Abstract
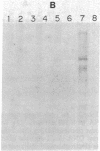
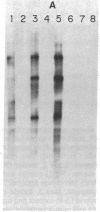
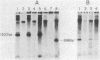
The mechanism of nucleolar dominance was studied in two lines of mouse-human somatic hybrids. Both lines had preferentially lost human chromosomes but had retained significant amounts of both mouse and human ribosomal genes (genes coding for the 18S, 5.8S, and 28S RNAs of ribosomes). However, the human ribosomal genes were repressed, and only mouse ribosomal genes were expressed. Soluble transcription extracts from the hybrids were able to initiate RNA synthesis accurately on a cloned mouse ribosomal gene but were unable to initiate accurately on a human ribosomal gene. This suggests that nucleolar dominance in these hybrids is due to the loss or inactivation of the gene for a specificity factor required to recognize the human ribosomal gene promoter.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busby S. J., Reeder R. H. Fate of amplified nucleoli in Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Jun;91(2):458–467. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S. J., Reeder R. H. Spacer sequences regulate transcription of ribosomal gene plasmids injected into Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90556-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Talavera A., Basilico C., Miller O. J. Suppression of production of mouse 28S ribosomal RNA in mouse-human hybrids segregating mouse chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):694–697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Human ribosomal RNA gene: nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region and comparison of three mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Reeder R. H. Preferential transcription of Xenopus laevis ribosomal RNA in interspecies hybrids between Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Tjian R. In vitro transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):575–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod D., Bird A. DNAase I sensitivity and methylation of active versus inactive rRNA genes in xenopus species hybrids. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Identification of the in vivo and in vitro origin of transcription in human rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3933–3949. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. J., Miller D. A., Dev V. G., Tantravahi R., Croce C. M. Expression of human and suppression of mouse nucleolus organizer activity in mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4531–4535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan G. T., Bakken A. H., Reeder R. H. Transcription of Xenopus borealis rRNA genes in nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):471–477. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., Schibler U., Huebner K., Croce C. M. Selective suppression of the transcription of ribosomal genes in mouse-human hybrid cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Mar;98(3):553–559. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040980313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roan J. G., Dunaway M. Spacer regulation of Xenopus ribosomal gene transcription: competition in oocytes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Baserga R. Reactivation of ribosomal RNA genes in human-mouse hybrid cells by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1566–1569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Dev V. G., Croce C. M., Baserga R. Reactivation of silent rRNA genes by simian virus 40 in human-mouse hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3885–3889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Galanti N., Jonak G. J., McKercher S., Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Baserga R. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: stimulation of cellular DNA synthesis and activation of rRNA genes by mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. K., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of Xenopus ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14375–14383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]