Abstract
The application of biomarkers in melanoma prognosis has been well recognized. However the ability of a single biomarker to predict melanoma patient outcome is usually limited. We previously examined the expression of ten biomarkers (Bim, BRG1, BRMS1, CTHRC1, ING4, NQO1, NF-κB-p50, PUMA, SNF5 and SOX4) in melanomas. To assess the value of a combined multiple biomarker system in melanoma prognosis, we compared the expression of each biomarker between various stages of melanoma, and determined the best combination of biomarkers for melanoma prognosis. Although the expression of six biomarkers (Bim, BRMS1, ING4, NQO1, PUMA and SOX4) was significantly decreased in AJCC III–IV stages of melanoma compared to AJCC I–II stages, the combined 6-biomarker index score exhibited higher variations than any individual biomarker in the same comparison. Moreover, the 6-biomarker index score was correlated with melanoma thickness, location and subtype, and predicted the outcome of melanoma patients more accurately than the individual biomarkers. Multivariate Cox regression analysis demonstrated that the 6-biomarker index score is an independent prognostic factor for melanoma. In conclusion, our study suggests that a multi-biomarker system test is valuable for improved outcome prediction in melanoma patients and for the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: biomarker, melanoma, prognosis, tissue microarray
Introduction
Melanoma is the most lethal form of skin cancer. Among all malignancies, the incidence of melanoma has exhibited the most rapid increase in the Caucasian population, apart from lung cancer in women (1). It is estimated that 68,130 new cases of cutaneous melanoma will be diagnosed, and 8,700 patients will die from melanoma in the US in 2010 (2).
Malignant melanoma is associated with very high mortality rates, particularly in cases of advanced disease. Patients with metastatic melanoma have an extremely poor prognosis (3). Therefore, the accurate prediction of melanoma metastasis and patient outcome is essential for the selection of the best therapeutic strategy and to improve patient survival. One way to improve prognostic assessment is the use of molecular biomarkers. Previously we investigated the expression of ten biomarkers (Bim, BRG1, BRMS1, CTHRC1, ING4, NQO1, NF-κB-p50, PUMA, SNF5 and SOX4) in melanomas; most were found to be important for melanoma prognosis (4–13). Here, we analyzed the expression of these ten biomarkers in 73 primary melanoma cases and 45 metastatic melanomas. We then compared the expression of these biomarkers between AJCC I–II stages (without metastasis) and AJCC III–IV stages (with metastasis) melanomas. We also compared the capability of each individual biomarker or combined biomarker system to predict patient outcome. Our data revealed that the 6-biomarker (Bim, BRMS1, ING4, NQO1, PUMA and SOX4) system delivers more accurate prognosis for melanoma patients than any individual biomarker.
Materials and methods
Ethics statement
The use of human skin tissues and the waiver of patient consent in this study were specifically approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Board of the University of British Columbia.
Study population
Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded biopsies were obtained from the 1990–1998 archives of the Department of Pathology at Vancouver General Hospital. A total of 73 primary melanomas and 45 metastatic melanomas were successfully evaluated for staining of all of the ten biomarkers. Clinicopathological data were available for all melanoma cases.
Re-evaluation of expression of each biomarker
The expression of the ten biomarkers was previously examined using tissue microarray (TMA) and immunohistochemistry (IHC). The detailed methodology for the TMA construction and staining for these biomarkers were previously reported (4–13). Information concerning the antibodies used in these studies is listed in Table I. We collected the raw readings for each individual biomarker and re-grouped the staining intensity and percentage of positive staining cells uniformly in this study. Staining intensity was defined as 0 (negative), 1 (weak), 2 (moderate) and 3 (strong), and the percentage of positive staining was scored according to 3 categories: 1 (0–33%), 2 (34–67%) and 3 (68–100%). The level of staining of each biomarker was finally evaluated by the immunoreactive score (IRS; 14), which was calculated by multiplying the score of the staining intensity by that of the percentage of positive cells. The IRS was then applied to the statistical analysis of the expression variation among the various stages of melanocytic lesions or the various subgroups directly.
Table I.
Antibodies for the ten biomarkers studied.
| Biomarker | Full name | Supplier | Clone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bim | BCL2-like 11 | NeoMarkers | Polyclonal |
| BRG1 | SWI/SNF related, matrix-associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4 | Santa Cruz | Polyclonal |
| BRMS1 | Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 | Donationa | Monoclonal |
| CTHRC1 | Collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 | Immunochem | Polyclonal |
| ING4 | Inhibitor of growth family, member 4 | ProteinTech | Polyclonal |
| NQO1 | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1 | Santa Cruz | Monoclonal |
| p50 | Nuclear factor of κ light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 | Santa Cruz | Polyclonal |
| PUMA | BCL2 binding component 3 | Imgenex | Polyclonal |
| SNF5 | SWI/SNF related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily b, member 1 | Abcam | Monoclonal |
| SOX4 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4 | Abcam | Polyclonal |
The BRMS1 antibody was provided by Dr Danny R. Welch, University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Calculating the index score for multiple biomarkers
To assess the value of the multiple biomarkers in melanoma prognosis, the index score was calculated for the multiple biomarkers. The expression levels of the 6 biomarkers, Bim, BRMS1, ING4, NQO1, PUMA and SOX4, were all higher in the primary stage (AJCC I and II) than in the advanced stage (AJCC III and IV) melanomas. Thus, the final index score was the sum of the IRS of all six biomarkers. For the survival analysis using the 6-biomarker system, the final index score was grouped into two categories: the low score group (0–16) and the high score group (17–48).
Statistical analysis
Graphpad PRISM version 5.0 and INSTAT 3 software (Graphpad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) were used to compare the change in expression of each individual biomarker or the combined multiple-biomarker system between various stages or subgroups. The correlation coefficient (R) was calculated with λ correlation statistical analysis. SPSS version 11.5 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the statistical analysis for patient survival. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant, and all tests of statistical significance were two-sided.
Results
Clinicopathological features of the melanoma biopsies
The clinicopathological features of all 118 melanoma biopsies in this study are summarized as follows. Of the 73 primary melanoma cases, 46 were men and 27 women, with ages ranging from 21 to 93 years (median, 59 years). In 47 cases, the tumors were ≤2.0-mm thick, while 26 tumors were >2.0 mm. Tumor ulceration was present in 15 cases at diagnosis. Regarding the histological subtype, there were 30 cases of superficial-spreading melanoma, 16 lentigo maligna melanomas, 10 nodular melanomas and another 17 unspecified cases. Sixteen melanomas were found in sun-exposed sites, including the head and neck, while the other 57 were located in sun-protected areas, including the arm, foot, leg and trunk. Forty-five patients with melanoma metastases were included in this analysis, 31 of which were men and 14 women, with ages ranging from 27 to 89 years (median, 60 years). AJCC criteria were also applied to all the melanoma patients in this study. Among the 118 cases, 41 patients had stage I tumors, while 29 were stage II, 26 stage III and 22 stage IV.
Six biomarkers are correlated with melanoma metastasis
Various levels of staining were observed for each biomarker in the various melanocytic lesions. We compared the expression profile of all ten biomarkers in the AJCC I–II and AJCC III–IV stage melanomas. Our data revealed that expression of the six biomarkers, Bim, BRMS1, ING4, NQO1, PUMA and SOX4, was significantly higher in the early stage (AJCC I–II) than in the advanced stage (AJCC III–IV) cases, suggesting that these six biomarkers are correlated with melanoma metastasis (Table II). We obtained the final index score for the 6-biomarker system and performed the correlation analysis. The correlation coefficients for Bim, BRMS1, ING4, NQO1, PUMA and SOX4 were 0.333, 0.146, 0.188, 0.146, 0.05 and 0.208, respectively, whereas this value reached 0.5 for the combined 6-biomarker system. Our data also revealed that a higher index score (17–48) was correlated with tumors ≤4.0 mm thick, sun-protected sites and superficial spreading melanomas (P=0.008, 0.030 and 0.003, respectively; Mann-Whitney test) (Fig. 1), but was not correlated with patient age, gender and ulceration.
Table II.
Comparison of the expression of the ten biomarkers between melanomas with and without metastasis.
| Biomarker | IRS mean value
|
P-valuea | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AJCC I–II (n=70) | AJCC III–IV (n=48) | ||
| Bim | 5.30 | 2.83 | 0.0001 |
| BRMS1 | 5.99 | 4.45 | 0.0030 |
| BRG1 | 6.09 | 6.08 | 0.9253 |
| CTHRC1 | 6.00 | 6.75 | 0.1342 |
| ING4 | 5.86 | 4.75 | 0.0239 |
| NQO1 | 4.96 | 2.75 | 0.0008 |
| NF-κB-p50 | 4.84 | 5.71 | 0.1424 |
| PUMA | 4.89 | 4.19 | 0.0379 |
| SNF5 | 5.84 | 5.87 | 0.9430 |
| SOX4 | 5.77 | 4.35 | 0.0115 |
| 6-Biomarker system | 26.99b | 18.98b | <0.0001 |
Calculated using the Mann-Whitney test.
Mean value of the combined six biomarkers, including Bim, BRMS1, ING4, NQO1, PUMA and SOX4.
Figure 1.
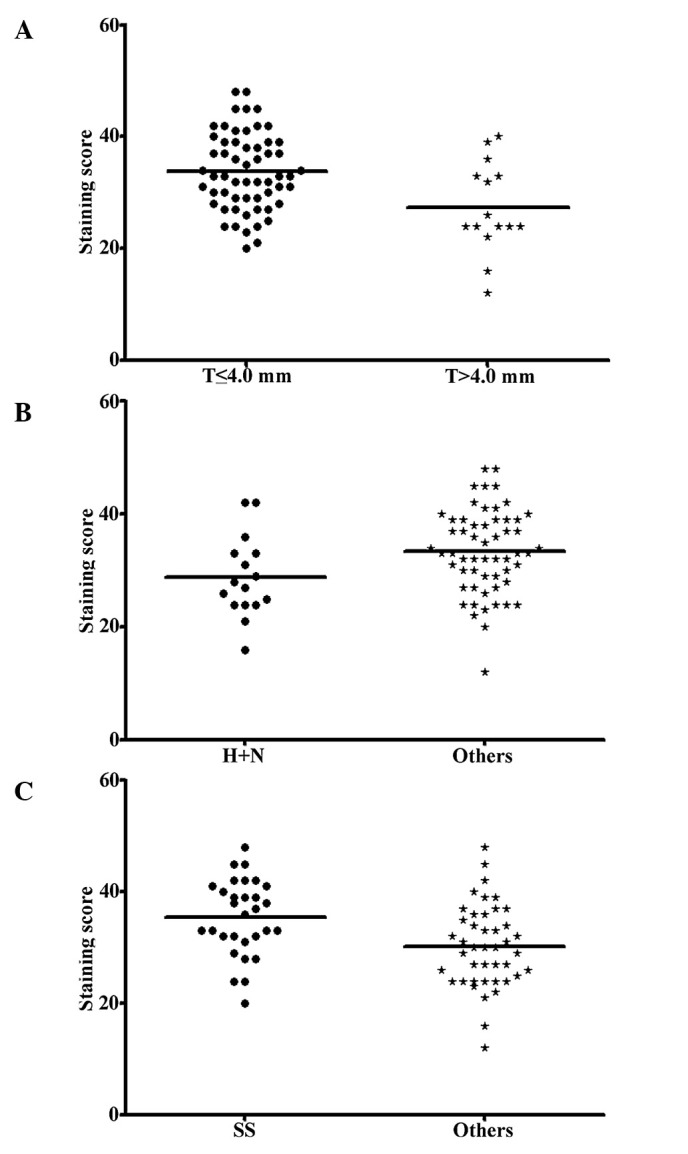
Correlations between the 6-biomarker index score and the clinicopathological parameters of the primary melanoma patients. (A) The 6-biomarker index score was significantly lower in melanomas >4.0-mm thick than in those ≤4.0 mm (P=0.008). (B) The combined 6-biomarker score was significantly lower in primary melanomas located in sun-exposed areas of the body (H+N) than in those found in sun-protected areas (P=0.030). (C) The 6-biomarker system revealed a higher score in superficial spread (SS) primary melanomas than in other histological subtypes (P=0.003). Mann-Whitney test for all.
Six-biomarker system provides better prognostic accuracy
Univariate Cox regression analysis revealed that five biomarkers, Bim, BRMS1, ING4, NQO1 and PUMA, were all significantly correlated with both overall and disease-specific 5-year survival in the 118 melanoma patients, while SOX4 was correlated with disease-specific 5-year survival only. The relative risk (RR) and P-value for each individual biomarker in the overall survival analysis ranged from the lowest RR of 0.461 (P=0.003) for ING4, to the highest RR of 0.626 (P=0.076) for SOX4. In disease-specific survival analysis, the RR and P-value for individual biomarkers ranged from the lowest RR of 0.408 (P=0.002) for BRMS1, to the highest RR of 0.527 (P=0.029) for SOX 4. However, when we combined these six biomarkers and performed this analysis, we found that the RR was decreased to 0.273 and 0.222 for overall and disease-specific survival (P=0.00001 and 0.000002), respectively (Table III). We then constructed the Kaplan-Meier curve for all 118 melanoma patients, and our data revealed that a high index score of the combined 6-biomarker system was significantly correlated with a more favorable 5-year patient survival in both overall and disease-specific survival analyses (P=0.0000 for both, log-rank test) (Fig. 2). Moreover, a multivariate Cox regression analysis indicated that a high index score was an independent prognostic factor for both overall and disease-specific 5-year survival (RR=0.237 and 0.208; 95% CI, 0.125–0.453 and 0.105–0.414; P=0.00001 and 0.000007, respectively) (Table IV).
Table III.
Univariate Cox regression analysis of individual and multiple biomarkers on 5-year patient survival in the 118 melanoma cases.
| Biomarker | Overall survival
|
Disease-specific survival
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR | 95% CI | P-value | RR | 95% CI | P-value | |
| Bim | 0.465 | 0.258–0.838 | 0.011 | 0.424 | 0.223–0.807 | 0.009 |
| BRMS1 | 0.575 | 0.343–0.965 | 0.036 | 0.408 | 0.230–0.723 | 0.002 |
| ING4 | 0.461 | 0.275–0.772 | 0.003 | 0.416 | 0.234–0.739 | 0.003 |
| NQO1 | 0.473 | 0.279–0.803 | 0.006 | 0.415 | 0.227–0.761 | 0.004 |
| PUMA | 0.514 | 0.304–0.868 | 0.013 | 0.421 | 0.230–0.770 | 0.005 |
| SOX4 | 0.626 | 0.373–1.049 | 0.076 | 0.527 | 0.297–0.935 | 0.029 |
| 6-Biomarkers | 0.273 | 0.152–0.490 | 1×10−5 | 0.222 | 0.119–0.415 | 2×10−6 |
Figure 2.
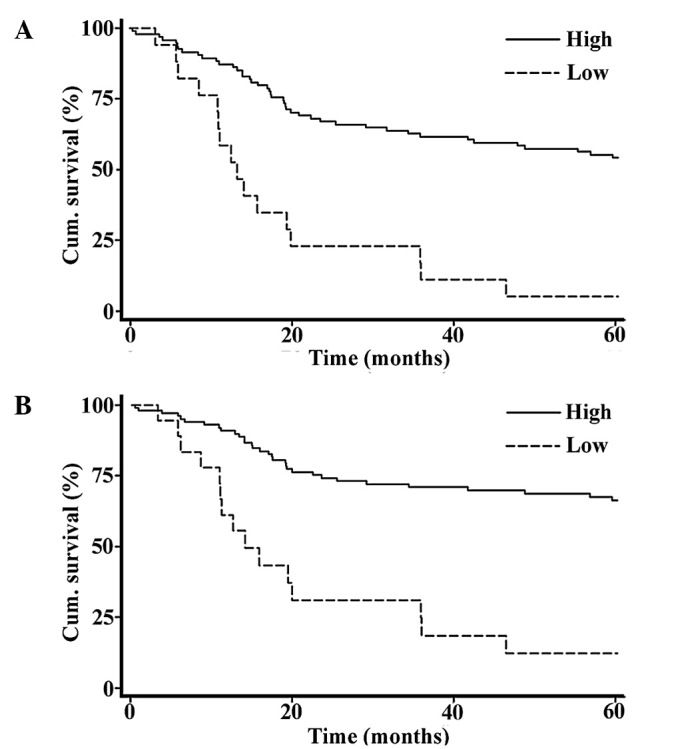
Correlation between the 6-biomarker index score and the 5-year survival of melanoma patients. A high combined 6-biomarker index score was correlated with (A) more favorable overall 5-year patient survival, and (B) disease-specific 5-year survival (n=118; P<0.001 for both, log-rank test).
Table IV.
Multivariate Cox regression analysis of the 6-biomarker index score on 5-year patient survival in the 118 melanoma cases.
| Variablesa | Overall survival
|
Disease-specific survival
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR | 95% CI | P-value | RR | 95% CI | P-value | |
| Age | 0.574 | 0.337–0.979 | 0.042 | 0.838 | 0.457–1.535 | 0.567 |
| Gender | 1.111 | 0.635–1.943 | 0.713 | 0.976 | 0.523–1.822 | 0.940 |
| 6-Biomarkerb | 0.237 | 0.125–0.453 | 1×10−5 | 0.208 | 0.105–0.414 | 7×10−6 |
Coding of variables: age was coded as 1, ≤59 years and 2, >59 years; gender was coded as 1, female and 2, male; score was coded as 1, low score (0–16) and 2, high score (17–48);
Score represents the 6-biomarker combined index score.
Discussion
Previous studies have revealed that numerous biomarkers are valuable for melanoma prognosis (15). Here, we found that the expression of six biomarkers, Bim, BRMS1, ING4, NQO1, PUMA and SOX4, differed significantly between AJCC I–II and AJCC III–IV stage melanomas, although the effect was limited for the individual biomarkers. However, the 6-biomarker combination revealed a closer correlation with melanoma metastasis and provided a better prognostic accuracy.
The correlation between the expression of the six biomarkers (Bim, BRMS1, ING4, NQO1, PUMA and SOX4) and melanoma metastasis observed in this study is consistent with previous findings. Bim was found to serve as a key factor in the regulation of apoptosis by interacting with all Bcl-2 members (16), and the loss of Bim was found to be critical for the pro-survival effect of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in melanoma. BRMS1 was reported to be a suppressor of metastasis in various types of cancer by inhibiting the expression of several metastasis-related genes (17–19). We previously reported that ING4 inhibited melanoma cell migration and invasion (7). In addition, ING4 was found to promote the apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells (20) and to suppress gliomas tumor growth and angiogenesis (21), while NQO1 was found to enhance apoptosis induced by β-lapachone treatment in prostate cancer cells (22). Moreover, the loss of PUMA was linked to deficient apoptosis and uncontrolled tumor cell growth (23), which may finally contribute to metastasis. SOX4 was reported to inhibit melanoma cell migration and cell invasion (4) and was also found to be necessary for the activation of p53 by stabilizing p53 and enhancing p53 acetylation under DNA damage stress (24). The function of these six biomarkers in inducing apoptosis and inhibiting cell migration and invasion also explains the correlation between the 6-biomarker index score and tumor thickness.
We found that a low 6-biomarker index score was correlated with primary melanomas located at sun-exposed sites. This can be explained by the functions of these biomarkers in apoptosis and DNA repair. Decreased expression of Bim, ING4, NQO1 and PUMA was found to result in reduced apoptosis (16,20,22,23,25), thus leading to the inability to repair severe DNA damage caused by UV. Furthermore, we previously revealed that NQO1 inhibits the degradation of p33ING1b, which plays an important role in the repair of UV-damaged DNA (26,27). The reason for the correlation between a higher 6-biomarker index score with superficial spreading melanoma is not known.
Statistical analysis demonstrated that the combined 6-biomarker index provided more accurate prediction of metastasis than any of the individual biomarkers, which may be attributed to the fact that these 6 biomarkers function to inhibit metastasis through different processes, including the induction of apoptosis, suppression of cell migration, invasion and angiogenesis, as well as promotion of DNA repair. Thus, the combination of these six biomarkers demonstrated a significant improvement in the predictive accuracy for metastasis. Furthermore, this 6-biomarker index score revealed an enhanced correlation with improved melanoma patient survival compared to any single biomarker using univariate Cox regression analysis, as metastasis is a major cause of melanoma patient death. This 6-biomarker system is of great significance in predicting melanoma metastasis and outcome, making it valuable in clinical practice and the development of novel therapeutic targets for human melanoma.
Acknowledgments
We thank Derek Dai, Hanyang Lin, Alison Karst, Kai Gao, Yabin Cheng and Seyed Mehdi Jafarnejad for the technical assistance and Dr Danny R. Welch for providing the BRMS1 antibody.
References
- 1.Howe HL, Wingo PA, Thun MJ, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer (1973 through 1998), featuring cancers with recent increasing trends. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:824–842. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.11.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer Statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. doi: 10.3322/caac.20073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jemal A, Thomas A, Murray T, Thun M. Cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2002;52:23–47. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.52.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jafarnejad SM, Wani AA, Martinka M, Li G. Prognostic significance of Sox4 expression in human cutaneous melanoma and its role in cell migration and invasion. Am J Pathol. 2010 Oct 15; doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100377. (E-pub ahead of print). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dai DL, Wang Y, Liu M, Martinka M, Li G. Bim expression is reduced in human cutaneous melanomas. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:403–407. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tang L, Dai DL, Su M, Martinka M, Li G, Zhou Y. Aberrant expression of collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 in human solid cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:3716–3722. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li J, Martinka M, Li G. Role of ING4 in human melanoma cell migration, invasion and patient survival. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:1373–1379. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gao K, Dai DL, Martinka M, Li G. Prognostic significance of nuclear factor-κB p105/p50 in human melanoma and its role in cell migration. Cancer Res. 2006;66:8382–8388. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Karst AM, Dai DL, Martinka M, Li G. PUMA expression is significantly reduced in human cutaneous melanomas. Oncogene. 2005;24:1111–1116. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lin H, Wong RP, Martinka M, Li G. Loss of SNF5 expression correlates with poor patient survival in melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:6404–6411. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lin H, Wong RP, Martinka M, Li G. BRG1 expression is increased in human cutaneous melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:502–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cheng Y, Li J, Martinka M, Li G. The expression of NAD(P) H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 is increased along with NF-κB p105/p50 in human cutaneous melanomas. Oncol Rep. 2010;23:973–979. doi: 10.3892/or_00000722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li J, Cheng Y, Tai D, Martinka M, Welch DR, Li G. Prognostic significance of BRMS1 expression in human melanoma and its role in tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene. 2010 Oct 11; doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.470. (E–pub ahead of print). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Remmele W, Stegner HE. Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe. 1987;8:138–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Torabian S, Kashani-Sabet M. Biomarkers for melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 2005;17:167–171. doi: 10.1097/01.cco.0000154039.07466.5d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, et al. Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell. 2005;17:393–403. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.12.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Vaidya KS, Harihar S, Phadke PA, et al. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor-1 differentially modulates growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:28354–28360. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710068200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hedley BD, Welch DR, Allan AL, et al. Down-regulation of osteopontin contributes to metastasis suppression by breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:526–534. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yang J, Zhang B, Lin Y, Yang Y, Liu X, Lu F. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 inhibits SDF-1alpha-induced migration of non-small cell lung cancer by decreasing CXCR4 expression. Cancer Lett. 2008;269:46–56. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shiseki M, Nagashima M, Pedeux RM, et al. p29ING4 and p28ING5 bind to p53 and p300, and enhance p53 activity. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2373–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Garkavtsev I, Kozin SV, Chernova O, et al. The candidate tumour suppressor protein ING4 regulates brain tumour growth and angiogenesis. Nature. 2004;428:328–332. doi: 10.1038/nature02329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Planchon SM, Pink JJ, Tagliarino C, Bornmann WG, Varnes ME, Boothman DA. β-Lapachone-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells: involvement of NQO1/xip3. Exp Cell Res. 2001;267:95–106. doi: 10.1006/excr.2001.5234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yu J, Zhang L. PUMA, a potent killer with or without p53. Oncogene. 2008;27(Suppl 1):S71–S83. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pan X, Zhao J, Zhang WN, et al. Induction of SOX4 by DNA damage is critical for p53 stabilization and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:3788–3793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810147106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li X, Zhang Q, Cai L, et al. Inhibitor of growth 4 induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 via Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondria apoptosis pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135:829–835. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0519-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Garate M, Wong RP, Campos EI, Wang Y, Li G. NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 inhibits the proteasomal degradation of the tumour suppressor p33(ING1b) EMBO Rep. 2008;9:576–581. doi: 10.1038/embor.2008.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Li J, Wang Y, Wong RP, Li G. The role of ING tumor suppressors in UV stress response and melanoma progression. Curr Drug Targets. 2009;10:455–464. doi: 10.2174/138945009788185031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


