Abstract
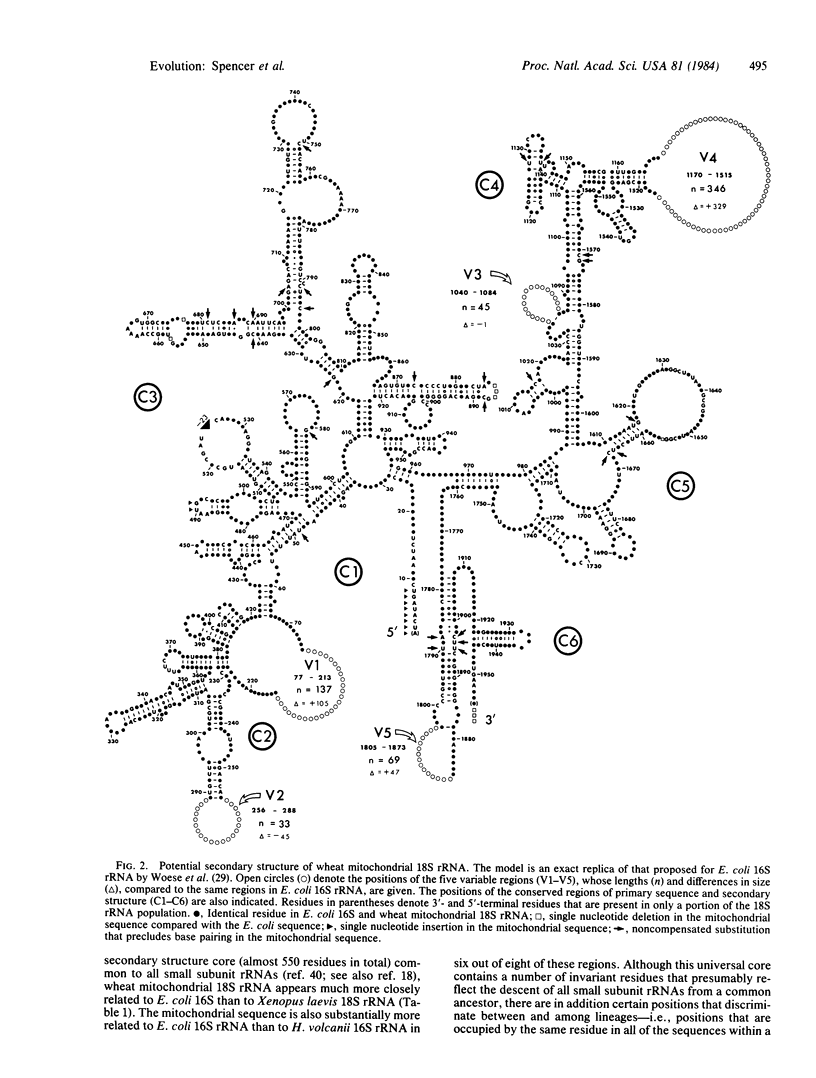
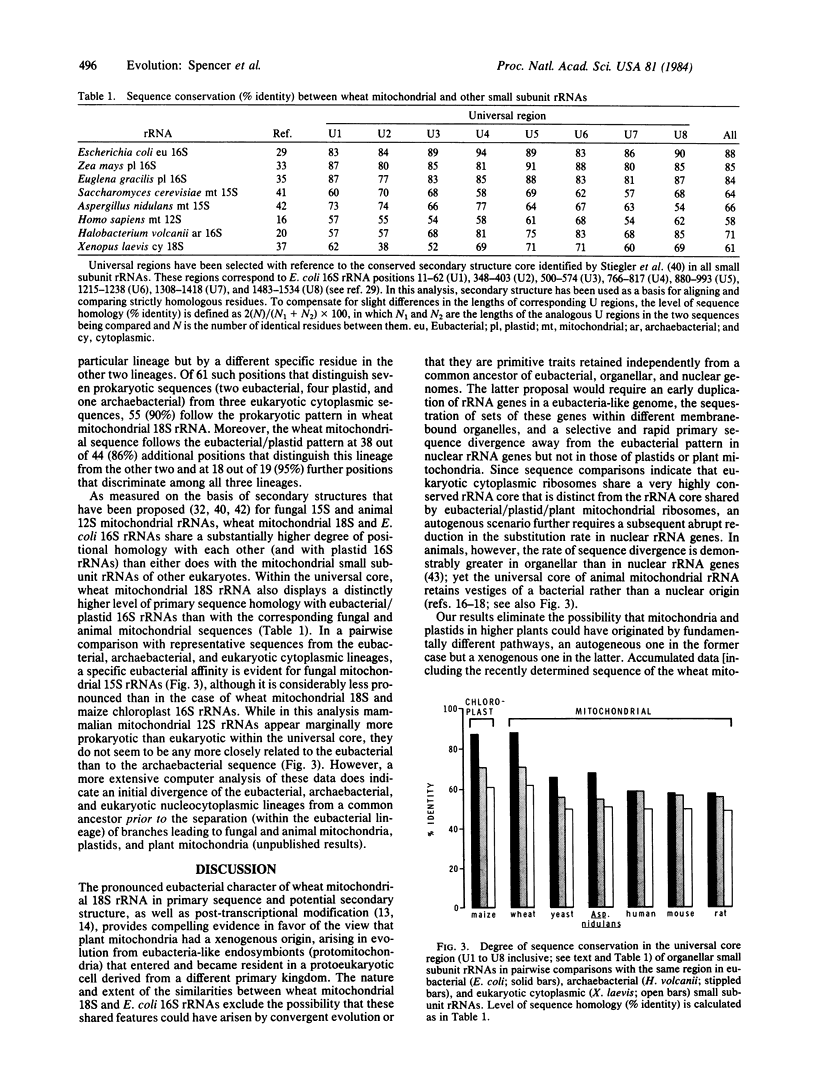
We present here the nucleotide sequence of the small subunit (18S) rRNA gene from wheat mitochondria. Aside from five discrete variable domains, this gene and the analogous (16S) rRNA gene in Escherichia coli show essentially a one-to-one correspondence in their potential secondary structures, with regions accounting for 86% of the bacterial 16S rRNA having a strict secondary structure counterpart in the mitochondrial 18S rRNA. Primary sequence identity between the two rRNAs ranges from 73% to 85% (76% overall) within regions of conserved secondary structure. Within a smaller secondary structure core common to all small subunit rRNAs, the wheat mitochondrial sequence shares substantially more primary sequence identity with the E. coli (eubacterial) sequence (88%) than with the small subunit rRNA sequences of Halobacterium volcanii (an archaebacterium) (71%) or Xenopus laevis cytoplasm (61%). Moreover, the wheat mitochondrial sequence contains a very high proportion of certain lineage-specific residues that distinguish eubacterial/plastid 16S rRNAs from archaebacterial 16S and eukaryotic cytoplasmic 18S rRNAs. These data establish that the ancestry of the wheat mitochondrial 18S rRNA gene can be traced directly and specifically to the eubacterial primary kingdom, and the data provide compelling support for a relatively recent xenogenous (endosymbiotic) origin of plant mitochondria from eubacteria-like organisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibb M. J., Van Etten R. A., Wright C. T., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogorad L. Evolution of organelles and eukaryotic genomes. Science. 1975 May 30;188(4191):891–898. doi: 10.1126/science.1138359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonen L., Cunningham R. S., Gray M. W., Doolittle W. F. Wheat embryo mitochondrial 18S ribosomal RNA: evidence for its prokaryotic nature. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Mar;4(3):663–671. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonen L., Gray M. W. Organization and expression of the mitochondrial genome of plants I. The genes for wheat mitochondrial ribosomal and transfer RNA: evidence for an unusual arrangement. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):319–335. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao S., Sederoff R. R., Levings C. S. Partial Sequence Analysis of the 5S to 18S rRNA Gene Region of the Maize Mitochondrial Genome. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):190–193. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Schwartz R. M. Evidence on the origin of eukaryotic mitochondria from protein and nucleic acid sequences. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;361:92–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb46513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Sequence of the chloroplast 16S rRNA gene and its surrounding regions of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7609–7620. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C., Anderson S., Nierlich D. P. Distinctive sequence of human mitochondrial ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):460–467. doi: 10.1038/286460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf L., Roux E., Stutz E., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of a Euglena gracilis chloroplast gene coding for the 16S rRNA: homologies to E. coli and Zea mays chloroplast 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6369–6381. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Doolittle W. F. Has the endosymbiont hypothesis been proven? Microbiol Rev. 1982 Mar;46(1):1–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.1.1-42.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. Mitochondrial genome diversity and the evolution of mitochondrial DNA. Can J Biochem. 1982 Mar;60(3):157–171. doi: 10.1139/o82-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R., Lanter J. M., Woese C. R. Sequence of the 16S Ribosomal RNA from Halobacterium volcanii, an Archaebacterium. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):656–659. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4611.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köchel H. G., Küntzel H. Mitochondrial L-rRNA from Aspergillus nidulans: potential secondary structure and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4795–4801. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köchel H. G., Küntzel H. Nucleotide sequence of the Aspergillus nidulans mitochondrial gene coding for the small ribosomal subunit RNA: homology to E. coli 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5689–5696. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küntzel H., Köchel H. G. Evolution of rRNA and origin of mitochondria. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):751–755. doi: 10.1038/293751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R. The exon:intron structure of some mitochondrial genes and its relation to mitochondrial evolution. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;82:1–98. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60823-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Hayashida H., Kikuno R., Hasegawa M., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Molecular clock of silent substitution: at least six-fold preponderance of silent changes in mitochondrial genes over those in nuclear genes. J Mol Evol. 1982;19(1):28–35. doi: 10.1007/BF02100221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff R. A., Mahler H. R. The non symbiotic origin of mitochondria. Science. 1972 Aug 18;177(4049):575–582. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4049.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubtsov P. M., Musakhanov M. M., Zakharyev V. M., Krayev A. S., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. I. The complete nucleotide sequence of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5779–5794. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus laevis 18S ribosomal RNA inferred from gene sequence. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):205–208. doi: 10.1038/291205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. 3'-Terminal sequence of wheat mitochondrial 18S ribosomal RNA: further evidence of a eubacterial evolutionary origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3921–3932. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G., Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Guilley H. New rapid gel sequencing method for RNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):833–836. doi: 10.1038/269833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F., Fukuhara H. Séquence nucléotidique du gène de l'ARN ribosomique 15S mitochondrial de la levure. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1980 Dec 8;291(12):933–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. A general secondary-structure model for procaryotic and eucaryotic RNAs from the small ribosomal subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;120(3):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Zuker M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. Structural organization of the 16S ribosomal RNA from E. coli. Topography and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2153–2172. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohdoh N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of 16S ribosomal RNA gene from tobacco chloroplasts. Gene. 1982 Feb;17(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torczynski R., Bollon A. P., Fuke M. The complete nucleotide sequence of the rat 18S ribosomal RNA gene and comparison with the respective yeast and frog genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4879–4890. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzzell T., Spolsky C. Mitochondria and plastids as endosymbionts: a revival of special creation? Am Sci. 1974 May-Jun;62(3):334–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzzell T., Spolsky C. Two data sets: alternative explanations and interpretations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;361:481–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb46540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whatley F. R. The establishment of mitochondria: Paracoccus and Rhodopseudomonas. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;361:330–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb46529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Gupta R., Siegel R. B., Stahl D. A., Kop J., Crawford N., Brosius J., Gutell R., Hogan J. J. Secondary structure model for bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA: phylogenetic, enzymatic and chemical evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2275–2293. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Glotz C., Brimacombe R. Secondary structure comparisons between small subunit ribosomal RNA molecules from six different species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3621–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


