Abstract
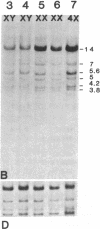
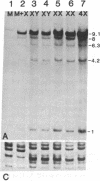
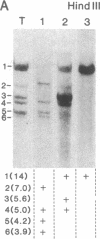
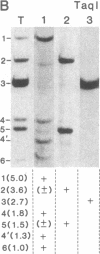
Hemophilia B is an X-linked disease caused by a functional deficiency in coagulation factor IX. A cDNA clone corresponding to factor IX has been used to detect homologous sequences in the human genome. All DNA fragments hybridizing to the probe, under medium- or high-stringency conditions, are X-linked, and the patterns obtained suggest that a single large (greater than or equal to 20 kilobases) gene is detected. The gene has been mapped to the q26-q27 region of the long arm of the X chromosome by hybridization to DNA from a panel of human-mouse hybrid cell lines. A search for restriction fragment length polymorphisms using seven restriction enzymes has led to the detection of a Taq I polymorphism, with allelic frequencies of about 0.71 and 0.29. This genetic marker should be useful for the detection of carriers of the hemophilia B trait and for prenatal diagnosis in informative families and, more generally, for the establishment of a linkage map of the human X chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Kuo M. T., Dretzen G., Chambon P. Differential nuclease sensitivity of the ovalbumin and beta-globin chromatin regions in erythrocytes and oviduct cells of laying hen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2737–2750. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer S. H., Graham J. B. Linkage Between the X Chromosome Loci for Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Electrophoretic Variation and Hemophilia A. Am J Hum Genet. 1965 Jul;17(4):320–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Chinault A. C., Konecki D. S., Melton D. W., Caskey C. T. Cloned cDNA sequences of the hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase gene from a mouse neuroblastoma cell line found to have amplified genomic sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Davis P. D., Graham J. B., Dodds W. J. Expression and linkage of genes for X-linked hemophilias A and B in the dog. Blood. 1973 Apr;41(4):577–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Gould K. G., Rees D. J., Brownlee G. G. Molecular cloning of the gene for human anti-haemophilic factor IX. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):178–180. doi: 10.1038/299178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Cioccio R. A., Voss R., Krim M., Grzeschik K. H., Siniscalco M. Identification of human RNA transcripts among heterogeneous nuclear RNA from man-mouse somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1868–1872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeschik K. H. Assignment of a structural gene for beta-glucuronidase to human chromosome C7. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Sep;2(5):401–410. doi: 10.1007/BF01542721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer A., Levin M., Heilig R., Daegelen D., Kahn A., Mandel J. L. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human skeletal muscle alpha actin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3503–3516. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellkuhl B., Mayr W. R., Grzeschik K. H. Localization of MPI, PKM2, IDHM, and the alpha subunit of hexosaminidase (HEXA) to the q21 leads to qter region of human chromosome 15. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):503–505. doi: 10.1159/000131008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellkuhl B., de la Chapelle A., Grzeschik K. H. Different patterns of X chromosome inactivity in lymphocytes and fibroblasts of a human balanced X;autosome translocation. Hum Genet. 1982;60(2):126–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00569697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hors-Cayla M. C., Junien C., Heuertz S., Mattei J. F., Frézal J. Regional assignment of arylsulfatase A, mitochondrial aconitase and NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase by somatic cell hybridization. Hum Genet. 1981;58(2):140–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00278698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., de la Salle H., Schamber F., Balland A., Kohli V., Findeli A., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. Isolation of a human anti-haemophilic factor IX cDNA clone using a unique 52-base synthetic oligonucleotide probe deduced from the amino acid sequence of bovine factor IX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2325–2335. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama K., Ericsson L. H., Enfield D. L., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Davie E. W., Titani K. Comparison of amino acid sequence of bovine coagulation Factor IX (Christmas Factor) with that of other vitamin K-dependent plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4990–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6461–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Crowder W. E., Nyhan W. L., Caskey C. T. A three-allele restriction-fragment-length polymorphism at the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase locus in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4035–4039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen A. S., McBride O. W., Otey M. C. Isolation of unique sequence human X chromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2419–2428. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai G. S., Sprenkle J. A., Do T. T., Mareni C. E., Migeon B. R. Localization of loci for hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and biochemical evidence of nonrandom X chromosome expression from studies of a human X-autosome translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2810–2813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. H., TRUEMAN R. G. COMBINED HEMOPHILIA AND CHRISTMAS DISEASE. Blood. 1964 Sep;24:281–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seravalli E., DeBona P., Velivasakis M., Pagan-Charry I., Hershberg A., Siniscalco M. Further data on the cytologic mapping of the human X chromosome with man-mouse cell hybrids. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1976;12(7):219–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Sam J., Simmer R. L., Keith D. H., Shively L., Teplitz M., Itakura K., Gartler S. M., Riggs A. D. Isolation of a cDNA clone for human X-linked 3-phosphoglycerate kinase by use of a mixture of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides as a detection probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):802–806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER D. L., COPELAND D. L., GRAHAM J. B. Linkage of color blindness to hemophilias A and B. Am J Hum Genet. 1962 Jun;14:149–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]