Abstract
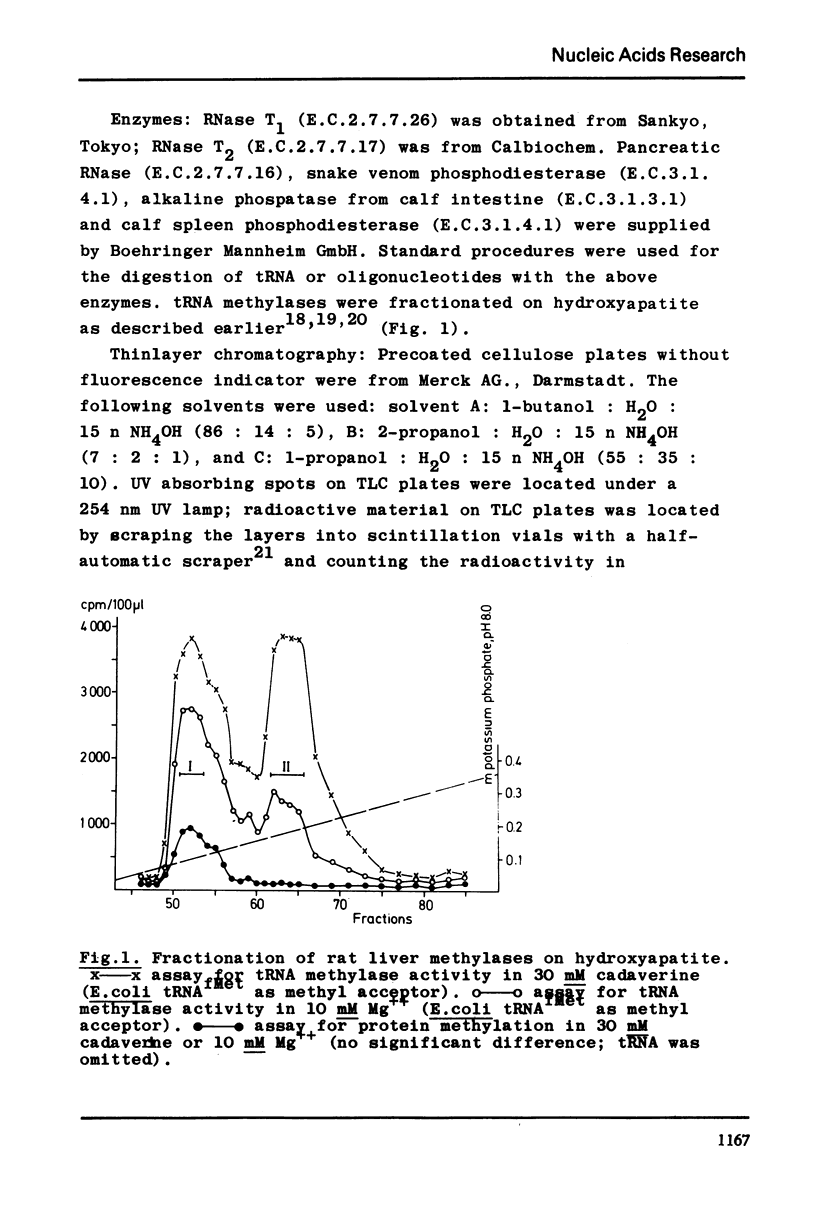
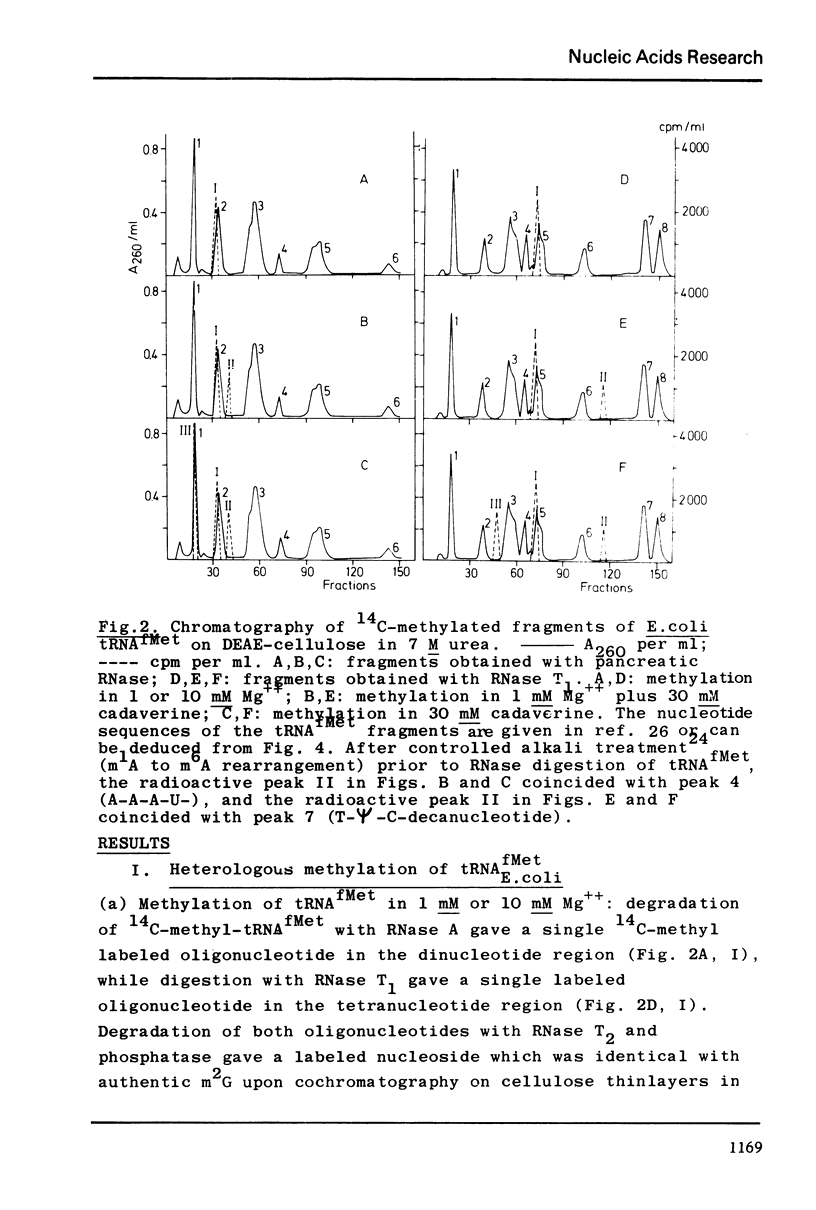
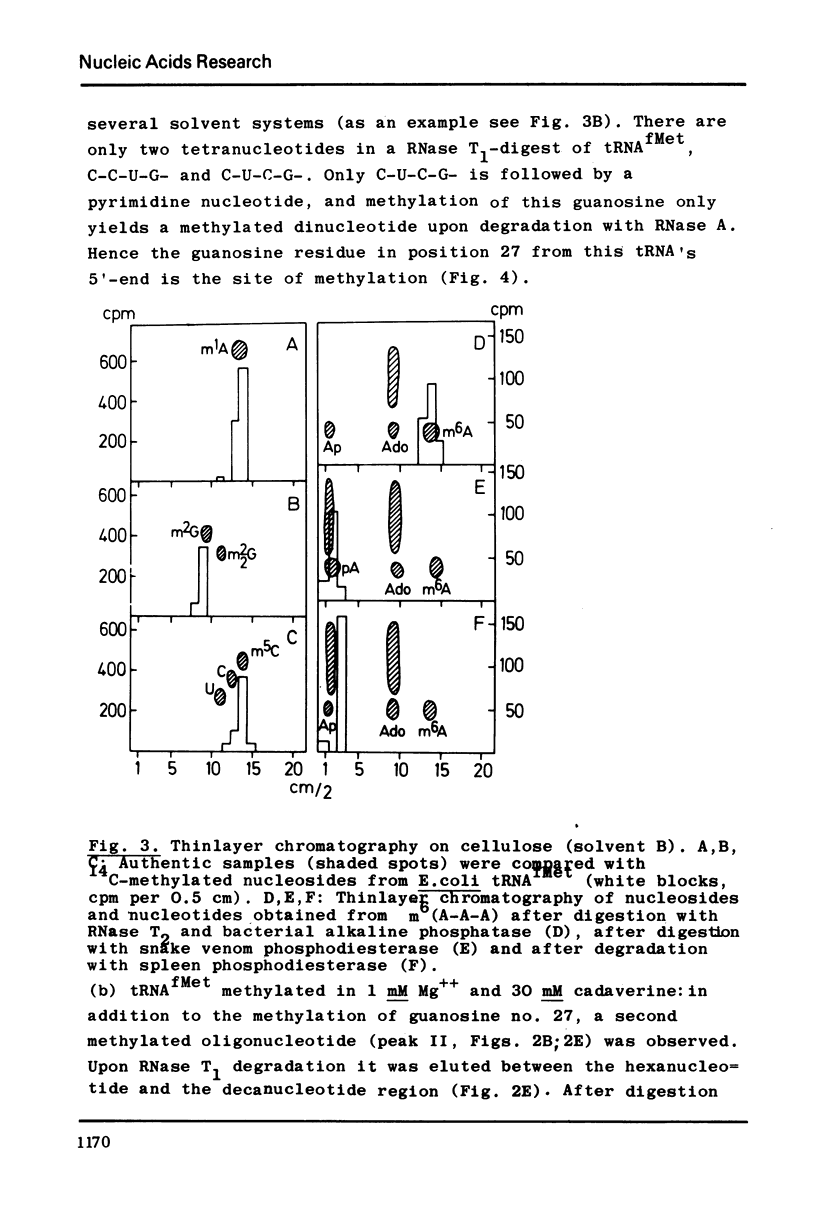
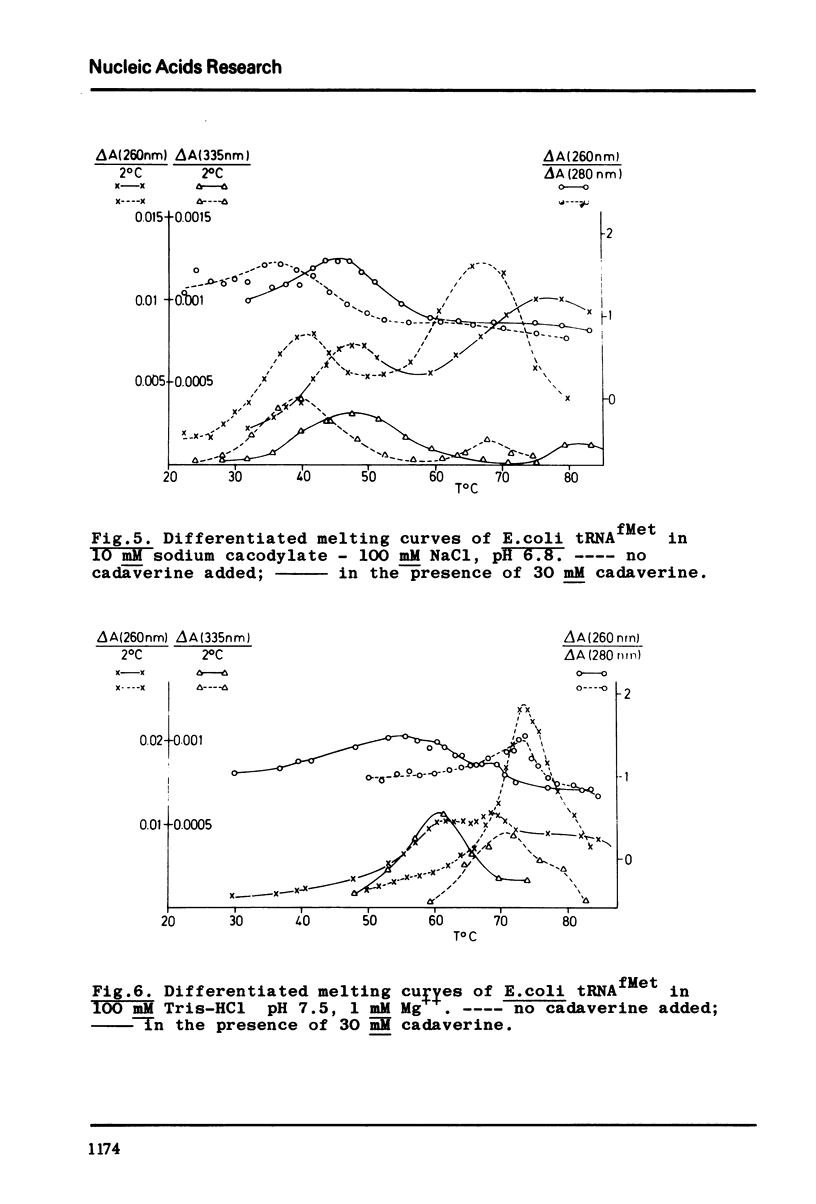
A partially purified tRNA methylase fraction from rat liver, containing m2G- m1A- and m5C-methylase, was used to study the influence of Mg++ and of the biogenic polyamine cadaverine on the enzymatic methylation of E.coli tRNAfMetin vitro. In presence of 1 or 10 mM Mg++, guanosine no. 27 was methylated to m2G. In 1 mM Mg++ plus 30 mM cadaverine, guanosine in position 27 and adenosine in position 59 were methylated. In presence of 30 mM cadaverine alone tRNAfMet accepted three methyl groups: in addition to guanosine no. 27 and adenosine no. 59 cytidine no. 49 was methylated. In order to correlate tRNAfMet tertiary structure changes with the methylation patterns, differentiated melting curves of tRNAfMet were measured under the methylation conditions. It was shown that the thermodynamic stability of tRNAfMet tertiary structure is different in presence of Mg++, or Mg++ plus cadaverine, or cadaverine alone. From the differentiated melting curves and from the methylation experiments one can conclude that at 37° in the presence of Mg++ tRNAfMet has a compact structure with the extra loop and the TψC-loop protected by tertiary structure interactions. In Mg++ plus cadaverine, the TψC-loop is available, while the extra loop is yet engaged in teritary structure (G-15: C-49) interactions. In cadaverine alone, the TψC-loop and the extra loop are free; hence under these conditions the open tRNAfMet clover leaf may be the substrate for methylation. In general, cadaverine destabilizes tRNA tertiary structure in the presence of Mg++, and stabilizes tRNAfMet tertiary structure in the absence of Mg++. This may be explained by a competition of cadaverine with Mg++ for specific binding sites on the tRNA. On the basis of these experiments a possible role of biogenic polyamines in vivo may be discussed: as essential components of procaryotic and eucaryotic ribosomes they may together with ribosomal factors facilitate tRNA-ribosome binding during protein biosynthesis by opening the tRNA tertiary structure, thus making the tRNA's TψC-loop available for interaction with the complementary sequence of the ribosomal 5S RNA.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham K. A. Studies on DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli. 1. The mechanism of polyamine induced stimulation of enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Jun;5(1):143–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baguley B. C., Wehrli W., Staehelin M. In vitro methylation of yeast serine transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1645–1649. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. S., LICHTENSTEIN J. Polyamines and ribosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2112–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore A. R., Brown D. M., Smith J. D. Selective reaction of methoxyamine with cytosine bases in tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 28;59(2):359–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S., Morgan S., Streibel E. The polyamine content of the tRNA of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):669–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P. E., Crothers D. M. Conformational changes of transfer ribonucleic acid. Relaxation kinetics of the early melting transition of methionine transfer ribonucleic acid (Escherichia coli). Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 7;11(23):4368–4374. doi: 10.1021/bi00773a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer F. Three-dimensional structure of tRNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1971;11:391–421. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Marcker K. A., Clark B. F., Cory S. Nucleotide sequence of N-formyl-methionyl-transfer RNA. Nature. 1968 Apr 20;218(5138):232–233. doi: 10.1038/218232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Marcker K. A., Clark B. F., Cory S. The nucleotide sequence of N-formyl-methionyl-transfer RNA. Products of complete digestion with ribonuclease T-1 and pancreatic ribonuclease and derivation of their sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(2):244–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Marcker K. A. The nucleotide sequence of N-formyl-methionyl-transfer RNA. Partial digestion with pancreatic and T-1 ribonuclease and derivation of the total primary structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(2):256–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K. Recognition of tRNA by the ribosome. A possible role of 5 S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1973 Oct 1;36(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley H. W., Rosenheim O., Starling W. W. The Chemical Constitution of Spermine: Structure and Synthesis. Biochem J. 1926;20(5):1082–1094. doi: 10.1042/bj0201082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan B. Z., Weiss J. F., Kelmers A. D. Separation and comparison of primary structures of three formylmethionine tRNAs from E. coli K-12 MO. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):320–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Sprinzl M., Pongs O. The involvement of 5S RNA in the binding of tRNA to ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):942–948. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90785-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam I., Millward S., Blew D., von Tigerstrom M., Wimmer E., Tener G. M. The separation of soluble ribonucleic acids on benzoylated diethylaminoethylcellulose. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3043–3056. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross H. J., Wildenauer D. Enzymatic methylations. I. Isonicotinic acid hydrazide: an inhibitor of tRNA and protein methylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):1215–1220. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90964-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross H. J., Wildenauer D. Enzymatic methylations. II. In vitro inhibition of tRNA and protein methylation by nicotinamide and isonicotinic acid hydrazide: activation of a s-adenosylmethionine-splitting enzyme in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):58–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90343-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt F., Grummt I., Gross H. J., Sprinzl M., Richter D., Erdmann V. A. Effects of T psi CG on the enzymatic binding of eukaryotic and prokaryotic initiator tRNAs to rat liver ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 15;42(1):15–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Thiebe R., Zachau H. G. Preparation and characterization of fragments from yeast tRNA phe . Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):132–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Takeda Y. Polyamines and protein synthesis. VI. Role of spermine in aminoacyl-tRNA formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 16;213(1):240–243. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. H., Quigley G. J., Suddath F. L., McPherson A., Sneden D., Kim J. J., Weinzierl J., Rich A. Three-dimensional structure of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA: folding of the polynucleotide chain. Science. 1973 Jan 19;179(4070):285–288. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4070.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino Y., Nishimura S. Nucleotide sequence specificities of guanylate residue-specific tRNA methylases from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):306–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino Y., Seno T., Nishimura S. Fragmented E. coli methionine tRNA f as methyl acceptor for rat liver tRNA methylase: alteration of the site of methylation by the conformational change of tRNA structure resulting from fragmentation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):476–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90638-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWLEY P. D., BROOKES P. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE ALKYLATION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS AND THEIR CONSTITUENT NUCLEOTIDES. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:127–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0890127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leboy P. S. Influence of polyamines and salts on changing patterns of tRNA methylation. FEBS Lett. 1971 Aug 1;16(2):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80347-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leboy P. S. Stimulation of soluble ribonucleic acid methylase activity by polyamines. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1577–1584. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. Detailed molecular model for transfer ribonucleic acid. Nature. 1969 Nov 22;224(5221):759–763. doi: 10.1038/224759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura S., Harada F., Narushima U., Seno T. Purification of methionine-, valine-, phenylalanine- and tyrosine-specific tRNA from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):133–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofengand J., Henes C. The function of pseudouridylic acid in transfer ribonucleic acid. II. Inhibition of amino acyl transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complex formation by ribothymidylyl-pseudouridylyl-cytidylyl-guanosine 3'-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6241–6253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E. Specificity of transfer ribonucleic acid methylases from normal mouse colon and 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon tumours. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):40P–40P. doi: 10.1042/bj1290040p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E. The effects of diamines and polyamines on enzymic methylation of nucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 8;232(4):630–642. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90755-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipps G. R. Analysis of purified tRNA species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):345–357. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. W., Clark B. F. Primary structure of a mouse myeloma cell initiator transfer RNA. Nature. 1974 Feb 22;247(5442):516–518. doi: 10.1038/247516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesner D., Maass G., Thiebe R., Philippsen P., Zachau H. G. The conformational transitions in yeast tRNAPhe as studied with tRNAPhe fragments. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):76–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz U., Lührmann R., Gassen H. G. On the mRNA induced conformational change of AA-tRNA exposing the T-pse-C-G sequence for binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90677-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno T., Kobayashi M., Nishimura S. Recovery of transfer RNA functions by combining fragmented Escherichia coli formylmethionine transfer RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 22;190(2):285–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheid B., Nelson J. H., Jr Transfer RNA methylase activity and polyamine concentrations in regenerating rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 28;324(1):69–71. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shershneva L. P., Venkstern T. V., Bayev A. A. A study of tRNA methylase action. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 15;29(2):132–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shershneva L. P., Venkstern T. V., Bayev A. A. Acceptor activity of hypermethylated E. coli tRNAf-Met. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Feb;1(2):235–243. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simsek M., RajBhandary U. L., Boisnard M., Petrissant G. Nucleotide sequence of rabbit liver and sheep mammary gland cytoplasmic initiatory transfer RNAs. Nature. 1974 Feb 22;247(5442):518–520. doi: 10.1038/247518a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suddath F. L., Quigley G. J., McPherson A., Sneden D., Kim J. J., Kim S. H., Rich A. Three-dimensional structure of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA at 3.0angstroms resolution. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):20–24. doi: 10.1038/248020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Igarashi K. Polyamines and protein synthesis. IV. Stimulation of aminoacyl transfer RNA formation by polyamines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Dec 4;37(6):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Tanaka K. Effect of polyamines on the binding of dihydrostreptomycin and N-acetylphenylalanyl-tRNA to ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 17;40(2):423–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnock G., Birch B. Binding of putrescine and spermidine to ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Mar 15;33(3):467–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C., Baller J., Doty P. Complementary oligonucleotide binding to the anticodon loop of fMet-transfer RNA. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):508–510. doi: 10.1038/225508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanke C., Römer R., Maass G. The binding of ethidium bromide to different conformations of tRNA. Unfolding of tertiary structure. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Mar 15;33(3):511–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uziel M., Cohn W. E. Desalting of nucleotides by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 15;103(3):539–541. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFELD P. R. A method for the determination of nucleotide sequence in polyribonucleotides. Biochem J. 1954 Nov;58(3):390–396. doi: 10.1042/bj0580390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. V., Srinivasan P. R. The effect of polyamines on the methylation of Escherichia coli methyl-deficient transfer RNA by their homologous methylases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 27;238(3):447–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90619-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZILLIG W., KRONE W., ALBERS M. [Investigations on the biosynthesis of proteins. III. Contribution to the knowledge of the composition and structure of ribonucleoprotein particles]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1959;317:131–143. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1959.317.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



