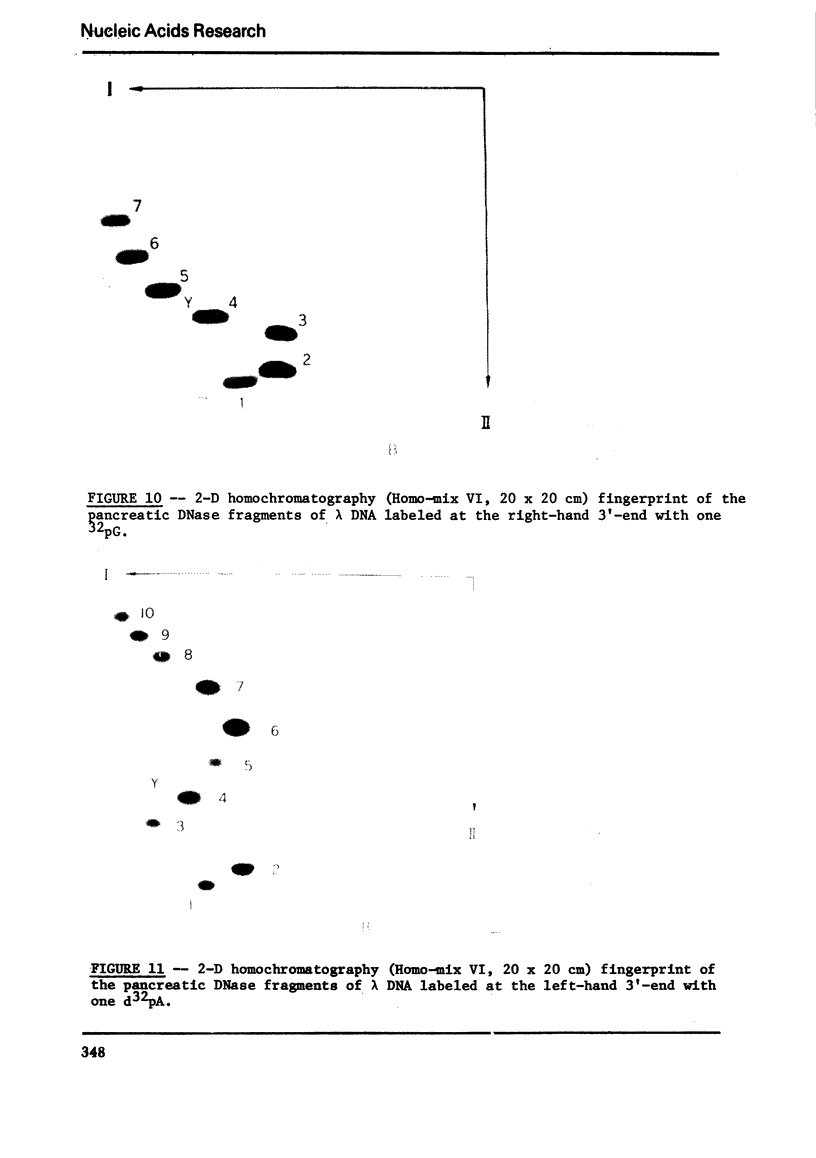
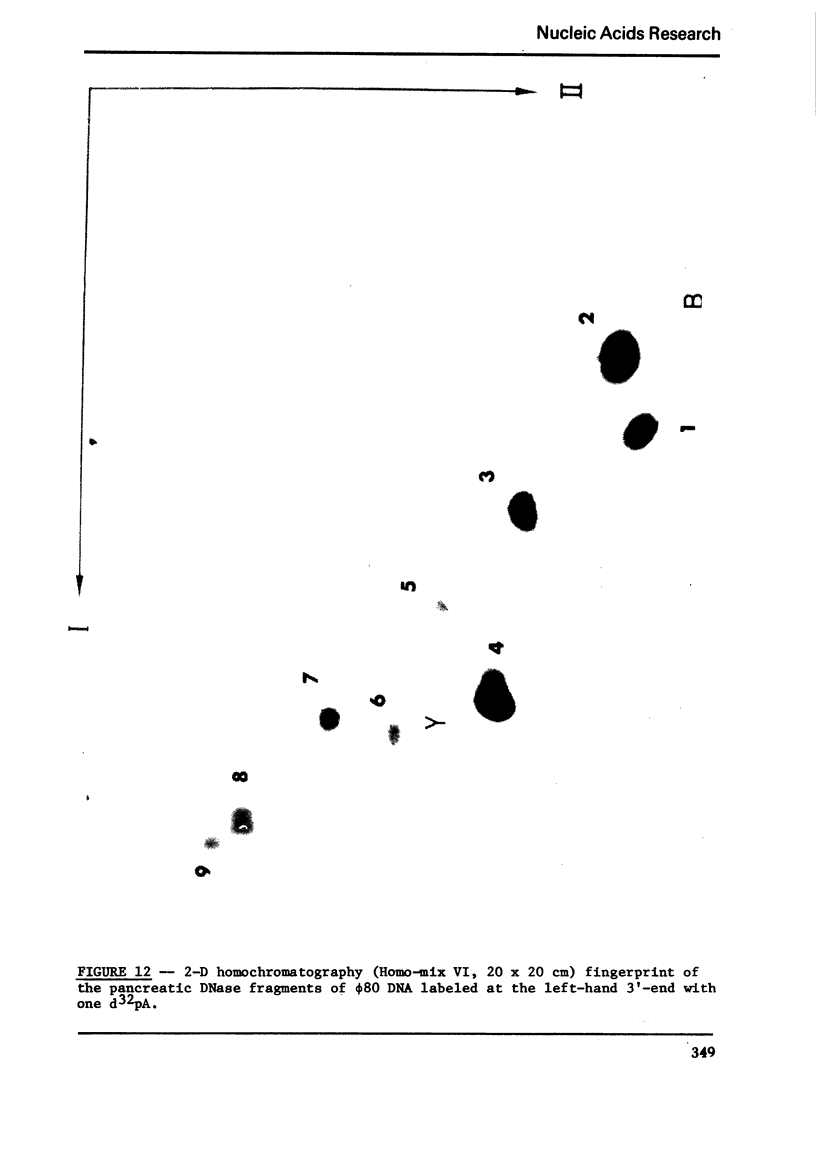




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bambara R., Padmanabhan R., Wu R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. X. Complete nucleotide sequence of the cohesive ends of bacteriophage phi80 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):741–744. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezinski D. P., Wang J. C. The 3'-terminal nucleotide sequences of lambda DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90854-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F. Chromatography of 32P-labelled oligonucleotides on thin layers of DEAE-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T. The 3'-terminal nucleotide sequences of T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 14;66(2):209–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90474-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghangas G. S., Jay E., Bambara R., Wu R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. XI. The 3' terminal sequences of bacteriophage lambda and phi 80 DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):998–1007. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90793-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E. Separation of 32P-labelled ribonucleic acid components. The use of polyethylenimine-cellulose (TLC) as a second dimension in separating oligoribonucleotides of '4.5 S' and 5 S from E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromkova R., Goodgal S. H. Action of haemophilus endodeoxyribonuclease on biologically active deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):987–992. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.987-992.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedgpeth J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. DNA nucleotide sequence restricted by the RI endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K. I., Gonçalves J. M., Houts G. E., Bollum F. J. Deoxynucleotide-polymerizing enzymes of calf thymus gland. II. Properties of the terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2780–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Smith H. O. A restriction enzyme from Hemophilus influenzae. II. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):393–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling V. Pyrimidine sequences from the DNA of bacteriophages fd, fl, and phi X174. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Khorana H. G. Studies on polynucleotides. CXXII. The dodecanucleotide sequence adjoining the C-C-A end of the tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid gene. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3489–3499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Davis R. W. Cleavage of DNA by R 1 restriction endonuclease generates cohesive ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3370–3374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M., Yuan R., Heywood J. Restriction and modification of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:447–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Murray N. E. Terminal nucleotide sequences of DNA from temperate coliphages. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 30;243(126):134–139. doi: 10.1038/newbio243134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. Nucleotide 'maps' of digests of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;118(5):831–841. doi: 10.1042/bj1180831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. Nucleotide sequence analysis with polynucleotide kinase and nucleotide "mapping" methods. 5'-Terminal sequences of deoxyribonucleic acid from bacteriophages lambda and 424. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):569–582. doi: 10.1042/bj1310569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan R., Wu R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. IX. Use of oligonucleotides of defined sequence as primers in DNA sequence analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1295–1302. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90852-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Kössel H. Synthetic polynucleotides. Enzymic synthesis of ribonucleotide terminated oligodeoxynucleotides and their use as primers for the enzymic synthesis of polydeoxynucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Oct 14;22(3):310–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack G. H., Jr, Nathans D. Studies of SV40 DNA. VI. Cleavage of SV40 DNA by restriction endonuclease from Hemophilus parainfluenzae. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):517–520. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Brownlee G. G., Barrell B. G. A two-dimensional fractionation procedure for radioactive nucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):373–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Donelson J. E., Coulson A. R., Kössel H., Fischer D. Use of DNA polymerase I primed by a synthetic oligonucleotide to determine a nucleotide sequence in phage fl DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Mitchell A. R. Chromatography of nucleic acid digests on thin layers of cellulose impregnated with polyethyleneimine. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(4):613–617. doi: 10.1042/bj1230613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel P. H., Englund P. T., Murray K., Old R. W. The 3'-terminal nucleotide sequences of bacteriophage lambda DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1151–1155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Richardson C. C. The 5'-terminal dinucleotides of the separated strands of T7 bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1967 Feb 14;23(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 19;236(68):198–200. doi: 10.1038/newbio236198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Taylor E. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. II. Complete nucleotide sequence of the cohesive ends of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):491–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Tu C. D., Padmanabhan R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. XII. The chemical synthesis and sequence analysis of a dodecadeoxynucleotide which binds to the endolysin gene of bacteriophage lambda. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 19;55(4):1092–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]