Abstract
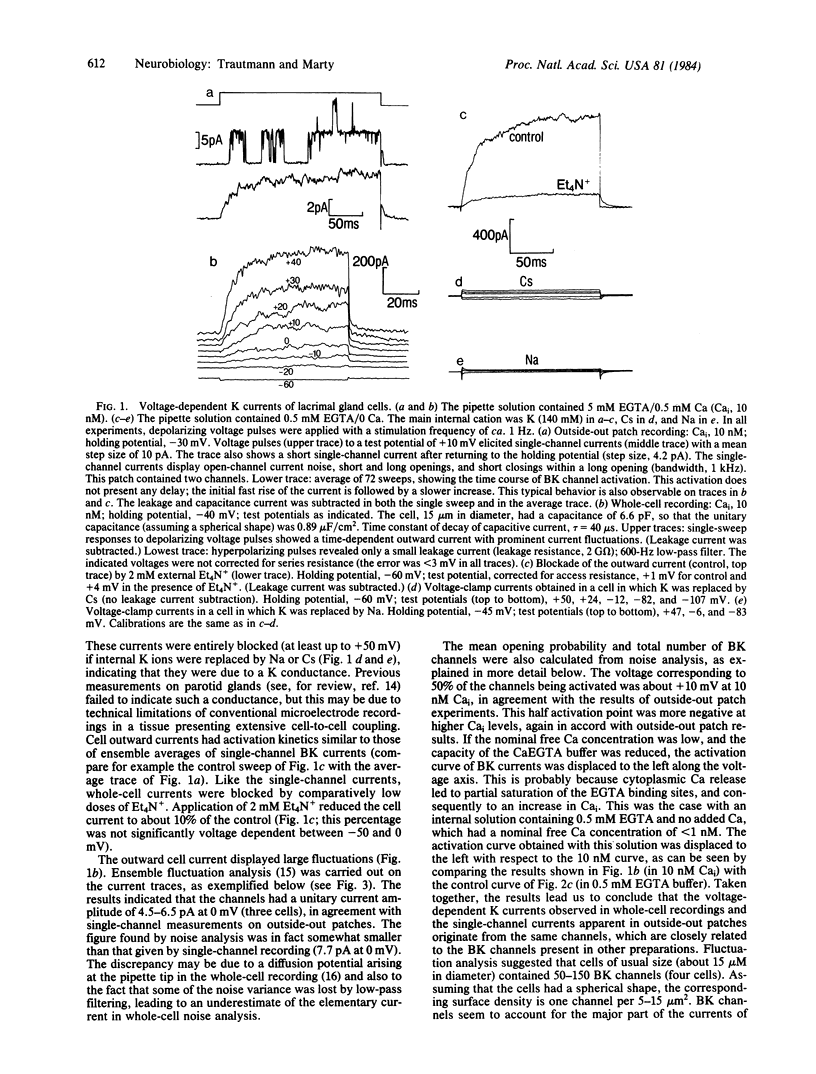
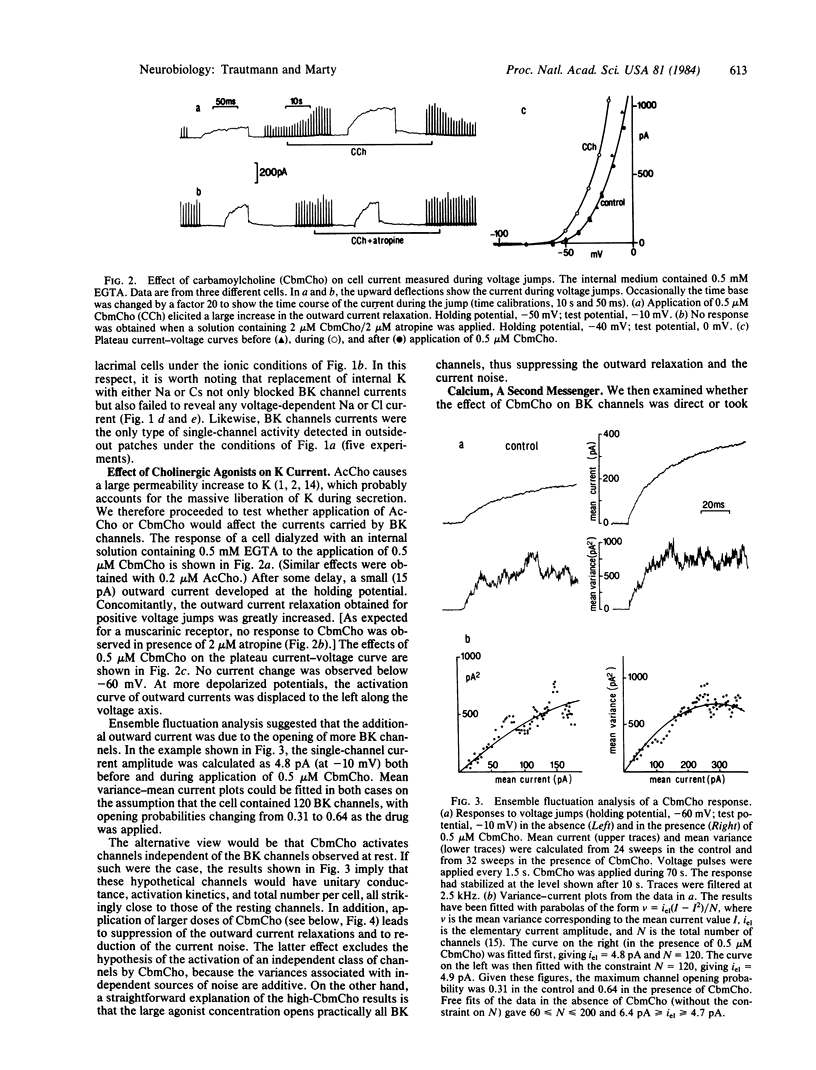
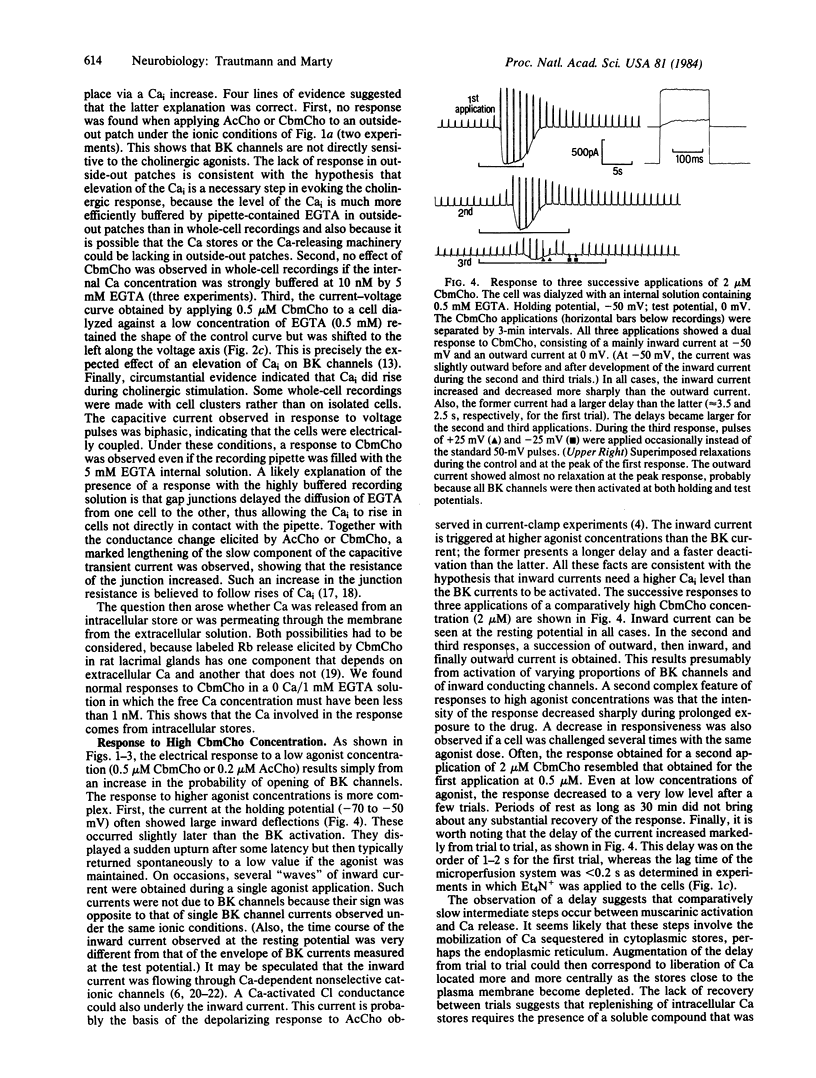
Electrical properties of the membranes of lacrimal gland cells were investigated using patch-clamp techniques [Hamill, O.P., Marty A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B. & Sigworth, F.J. (1981) Pflügers Arch. 391, 85-100]. The membranes were found to contain a specific kind of voltage- and Ca2+ -activated K+ channel ("BK channels"). These channels account for the strong rectification of the cell current-voltage curve as obtained in tight-seal whole-cell recordings. Application of low concentrations of carbamoylcholine (CbmCho, 0.5 microM) activated the BK channels. No effect was obtained in the presence of atropine (2 microM) or when dialyzing the cell with a strong CaEGTA buffer. The latter result, together with other findings, suggests that CbmCho exerts its action on BK channels by increasing the intracellular Ca2+ concentration. This Ca2+ concentration increase presumably occurred via liberation from a cytoplasmic Ca2+ store, because the response remained unaffected in the absence of extracellular Ca2+. At higher CbmCho concentration (2 microM), an inward current was observed, which was assumed to result from activation of another type of Ca2+ -regulated channel.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L., House C. R. Stimulus-response coupling in gland cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:55–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Intracellular Ca2+ injection causes membrane hyperpolarization and conductance increase in lacrimal acinar cells. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Nov 14;377(2):185–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Membrane potential, resistance, and intercellular communication in the lacrimal gland: effects of acetylcholine and adrenaline. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:507–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: acetylcholine-evoked electrical uncoupling and its ionic dependency. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:81–06. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanagasuntheram P., Randle P. J. Calcium metabolism and amylase release in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):547–564. doi: 10.1042/bj1600547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. A receptor for protons in the nerve cell membrane. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2325–2327. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channel in baso-lateral acinar cell membranes of mammalian salivary glands. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):827–829. doi: 10.1038/302827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Peterson O. H. Single-channel currents in isolated patches of plasma membrane from basal surface of pancreatic acini. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):159–161. doi: 10.1038/299159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parod R. J., Putney J. W., Jr The role of calcium in the receptor mediated control of potassium permeability in the rat lacrimal gland. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:371–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H. Electrophysiology of mammalian gland cells. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jul;56(3):535–577. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.3.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Stimulus-permeability coupling: role of calcium in the receptor regulation of membrane permeability. Pharmacol Rev. 1978 Jun;30(2):209–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose B., Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of a cell junction and the local cytoplasmic free ionized calcium concentration: a study with aequorin. J Membr Biol. 1976 Aug 27;28(1):87–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01869692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Eimerl S., Schramm M. A calcium ionophore simulating the action of epinephrine on the alpha-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):128–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Camardo J. S., Kandel E. R. Serotonin and cyclic AMP close single K+ channels in Aplysia sensory neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):413–417. doi: 10.1038/299413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:97–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


