Abstract
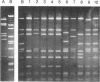
We have developed a new recombinant DNA cloning system to isolate directly the functional unit of the human thymidine kinase (TK) gene. The system utilizes a cosmid vector that can shuttle cloned DNA sequences between bacteria and mammalian cells. A complete human cosmid library was constructed and DNA from the total library was transfected to mouse L cells deficient in TK (LTK-) by calcium phosphate precipitation. The transfected cells were then selected with hypoxanthine/aminopterin/thymidine (HAT) medium, and one HAT-resistant cell clone was isolated. This cell line became resistant to HAT selection by acquiring the TK gene derived from the human cosmid library. As the cosmid vector contains the cohesive ends of the bacteriophage, we could directly retrieve the human DNA sequences from the transformed mouse L cells. Total DNA from the transformed TK+ L cells was packaged in vitro with lysogenic bacterial extracts and used to infect Escherichia coli. One of the two recombinant cosmids isolated contained a 43.8-kilobase human DNA insert and was capable of converting TK- L cells to the TK+ phenotype in both acute and stable transformation assays. Thus, we have isolated the functional human TK gene in this recombinant cosmid. The gene was further localized on a 14.5-kilobase BamHI DNA fragment, and it transcribed a mature mRNA of about 1,500 nucleotides. This method of gene isolation has several special features: (i) an intact structural gene can be cloned directly based on its function without knowledge of its amino acid or nucleotide sequence; (ii) the functional gene sequences can be recovered faster and more efficiently than with the usual DNA transfection method; and (iii) in conjunction with cell-sorting techniques, this method can be used to clone genes encoding cell surface markers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbosa J. A., Kamarck M. E., Biro P. A., Weissman S. M., Ruddle F. H. Identification of human genomic clones coding the major histocompatibility antigens HLA-a2 and HLA-B7 by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6327–6331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw H. D., Jr Molecular cloning and cell cycle-specific regulation of a functional human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5588–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman M. L., Tsui L. C., Buchwald M., Siminovitch L. Introduction and recovery of a selectable bacterial gene from the genome of mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;2(8):966–976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.8.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad S. E., Liu C. P., Botchan M. R. Fragment spanning the SV40 replication origin is the only DNA sequence required in cis for viral excision. Science. 1982 Dec 17;218(4578):1223–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.6293055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Bovine papillomavirus vector that propagates as a plasmid in both mouse and bacterial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4030–4034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Wong E. A., Wahl G., Capecchi M. R. Patterns of integration of DNA microinjected into cultured mammalian cells: evidence for homologous recombination between injected plasmid DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1372–1387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Esty A. C., Bernard H. U., Friedmann T. Isolation of a genomic clone partially encoding human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5038–5041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Dozy A. M. Polymorphism of DNA sequence adjacent to human beta-globin structural gene: relationship to sickle mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5631–5635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavathas P., Herzenberg L. A. Stable transformation of mouse L cells for human membrane T-cell differentiation antigens, HLA and beta 2-microglobulin: selection by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):524–528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo A., Yamamoto F., Furusawa M., Kuroiwa A., Natori S., Obinata M. Structure of thymidine kinase gene introduced into mouse Ltk- cells by a new injection method. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner P. J., Levinson B. B., Goodman H. M. A plasmid that replicates in both mouse and E. coli cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):527–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Kan Y. W. Versatile cosmid vectors for the isolation, expression, and rescue of gene sequences: studies with the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5225–5229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. F., Yamaizumi M., Murphy P. D., Egg A., Ruddle F. H. Partial purification and characterization of the mRNA for human thymidine kinase and hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4290–4294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. F., Zhao S. Y., Ruddle F. H. Genomic cloning and preliminary characterization of the human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6528–6532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy I., Pellicer A., Jackson J. F., Sim G. K., Silverstein S., Axel R. Isolation of transforming DNA: cloning the hamster aprt gene. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):817–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90558-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Warren R., Palmiter R. D. The mouse metallothionein-I gene is transcriptionally regulated by cadmium following transfection into human or mouse cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Lipsich L., Wigler M. Isolation of the chicken thymidine kinase gene by plasmid rescue. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):207–210. doi: 10.1038/285207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Wigler M. Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulciani S., Santos E., Lauver A. V., Long L. K., Robbins K. C., Barbacid M. Oncogenes in human tumor cell lines: molecular cloning of a transforming gene from human bladder carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2845–2849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Transformation and replication in mouse cells of a bovine papillomavirus--pML2 plasmid vector that can be rescued in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Jelinek W. R. The Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1065–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6281889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Harrison P. R., Paul J. Replication and amplification of recombinant plasmid molecules as extra chromosomal elements in transformed mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Mulligan R., Berg P. Expression of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase complementary deoxyribonucleic acid in simian virus 40 vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):854–864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]