Abstract
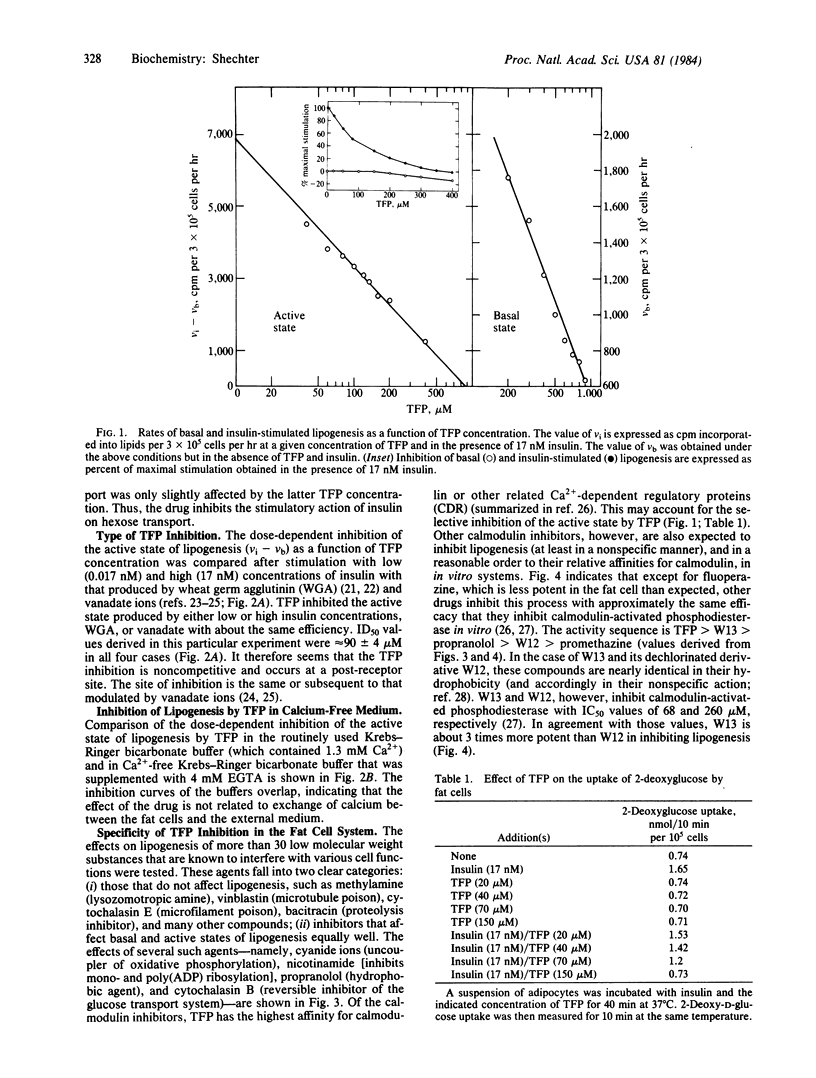
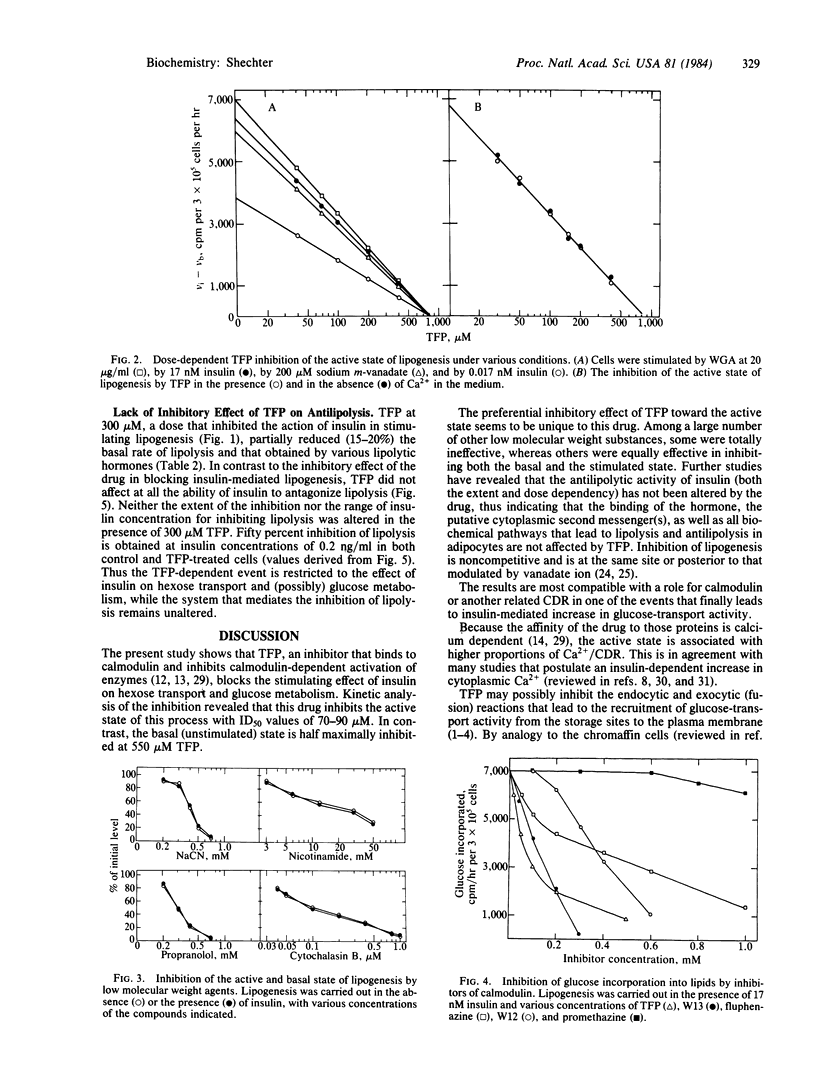
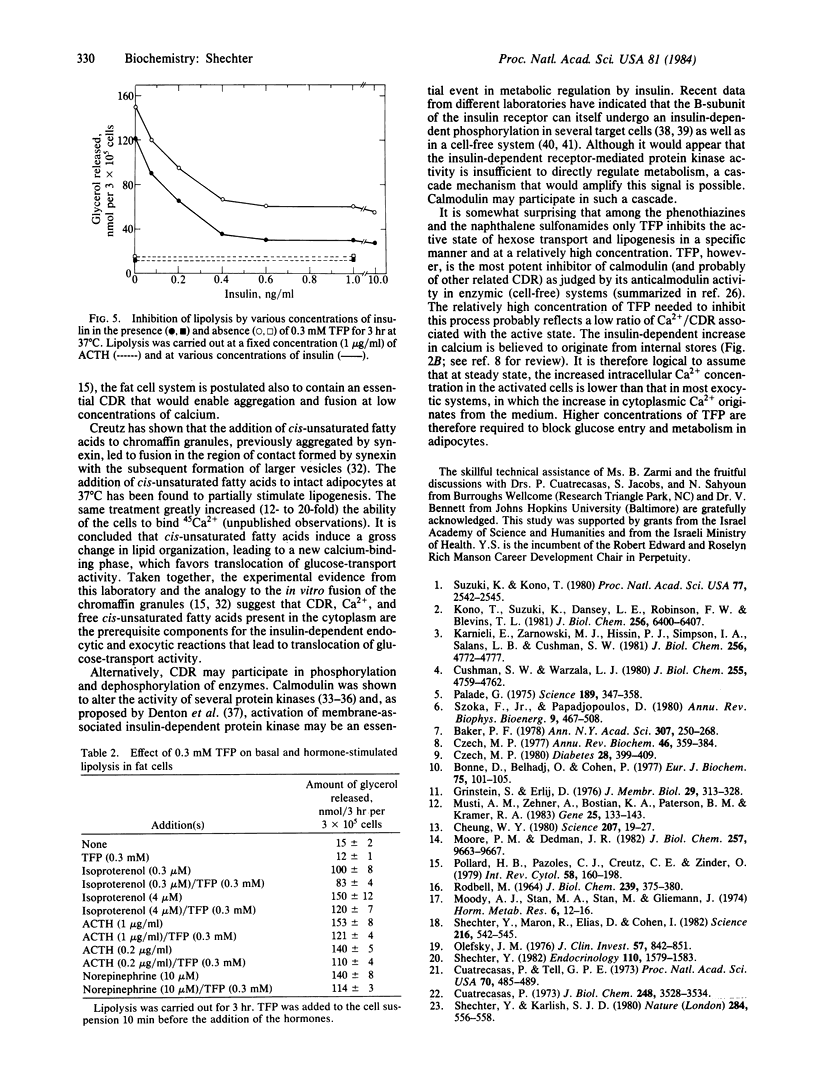
One of the specific inhibitors of calmodulin action, trifluoperazine, blocked the stimulating action of insulin on 2-deoxyglucose uptake and glucose metabolism. The inhibitory effect of insulin on lipolysis was not altered by the drug. The active (insulin-stimulated) state and the basal state of lipogenesis were inhibited half-maximally at 80 and 550 microM trifluoperazine, respectively. 2-Deoxyglucose uptake was inhibited half-maximally at a trifluoperazine concentration of 70 microM. Other less potent calmodulin inhibitors also inhibited glucose metabolism in fat cells but in a nonspecific manner. The inhibition was noncompetitive and was not altered in Ca2+- free medium. The stimulating activity of wheat germ agglutinin and of sodium vanadate were also inhibited by trifluoperazine. The dose-dependent inhibitions were indistinguishable whether the active (stimulated) state was produced by insulin, wheat germ agglutinin, or vanadate. The data indicate that a late event in the sequence that ultimately leads to enhanced glucose transport activity in fat cells is specifically inhibited by trifluoperazine. The possible involvement of calmodulin or another related Ca2+-dependent regulatory protein in the exocytic (fusion) reaction that recruits glucose-transport activity from storage sites to the plasma membranes is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F. The regulation of intracellular calcium in giant axons of Loligo and Myxicola. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:250–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne D., Belhadj O., Cohen P. Modulation by calcium of the insulin action and of the insulin-like effect of ocytocin on isolated rat lipocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):101–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Elbrink J., Martin B. R. Insulin controlling calcium distribution in muscle and fat cells. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1974;191:137–143. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.077s0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. cis-Unsaturated fatty acids induce the fusion of chromaffin granules aggregated by synexin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):247–256. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin with the insulin receptor of fat cells and liver. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3528–3534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Tell G. P. Insulin-like activity of concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin--direct interactions with insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Insulin action and the regulation of hexose transport. Diabetes. 1980 May;29(5):399–409. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.5.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Molecular basis of insulin action. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:359–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degani H., Gochin M., Karlish S. J., Shechter Y. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies and insulin-like effects of vanadium in rat adipocytes. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5795–5799. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Brownsey R. W., Belsham G. J. A partial view of the mechanism of insulin action. Diabetologia. 1981 Oct;21(4):347–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00252681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., Kleinzeller A. The insulin-mimetic effects of vanadate in isolated rat adipocytes. Dissociation from effects of vanadate as a (Na+-K+)ATPase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5306–5312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Erlij D. Action of insulin and cell calcium: effect of ionophore A23187. J Membr Biol. 1976 Nov 29;29(4):313–328. doi: 10.1007/BF01868968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. C., Bates M. D., Cormier M. J., Rosen G. M., Conn P. M. Synthesis and characterization of calmodulin antagonistic drugs. Methods Enzymol. 1983;102:195–204. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)02020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blith D. L., Karlsson F. A., Häring H. U., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulation of phosphorylation of the beta subunit of the insulin receptor. Formation of both phosphoserine and phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9891–9894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blithe D. L., Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):667–669. doi: 10.1038/298667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Suzuki K., Dansey L. E., Robinson F. W., Blevins T. L. Energy-dependent and protein synthesis-independent recycling of the insulin-sensitive glucose transport mechanism in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6400–6407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin R. M., Weiss B. Binding of trifluoperazine to the calcium-dependent activator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;13(4):690–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody A. J., Stan M. A., Stan M., Gliemann J. A simple free fat cell bioassay for insulin. Horm Metab Res. 1974 Jan;6(1):12–16. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Dedman J. R. Calcium-dependent protein binding to phenothiazine columns. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9663–9667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musti A. M., Zehner Z., Bostian K. A., Paterson B. M., Kramer R. A. Transcriptional mapping of two yeast genes coding for glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase isolated by sequence homology with the chicken gene. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson G. A., Andrews M. L., Karnovsky M. J. Control of erythrocyte shape by calmodulin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):730–735. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. The effects of spontaneous obesity on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation of isolated rat adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):842–851. doi: 10.1172/JCI108360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H., Greengard P. Ca2+-dependent protein phosphorylation system in membranes from various tissues, and its activation by "calcium-dependent regulator". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5432–5436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H., Greengard P. Stimulation of brain membrane protein phosphorylation by calcium and an endogenous heat-stable protein. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):478–479. doi: 10.1038/271478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y. Evaluation of adenosine or related nucleosides as physiological regulators of lipolysis in adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1982 May;110(5):1579–1583. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-5-1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Karlish S. J. Insulin-like stimulation of glucose oxidation in rat adipocytes by vanadyl (IV) ions. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):556–558. doi: 10.1038/284556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Maron R., Elias D., Cohen I. R. Autoantibodies to insulin receptor spontaneously develop as anti-idiotypes in mice immunized with insulin. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.7041258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Comparative properties and methods of preparation of lipid vesicles (liposomes). Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:467–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Ohmura T., Hidaka H. Hydrophobic interaction of the Ca2+-calmodulin complex with calmodulin antagonists. Naphthalenesulfonamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Kowalski A. Phosphorylation of the hepatic insulin receptor: stimulating effect of insulin on intact cells and in a cell-free system. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 5;143(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman D. M., Singh T. J., Wang J. H. The modulator-dependent protein kinase. A multifunctional protein kinase activatable by the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein of the cyclic nucleotide system. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3387–3390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Yazawa M., Kakiuchi S., Ohshima M., Uenishi K. Identification of an activator protein for myosin light chain kinase as the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1338–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



