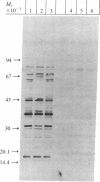
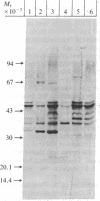
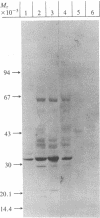
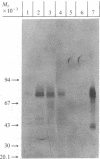
Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-genome-negative human lymphoma lines, Ramos and BJAB, can be converted by EBV in vitro into EBV-genome-positive virus nonproducer lines. These cell lines have been used to identify surface antigens unique to EBV, with the expectation that such determinants might be related to the antigenic target responsible for EBV-specific immunosurveillance. Antisera prepared in rabbits immunized with either whole cells or purified plasma membranes were used in immunoblot experiments to analyze antigenic differences resulting from expression of the resident EBV genome. Unexpectedly, an increase in polypeptides of 32 and 70 kilodaltons was consistently observed in the EBV-converted Ramos lines. In contrast, these antigens were not expressed in BJAB or in its EBV-converted lines. These data suggested that p32 and gp70 might be murine leukemia virus (MuLV)-coded antigens because Ramos, but not BJAB, had been passaged in athymic nude mice during establishment of this cell line. This conclusion was confirmed by using antisera specific for MuLV p30 and gp70. Retroviral antigens were expressed constitutively at low levels in Ramos. Quantitative immunoblotting showed that EBV conversion of Ramos amplified the expression of MuLV proteins 3- to 5-fold. The molecular mechanism responsible for the enhanced expression is unknown. The biological relevance of this phenomenon is also not clear, but the interaction between a DNA and a RNA tumor virus in a Burkitt lymphoma line that carries both viruses may have important biological consequences in relation to retrovirus latency and tumor induction. These results also show that caution must be used when ascribing "uniqueness" to EBV-determined antigens, particularly in the Ramos lines. This warning extends also to the use of Ramos cell lines as immunogens, because immunization of rabbits elicited antibodies that recognized proteins of the same size as the retroviral antigens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson-Anvret M., Lindahl T. Integrated viral DNA sequences in Epstein-Barr virus-converted human lymphoma lines. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):710–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.710-718.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson M., Lindahl T. Epstein-Barr virus DNA in human lymphoid cell lines: in vitro conversion. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsma J., Miller G. Nucleic acid spot hybridization: rapid quantitative screening of lymphoid cell lines for Epstein-Barr viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6851–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., Kieff E. Long internal direct repeat in Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):286–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.286-294.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Beisel C., Hummel M., King W., Fennewald S., Cheung A., Heller M., Raab-Traub N., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (B95-8) DNA VII: molecular cloning and detailed mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eva A., Robbins K. C., Andersen P. R., Srinivasan A., Tronick S. R., Reddy E. P., Ellmore N. W., Galen A. T., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Cellular genes analogous to retroviral onc genes are transcribed in human tumour cells. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):116–119. doi: 10.1038/295116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Merkt B., Bornkamm G. W., Hausen H. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus originating from P3HR-1 cells. I. Studies on EBNA induction. Int J Cancer. 1977 Mar 15;19(3):317–323. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Ho H. C., Burtin P., Cachin Y., Clifford P., de Schryver A., de-Thé G., Diehl V., Klein G. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, other head and neck neoplasms, and control groups. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Jan;44(1):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jett M., Seed T. M., Jamieson G. A. Isolation and characterization of plasma membranes and intact nuclei from lymphoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2134–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Manneborg A., Steinitz M. Differences in EBV receptor concentration between in vitro EBV-converted lymphoma sublines reflect biological differences between the converting viral substrains. Int J Cancer. 1979 Feb;23(2):197–200. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Purtilo D. Summary: symposium on Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoproliferative diseases in immunodeficient patients. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4302–4304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz H., Pedersen N., Higgins J., Hübscher U., Troy F. A., Theilen G. H. Humoral immune reactivity to feline leukemia virus and associated antigens in cats naturally infected with feline leukemia virus. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3642–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G., Clements G. Establishment and characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBC)-negative lymphoblastoid B cell line (BJA-B) from an exceptional, EBV-genome-negative African Burkitt's lymphoma. Biomedicine. 1975 Jul;22(4):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moar M. H., Siegert W., Klein G. Autoradiographic detection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated early antigen in a variety of EBV DNA-containing lymphoblastoid cell lines previously designated as nonproducers. Intervirology. 1978;9(6):333–343. doi: 10.1159/000148955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz M., Klein G. Further studies on the differences in serum dependence in EBV negative lymphoma lines and their in vitro EBV converted, virus-genome carrying sublines. Eur J Cancer. 1977 Nov;13(11):1269–1275. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(77)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., Fenyö E. M., Klein G. Moloney leukemia virus-induced cell surface antigen: detection and characterization in sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5270–5274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Goddard J. G., Berns A., Verma I. M. Structure of Moloney murine leukemia viral DNA: nucleotide sequence of the 5' long terminal repeat and adjacent cellular sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M. Enhancing elements for activation of eukaryotic promoters. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):17–18. doi: 10.1038/297017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]