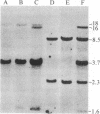
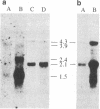
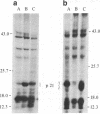
Abstract
By inducing mouse thymomas with carcinogens and gamma-radiation, we have studied the potential of tumor DNA to induce foci in rodent fibroblasts. A high percentage of the tumors used transformed the cultured cells, and the oncogenic phenotype segregated with extra copies of the c-ras gene family. There appears to be selectivity in the activated gene because so far all analyzed tumors induced by carcinogen have activated the N-ras gene, and those induced by radiation have activated the K-ras gene. The K-ras gene is the cellular counterpart of the viral ras oncogene in Kirsten murine sarcoma virus, but the N-ras has not yet been found in a retrovirus. The transformed cells have a marked increase in expression of the oncogene at the RNA and protein level. This model system might be a powerful tool in the study of leukemogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball J. K., McCarter J. A. Repeated demonstration of a mouse leukemia virus after treatment with chemical carcinogens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Apr;46(4):751–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balmain A., Pragnell I. B. Mouse skin carcinomas induced in vivo by chemical carcinogens have a transforming Harvey-ras oncogene. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):72–74. doi: 10.1038/303072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. M. Cellular transforming genes. Science. 1982 Aug 27;217(4562):801–806. doi: 10.1126/science.6285471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. M., Neiman P. E. Transforming genes of neoplasms induced by avian lymphoid leukosis viruses. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):656–659. doi: 10.1038/287656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. M., Okenquist S., Silverman L. Transforming activity of DNA of chemically transformed and normal cells. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):418–421. doi: 10.1038/284418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Pellicer A., Axel R., Meselson M. Integration, transcription, and control of a Drosophila heat shock gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duran-Reynals M. L., Cook C. Resistance to skin tumorigenesis by 3-methylcholanthrene in mice susceptible to leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Mar;52(3):1001–1003. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.3.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A., Marshall C. J., Spurr N. K., Weiss R. A. Identification of transforming gene in two human sarcoma cell lines as a new member of the ras gene family located on chromosome 1. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):396–400. doi: 10.1038/303396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran-Ghera N. Relationship between tumour cell and host in chemical leukaemogenesis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 21;246(151):84–86. doi: 10.1038/newbio246084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi V. V., Frei J. V. Effects of dose and schedule of methylnitrosourea on incidence of malignant lymphoma in adult female mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Aug;45(2):335–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S. On the natural history of the murine leukemias: presidential address. Cancer Res. 1967 Aug;27(8):1325–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krontiris T. G., Cooper G. M. Transforming activity of human tumor DNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1181–1184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. A., Sainten A., Cooper G. M. Activation of related transforming genes in mouse and human mammary carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5185–5189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meruelo D., Offer M., Flieger N. Genetics of susceptibility for radiation-induced leukemia. Mapping of genes involved to chromosomes 1, 2, and 4, and implications for a viral etiology in the disease. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1201–1211. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naparstek Y., Holoshitz J., Eisenstein S., Reshef T., Rappaport S., Chemke J., Ben-Nun A., Cohen I. R. Effector T lymphocyte line cells migrate to the thymus and persist there. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):262–264. doi: 10.1038/300262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Tabin C. J., Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Human EJ bladder carcinoma oncogene is homologue of Harvey sarcoma virus ras gene. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):474–478. doi: 10.1038/297474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer A., Robins D., Wold B., Sweet R., Jackson J., Lowy I., Roberts J. M., Sim G. K., Silverstein S., Axel R. Altering genotype and phenotype by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1414–1422. doi: 10.1126/science.7414320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Goldfarb M., Shimizu K., Lama C., Fogh J., Wigler M. Human-tumor-derived cell lines contain common and different transforming genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90388-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulciani S., Santos E., Lauver A. V., Long L. K., Aaronson S. A., Barbacid M. Oncogenes in solid human tumours. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):539–542. doi: 10.1038/300539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulciani S., Santos E., Lauver A. V., Long L. K., Robbins K. C., Barbacid M. Oncogenes in human tumor cell lines: molecular cloning of a transforming gene from human bladder carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2845–2849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Reynolds R. K., Santos E., Barbacid M. A point mutation is responsible for the acquisition of transforming properties by the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):149–152. doi: 10.1038/300149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A., Pulciani S., Barbacid M. T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene is an activated form of the normal human homologue of BALB- and Harvey-MSV transforming genes. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):343–347. doi: 10.1038/298343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Padhy L. C., Murray M., Weinberg R. A. Transforming genes of carcinomas and neuroblastomas introduced into mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1981 Mar 19;290(5803):261–264. doi: 10.1038/290261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Shilo B. Z., Goldfarb M. P., Dannenberg A., Weinberg R. A. Passage of phenotypes of chemically transformed cells via transfection of DNA and chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5714–5718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Goldfarb M., Perucho M., Wigler M. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the transforming gene of a human neuroblastoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):383–387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Bradley S. M., Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A., Papageorge A. G., Scolnick E. M., Dhar R., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):143–149. doi: 10.1038/300143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C. Normal rat cell lines deficient in nuclear thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]