Abstract
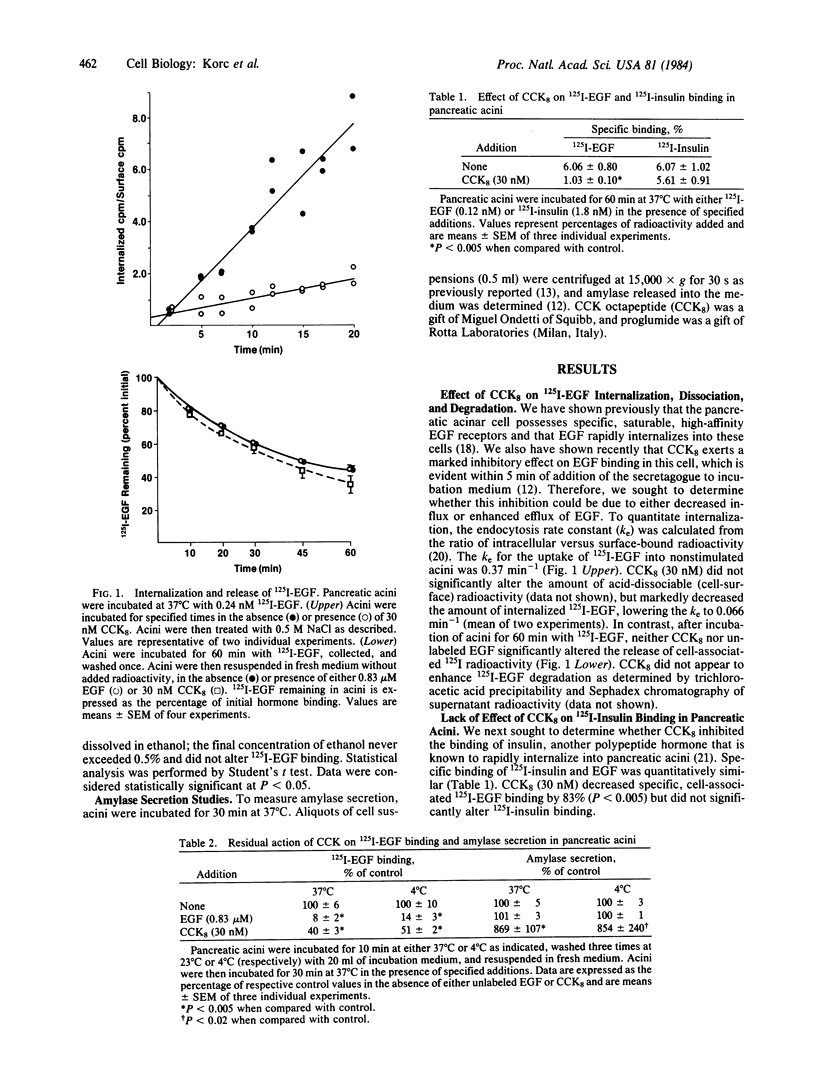
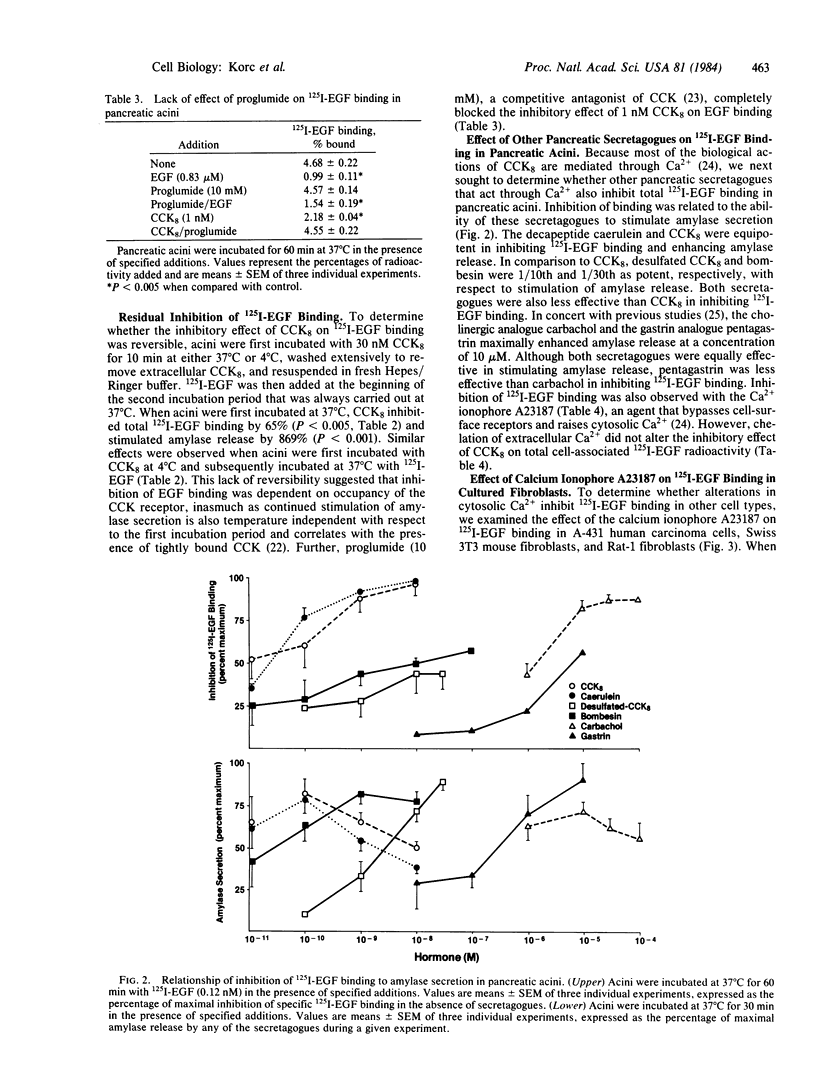
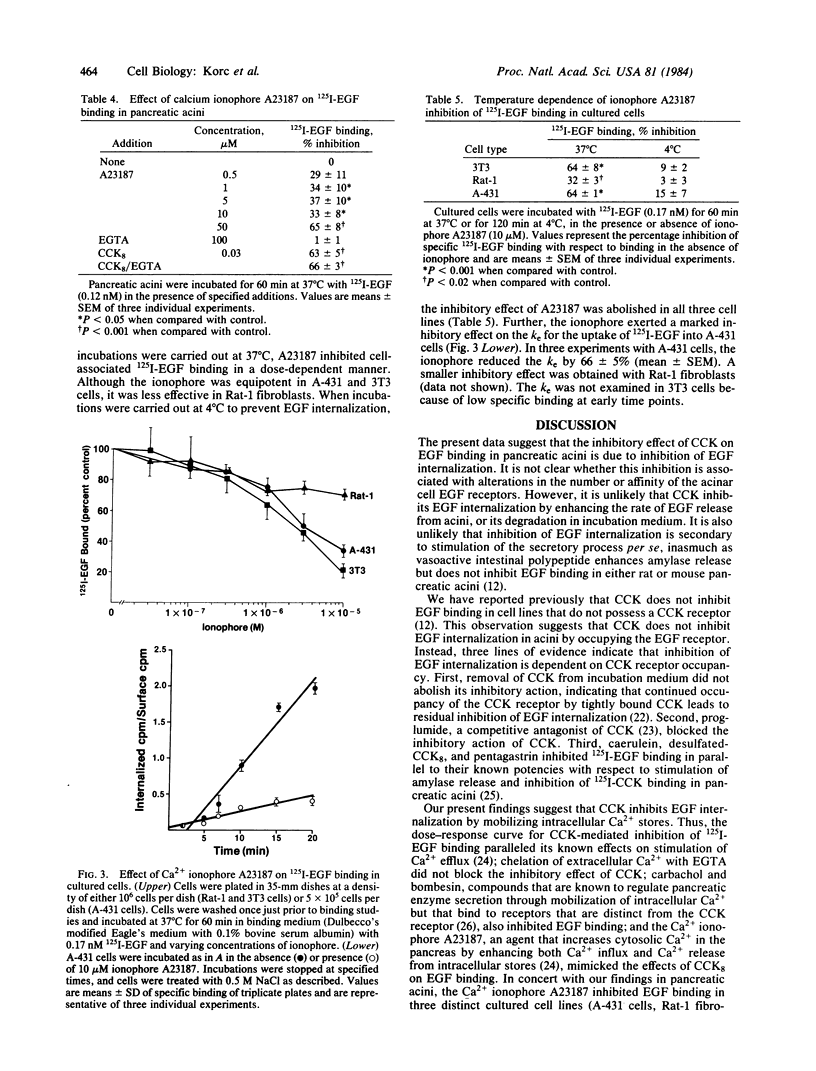
Cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK8), the COOH-terminal moiety of cholecystokinin (CCK), exerted a rapid inhibitory effect on total cell-associated 125I-labeled epidermal growth factor (125I-EGF) binding by decreasing the rate of EGF internalization in isolated rat pancreatic acini. Removal of CCK8 from incubation medium followed by extensive washing of acini did not abolish its inhibitory effect, indicating that its action was not readily reversible. Proglumide, a competitive antagonist of CCK8, blocked the inhibitory action of the secretagogue. Addition of CCK8 to cells previously exposed to 125I-EGF did not enhance the release of cell-associated 125I activity. CCK8 did not inhibit the binding of 125I-labeled insulin to pancreatic acini. Other pancreatic secretagogues that enhance digestive-enzyme release through Ca2+, including caerulein, bombesin, carbachol, gastrin, and the Ca2+ ionophore A23187, also inhibited cell-associated 125I-EGF radioactivity. Further, at 37 degrees C the ionophore A23187 inhibited specific 125I-EGF binding in human A-431 carcinoma cells, Swiss 3T3 cells, and Rat-1 fibroblasts, and this effect was abolished when 125I-EGF internalization was reduced by incubating cells at 4 degrees C. It is concluded that alterations in cellular Ca2+ in the pancreas and other cells lead to inhibition of EGF endocytosis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown K. D., Friedkin M., Rozengurt E. Colchicine inhibits epidermal growth factor degradation in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):480–484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M. Synthesis, intracellular transport and discharge of exportable proteins in the pancreatic acinar cell and other cells. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1978 May;53(2):211–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1978.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. M., Abdelmoumene S., Jensen R. T., Gardner J. D. Cholecystokinin-induced persistent stimulation of enzyme secretion from pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):G459–G465. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.240.6.G459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D. Regulation of pancreatic exocrine function in vitro: initial steps in the actions of secretagogues. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:55–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Kriz B. M., Wong K. Y., Hradek G., Jones A. L., Williams J. A. Insulin action in pancreatic acini from streptozotocin-treated rats. III. Electron microscope autoradiography of 125I-insulin. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):G69–G75. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.240.1.G69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Smith G. J. Binding of insulin to isolated nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahne W. F., Jensen R. T., Lemp G. F., Gardner J. D. Proglumide and benzotript: members of a different class of cholecystokinin receptor antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6304–6308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y., Kaneko Y., Matsuzaki F., Endo Y., Oda T. Teleocidin B inhibits binding of epidermal growth factor to cellular receptors probably by the same mechanism as phorbol esters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 16;97(3):926–931. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91465-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Matrisian L. M., Magun B. E. Direct modulation of epidermal growth factor binding by cholecystokinin. Life Sci. 1983 Aug 8;33(6):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Matrisian L. M., Planck S. R., Magun B. E. Binding of epidermal growth factor in rat pancreatic acini. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):1066–1073. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91408-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M. Regulation of pancreatic protein synthesis by cholecystokinin and calcium. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):G69–G75. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.1.G69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S. Saccharin and cyclamate inhibit binding of epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1042–1046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Pencev D., Vasanthakumar G., Schiffmann E., Pastan I. Inhibitors of endocytosis perturb phospholipid metabolism in rabbit neutrophils and other cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1929–1932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Larsen B. R., Finch J. S., Magun B. E. Further purification of epidermal growth factor by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins W. K., Ferris W. R., Shimizu N. Genetics of receptors for bioactive polypeptides: a variant of Swiss/3T3 fibroblasts resistant to a cytotoxic insulin accumulates lysosome-like vesicles. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;16(1):105–113. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380160110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Willingham M. C. Journey to the center of the cell: role of the receptosome. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):504–509. doi: 10.1126/science.6170111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Brown K. D., Pettican P. Vasopressin inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):716–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Collins M., Brown K. D., Pettican P. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to mouse cultured cells by fibroblast-derived growth factor. Evidence for an indirect mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3680–3686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaran H., Goldfine I. D., Deveney C. W., Wong K. Y., Williams J. A. Binding of cholecystokinin to high affinity receptors on isolated rat pancreatic acini. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1849–1853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Libermann T. A., Lax I., Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Biological role of epidermal growth factor-receptor clustering. Investigation with monoclonal anti-receptor antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):846–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Biologically active phorbol esters specifically alter affinity of epidermal growth factor membrane receptors. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):387–391. doi: 10.1038/279387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., Todaro G. J. Vitamin K3 (menadione) and related quinones, like tumor-promoting phorbol esters, alter the affinity of epidermal growth factor for its membrane receptors. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8735–8739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton W., Leof E., Pledger W. J., O'Keefe E. J. Modulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by platelet-derived growth factor and choleragen: effects on mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5567–5571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. A steady state model for analyzing the cellular binding, internalization and degradation of polypeptide ligands. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A. Regulation of pancreatic acinar cell function by intracellular calcium. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):G269–G279. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.238.4.G269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



