Abstract
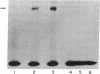
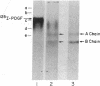
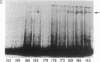
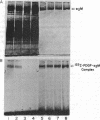
Attempts to measure the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) in human plasma resulted in the discovery of a specific plasma binding protein. The 125I-labeled PDGF (125I-PDGF)-plasma binding protein complex retained mitogenic activity but lost reactivity against rabbit anti-PDGF antiserum. Copurification of the plasma binding protein and alpha 2-macroglobulin (alpha 2M) in human plasma, the formation of a complex between 125I-PDGF and purified alpha 2M, and the comigration of the 125I-PDGF-plasma binding protein complex and the 125I-PDGF-alpha 2M complex in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and in pore-limiting polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis strongly suggested that alpha 2M is the plasma binding protein for 125I-PDGF. Immunoprecipitation of 125I-PDGF-alpha 2M and 125I-PDGF-plasma binding protein complexes by anti-human alpha 2M antiserum further established that alpha 2M and the plasma binding protein are the same molecule. Approximately 20% of 125I-PDGF is complexed by alpha 2M; further 125I-PDGF is complexed if the remaining 125I-PDGF is incubated with additional alpha 2M. Complex formation of 125I-PDGF with plasma or with alpha 2M was completely inhibited by 0.2 mM p-chloromercuric benzoate or 0.2 mM N-ethylmaleimide. The 125I-PDGF-alpha 2M complex or 125I-PDGF-plasma binding protein complex was not dissociated by 8 M urea, 1 M acetic acid, 0.1 M NaOH, or 1% NaDodSO4 but was dissociated by 2-mercaptoethanol, suggesting that the covalent binding of 125I-PDGF to alpha 2M occurs through a disulfide/sulfhydryl exchange reaction. The 125I-PDGF-alpha 2M complex (780,000 daltons) appears to contain two molecules of 125I-PDGF and two dimers of alpha 2M. The precise physiological role of the 125I-PDGF-alpha 2M interaction is unknown. alpha 2M may serve to limit PDGF released locally at sites of blood vessel injury. Alternatively, because of the nearly complete homology between the partial amino acid sequence of PDGF and the predicted amino acid sequence of the transforming protein of the simian sarcoma virus, p28sis, alpha 2M may play an important role in limiting the activity of a PDGF-like activity expressed by virus-transformed cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J. Alpha 2-macroglobulin. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):737–754. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comens P. G., Simmer R. L., Baker J. B. Direct linkage of 125I-EGF to cell surface receptors. A useful artifact of chloramine-T treatment. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):42–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Proffitt R. T., Baenziger J. U., Chang D., Kennedy B. B. Human platelet-derived growth factor. Purification and resolution into two active protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8896–8899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Senior R. M., Huang J. S., Griffin G. L. Chemotaxis of monocytes and neutrophils to platelet-derived growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):1046–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI110509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Devare S. G., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A., Antoniades H. N. Simian sarcoma virus onc gene, v-sis, is derived from the gene (or genes) encoding a platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.6304883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Seppä H. E., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R. Attachment of smooth muscle cells to collagen and their migration toward platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3669–3672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Human alpha2-macroglobulin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:639–652. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B., Vermeulen M., Swenson R. P. The temperature-sensitive bond in human alpha 2-macroglobulin is the alkylamine-reactive site. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3820–3823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Deuel T. F. Human platelet-derived growth factor: radioimmunoassay and discovery of a specific plasma-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):383–388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Kennedy B., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor. Specific binding to target cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8130–8136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Chao F. C., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Platelet alpha granules contain a growth factor for fibroblasts. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1043–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. L., Broekman M. J., Chernoff A., Lesznik G. R., Drillings M. Platelet alpha-granule proteins: studies on release and subcellular localization. Blood. 1979 Apr;53(4):604–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler N., Lipton A. Platelets as a source of fibroblast growth-promoting activity. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Aug;87(2):297–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90484-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Vogel A. The platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G. S., Sayers C. A., Barrett A. J. Further characterization of the covalent linking reaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1981 May 1;195(2):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1950453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Huang J. S., Walz D. A., Deuel T. F. Chemotactic activity of platelet alpha granule proteins for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):382–385. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppä H., Grotendorst G., Seppä S., Schiffmann E., Martin G. R. Platelet-derived growth factor in chemotactic for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):584–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Van den Berghe H. Functional modifications of alpha 2-macroglobulin by primary amines. I. Characterization of alpha 2 M after derivatization by methylamine and by factor XIII. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9016–9022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Scrace G. T., Whittle N., Stroobant P., Johnsson A., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):35–39. doi: 10.1038/304035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Witte L. D., Kaplan K. L., Lages B. A., Chernoff A., Nossel H. L., Goodman D. S., Baumgartner H. R. Heterogeneity in storage pool deficiency: studies on granule-bound substances in 18 patients including variants deficient in alpha-granules, platelet factor 4, beta-thromboglobulin, and platelet-derived growth factor. Blood. 1979 Dec;54(6):1296–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte L. D., Kaplan K. L., Nossel H. L., Lages B. A., Weiss H. J., Goodman D. S. Studies of the release from human platelets of the growth factor for cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1978 Mar;42(3):402–409. doi: 10.1161/01.res.42.3.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]