Abstract
The synthesis of phidianidines A and B, the first 1,2,4-oxadiazole-containing alkaloid, from the marine opisthobranch mollusk Phidiana militaris is reported. The synthesis proceeds in six steps from known indole acetic acids in 39.9% (phidianidine A) and 21% (phidianidine B) overall yields from commercially available materials. Biological characterization found that phidianidines A and B are selective inhibitors of DAT (versus SERT and NET) and a selective, potent ligand and partial agonist of the μ opioid receptor (versus δ- and κ-opioid receptors). Moreover, neither phidianidines A and B are cytotoxic, and thus represent an attractive starting point for chemical optimization; therefore, we piloted a number of chemistries and prepared a diverse series of unnatural analogs.
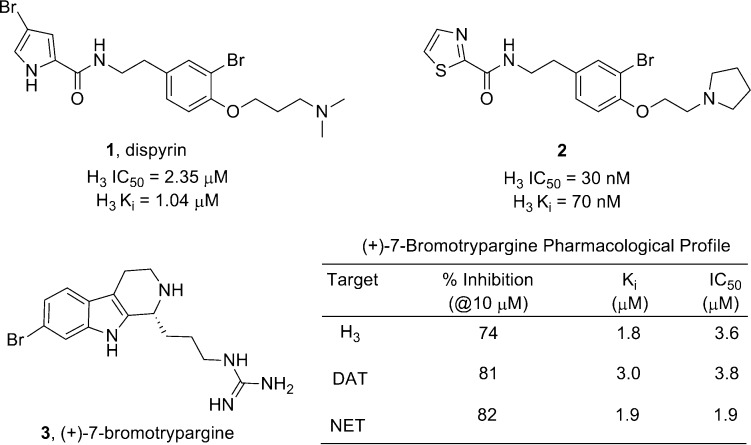
Natural products and marine natural products in particular, have been a highly successful source of novel lead series and marketed therapeutics for both peripheral and CNS indications.1,2 Research in our laboratories and others have identified a number of marine natural products3−7 that display high affinity for and functional inhibition of the histamine subtype 3 (H3) receptor. The H3 receptor is a Class A GPCR with therapeutic potential for obesity, epilepsy, sleep/wake cycle, schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s disease, neuropathic pain, and ADHD.8−10 Many natural products align with the well-defined H3 pharmacophore model, and we have employed this as a guide to select natural products for synthesis and biological evaluation at both H3 and other therapeutically relevant CNS targets.6,7,10,11 Recently (Figure 1), we synthesized dispyrin (1) based on this strategy and found that it did indeed possess activity as an H3 antagonist (Ki = 1.04 μM, IC50 = 2.35 μM).6 A subsequent optimization campaign led to the synthesis of a library of unnatural dispyrin analogues, such as 2, with significantly improved H3 activity (Ki = 70 nM, IC50 = 30 nM).7 Last year, we described the synthesis and evaluation of (+)-7-bromotrypargine (3) and were excited to find that in addition to H3 activity (Ki = 1.84 μM, IC50 = 3.6 μM), predicted based on the H3 pharmacophore model, 3 also proved to inhibit the dopamine transporter (DAT) and the norepinephrine transporter (NET), with IC50 values of 1.8 and 3.0 μM, respectively, without inhibiting the closely related serotonin transporter (SERT).11 This unique pharmacological profile for a marine alkaloid prompted our lab to synthesize and evaluate other marine alkaloids to assess their potential as leads for CNS indications.
Figure 1.
Dispyrin (1), a marine natural product with both affinity for and inhibition of H3, is a target of interest for numerous CNS indications. Optimization of 1 afforded unnatural analogues, such as 2, with increased potency and efficacy as H3 antagonists. (+)-7-Bromotrypargine (3), another natural product that, in addition to the predicted H3 activity, displayed a unique profile by inhibiting DAT and NET, while possessing no activity at SERT.
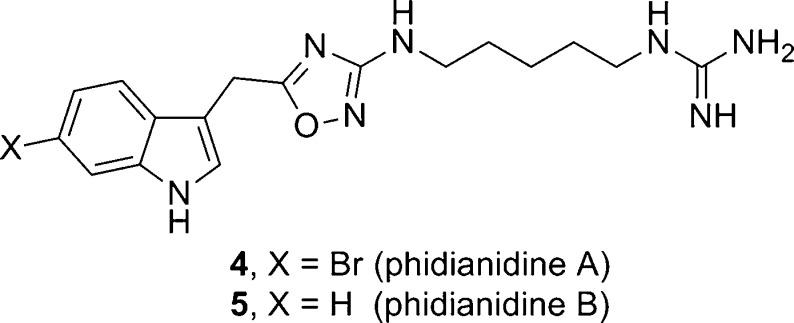
In 2011, Gavagnin, Guo, and co-workers reported on the isolation and characterization of two novel indole alkaloids, phidianidines A (4) and B (5), the first natural products identified that contain a 1,2,4-oxadiazole moiety (Figure 2).12 Compounds 4 and 5 share similar topology with 3 and conform to the H3 pharmacophore model;10 therefore, we initiated a synthesis campaign toward both 4 and 5 to provide sufficient material for pharmacological study. Our retrosynthesis followed the proposed biogenetic pathway by Gavagnin, Guo, and co-workers12 and utilizes a key coupling between indole acetic acids 6 and 7 and an appropriately oxidized, alkyl bis-guanidine 8 (Figure 3), the latter of which is derived from 1,5-diaminopentane 9. As we were writing our manuscript, a Letter appeared from Snider13 describing the synthesis of 4 and 5, starting from a 1,5-diazidopentane and a similar approach, requiring 8 steps and 19% overall yields. In their work, 4 and 5 were evaluated in the NCI 60 cell line panel and showed only 5–30% inhibition of cell growth.13
Figure 2.
Structures of phidianidines A(4) and B(5).
Figure 3.
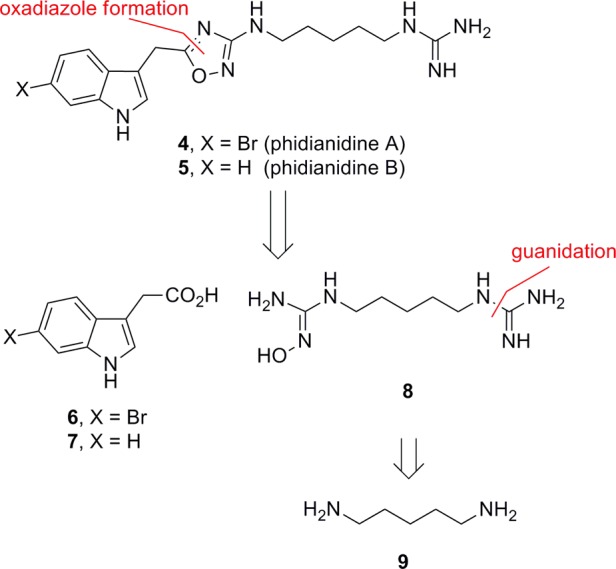
Retrosynthesis of phidianidines A (4) and B (5).
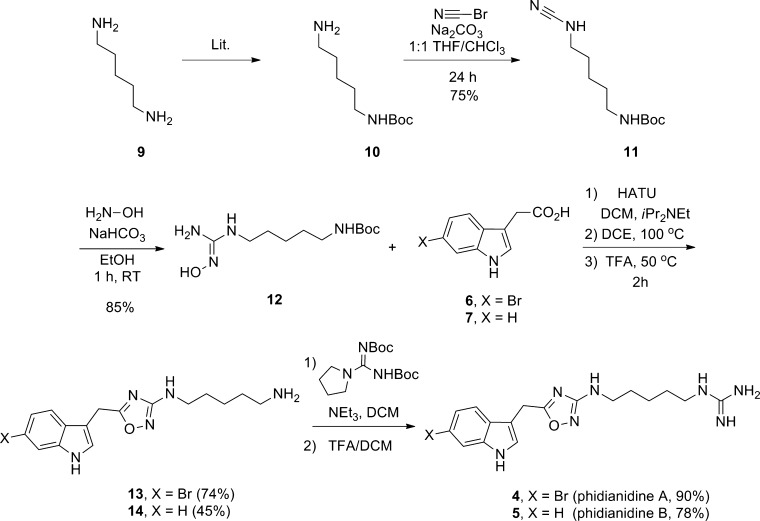
The total synthesis of phidianidines A (4) and B (5) is shown in Scheme 1. Commercially available mono-Boc protected 1,5-diaminopentane1410 is treated with cyanogen bromide to deliver 11. Exposure of 11 to hydroxylamine hydrochloride produces the key hydroxyguanidine coupling partner 12 in good yield. The requisite indole acetic acids 6 and 7 are available or can be readily prepared in a two step process from the corresponding indoles. A HATU-mediated coupling between 12 with either 6 or 7, followed by acidic cleavage of the Boc group, affords the desired 1,2,4-oxadizoles, in 74% yield for 13 and 45% yield for 14. Finally, guanidation and deprotection provides phidianidines A (4) and B (5) in overall yields of 39.9% and 21%, respectively, from commercially available materials. Overall yields are adjusted to 8% and 5% overall, respectively, if the synthesis commences with 9, which is also commercially available. Our synthetic 4 and 5 were in complete agreement with natural 4 and 5,12,15 as well as the data reported by Snider;13 moreover, the expedited route and high yields was amenable to unnatural analogue synthesis.
Scheme 1. Synthesis of Phidianidines A(4) and B(5).
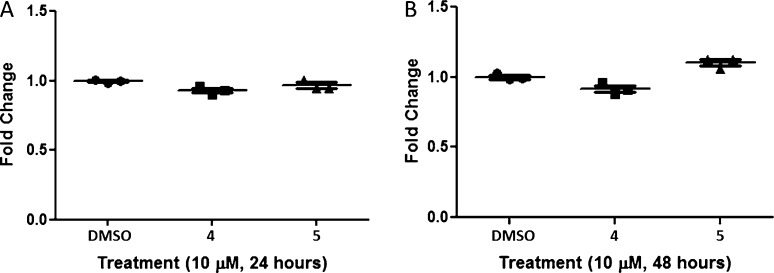
As 4 and 5 display a range of cytotoxicity across tumor and nontransformed cell lines,12,13 we first evaluated the cytotoxicity of 4 and 5 in HEK293 cells after both 24 and 48 h in a WST-1 cell proliferation assay.16−18 At concentrations of 10 μM, neither 4 nor 5 displayed any toxicity, relative to the DMSO control at 24 and 48 h time points (Figure 4). Thus, we advanced 4 and 5 into large panel screens to evaluate their potential as H3 ligands as well as other CNS targets of therapeutic relevance.
Figure 4.
Cytotoxicity assays in HEK293 cells using a WST-1 cell proliferation assay. (A) 25K cells plated at 24 h when treated with 10 μM 4 or 5 and DMSO. (B) 25K cells plated at 48 h when treated with 10 μM 4 or 5 and DMSO. Each point is a single biological replicate (N = 3) with 4 technical replicates per biological replicate.
Phidianidines A (4) and B (5) were then evaluated in an external panel of 68 GPCRs, ion channels, and transporters in radioligand binding assays18 in an attempt to identify discrete CNS targets with therapeutic relevance, a strategy that has been highly successful. Interestingly, both 4 and 5 displayed only very weak activity at H3 (25% inhibition at 10 μM and 33% inhibition at 10 μM, respectively). This was a surprising result, as 4 and 5 aligned well with the H3 pharmacophore model.6,7,10,11 Similar to 3,11 both 4 and 5 showed significant DAT activity (101% inhibition at 10 μM and 96% inhibition at 10 μM, respectively), but both possessed weak NET activity (52–68% inhibition at 10 μM) and no activity at SERT (Table 1).11,20 An even more exciting finding was the profile at the three opioid receptors.21,22 Phidianidine A (4) displayed 103% inhibition of the μ-opioid receptor (μOR) but no activity (−5% at 10 μM) at the δ- and κ-opioid receptors; importantly, phidianidine B (5) showed a similar profile. The μOR is a Class A GPCR that has been shown to be the OR subtype responsible for the analgesia of clinical opioids,21−24 and has been implicated in a number of other CNS pathologies.21−24 In order to discern early SAR, we also evaluated the amine precursor 13 en route to 4 in the same panel assay. In this instance, 13 not only displayed potent DAT and NET activity (98% and 86% inhibition at 10 μM, respectively) but also selective μOR activity (88% at 10 μM for μOR, 2% at 10 μM for δ- and κOR), suggesting the guanidine moiety of 4 is not essential for the pharmacological profiles.
Table 1. Pharmacological Profile of Phidianidines A (4), B (5), and Amine Precursor 13.
| cmpd | H3 | DAT | NET | SERT | opioid-μ | opioid-δ | opioid-κ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (% inhibition@ 10 μM)a | |||||||
| 4 | 25 | 101 | 68 | 22 | 103 | –5 | 3 |
| 5 | 33 | 96 | 45 | 16 | 97 | –6 | 5 |
| 13 | 23 | 98 | 86 | 21 | 88 | –2 | 7 |
Percent displacement of radioligand at human receptors at a compound concentration of 10 μM. H3, [3H]-N-a-methylhistadine; DAT, [125I]RTI-55; NET, [125I]RTI-55; SERT, [3H] paroxetine; opiate-μ, [3H] diprenorphine; opiate-δ, [3H] naltrindole; opiate-κ, [3H] diprenorphine.18
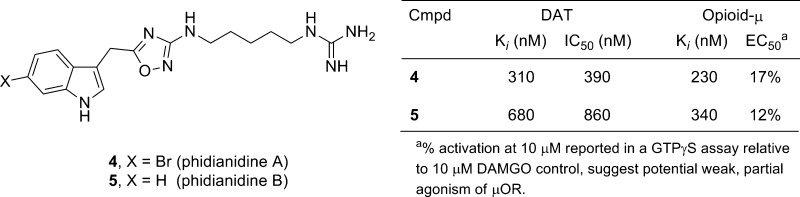
We then followed up the single point radioligand binding assays,19 with full concentration–response curves (CRCs) for 4, 5, and 13, and determined quantitative Ki values and IC50 values for DAT inhibition (Table 2).19 In parallel, we ran the standard GTPγS functional assay, measuring an increase in bound [35S]GTPγS relative to DAMGO response,19,25 to determine if 4, 5, and 13 were functional agonists of the μ-opioid receptor. We found that 4 and 5 were potent ligands for both DAT (Ki values of 310 nM and 680 nM, respectively) and μOR (Ki values of 230 nM and 340 nM, respectively). The amine precursor was weaker but still displayed submicromolar Ki values for both DAT and μOR (Ki values of 690 nM and 800 nM, respectively). All three compounds also displayed potent inhibition of DAT, with IC50 values ranging from 390 nM to 870 nM. In the GTPγS functional assay,19,2513 was inactive, but both 4 and 5 displayed weak, partial agonism (12–17% increase in bound [35S]GTPγS at 10 μM, relative to DAMGO response) of the μ-opioid receptor. While these represent very weak agonist responses, we were excited to identify a fundamentally new chemotype with high selectivity for binding to the μ-opioid receptor and an attractive lead for chemical optimization.
Table 2. Quantitative Pharmacological Profile of Phidianidines A (4), B (5), and Amine Precursor 13.
| DAT |
opioid-μ |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cmpd | Ki (nM) | IC50 (nM) | Ki (nM) | EC50a |
| 4 | 310 | 390 | 230 | 17% |
| 5 | 680 | 860 | 340 | 12% |
| 13 | 690 | 870 | 800 | 6% |
Percent activation at 10 μM reported in a GTPγS assay relative to 10 μM DAMGO control suggest potential weak, partial agonism of μOR.
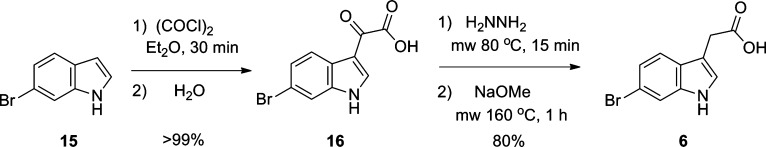
In order to optimize and develop SAR around the selective μOR activity, we require reliable, rapid chemistry to prepare unnatural analogues of 4 and 5 (Figure 5). As the data with 13 suggested the guanidine moiety is not required for μOR activity, key analogues would replace the guanidine functionality with other moieties that might enhance CNS exposure. Thus, we piloted a number of typical, high yielding reactions (acylation, sulfonylation, and urea formation) with 13 en route to unnatural analogues of 4 and 5. However, while 7 was commercially available in large quantities, the corresponding 6-bromo analogue 6 was cost prohibitive on the scale required to produce large numbers of analogues. Therefore, we developed a rapid two step sequence to access multigram quantities of 6 (Scheme 2). Friedel–Crafts acylation of 6-bromoindole 15 affords ketoacid 16 in quantitative yield. A microwave-assisted Wolff–Kishner reduction sequence then delivers the desired 6-bromoindole acetic acid 6 in 80% yield or 90% overall.26
Figure 5.
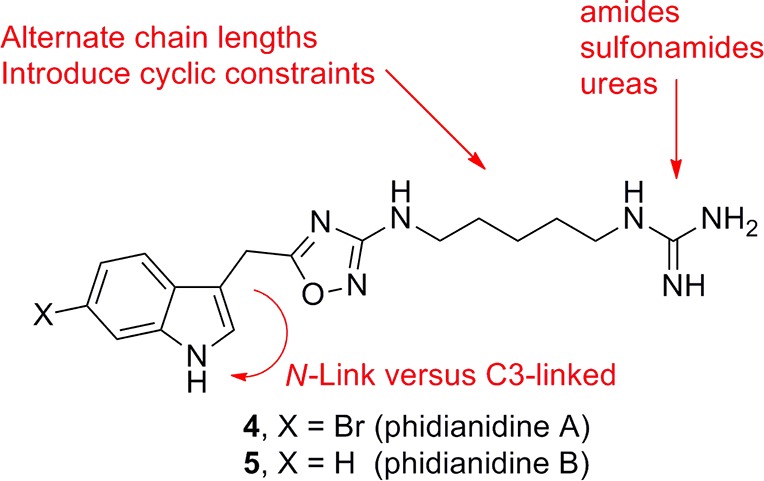
Initial plan for the synthesis of unnatural analogues of 4 and 5.
Scheme 2. Synthesis 6-Bromoindole Acetic Acid 6.
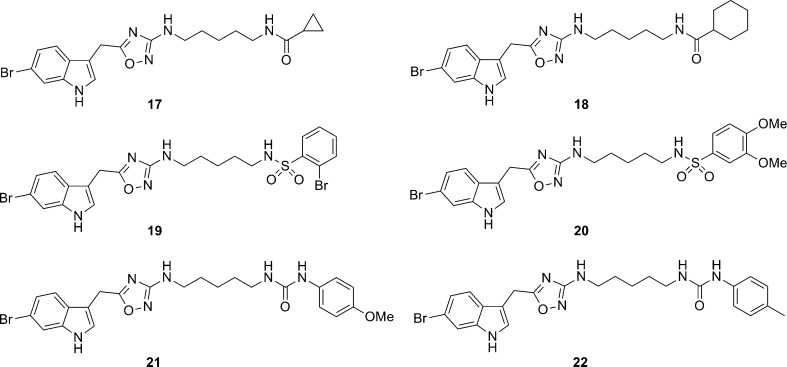
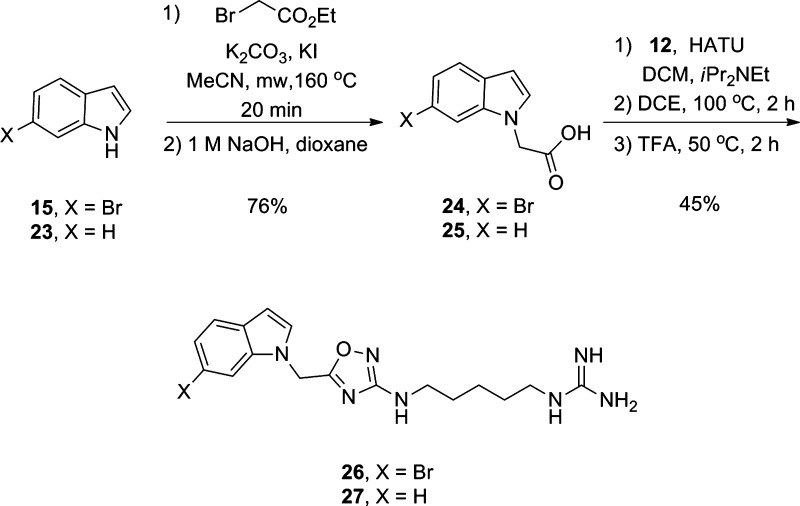
The first round of analogues were based on simple capping of the primary amine of 13 to afford amides (17 and 18), sulfonamide (19 and 20), and ureas (21 and 22) in place of the guanidine moiety of 4 (Figure 6). In an effort to add additional structural diversity, we developed chemistry to access N-linked congeners of 4 and 5 (Scheme 3). Here, indoles 15 and 23 were alkylated under microwave-assisted conditions and following ester hydrolysis provided N-linked acetic acids 24 and 25 in 76% isolated yields. A HATU-mediated amide coupling with 12, subsequent thermal dehydration, and Boc deprotection delivered the N-linked analogues 26 and 27 of 4 and 5 in 45% yield over three steps. Thus, the first unnatural analogues of 4 and 5 have been synthesized in short order and with significant structural diversity.
Figure 6.
Library of unnatural analogues of 4 with alternative moieties replacing the guanidine.
Scheme 3. Synthesis of N-Linked Unnatural Analogues 26 and 27 of 4 and 5.
In summary, we have completed the total synthesis of phidianidines A (4) and B (5), the first 1,2,4-oxadiazole-containing alkaloid, from the marine opisthobranch mollusk Phidiana militaris in six steps in 39.9% and 21% overall yields, respectively, from commercial materials. Biological evaluation of 4 and 5 (including advanced intermediate 13) proved them devoid of cytotoxicity at high doses over 48 h in HEK293 cells. Importantly, receptor profiling efforts identified 4 and 5 as potent ligands for, and inhibitors of, DAT, with little or no activity at the highly homologous NET and SERT. Even more exciting was the finding that 4 and 5 were potent ligands for the μ-opioid receptor, with no activity at the δ- or κ-opioid receptors, and that both displayed weak partial agonist μ-opioid activity. These data, and those generated with dispyrin and (+)-7-bromotrypargine, argue well for the continued synthesis and profiling of marine natural products as new sources of potent and selective ligands for CNS targets of therapeutic relevance. Moreover, the intriguing pharmacological profile of 4 and 5 led us to then explore chemistry to access unnatural analogues, and we prepared eight structurally and topologically diverse congeners. These chemistries will serve as the groundwork for a larger effort aimed at unnatural analogue synthesis to develop SAR around 4 and 5, and to enhance binding μOR affinity and agonist efficacy. Efforts toward these aims are in progress and will be reported in due course.
Methods
General
The general chemistry, experimental information and spectral data of all new compounds are supplied in the Supporting Information. Purity of all final compounds was determined by HPLC analysis is >98%.
Total Synthesis of Phidianidine A (4)
tert-Butyl (5-Aminopentyl)carbamate (10)
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (2.8 mL, 12.23 mmol) in 50 mL of 9:1 dioxane/water was added to a solution of 1,5-diaminopentane 9 (5 g, 48.93 mmol) in 50 mL of 9:1 dioxane/water over a period of 3.0 h. The solution was stirred at room temperature overnight and concentrated, and the residue was taken up in 50 mL of water. The precipitated N,N′-di-Boc-1,5-diaminopentane was removed by filtration through a fritted glass funnel, and the filtrate was extracted with DCM (50 mL × 4). The combined organic extracts were washed by water (20 mL × 2), then dried by magnesium sulfate. Removing the solvent yielded 2.14 g of 10 (22% based on 1,5-diaminopentane and 80% based on di-tert-butyl dicarbonate) as a colorless oil that solidified upon drying. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, δ (ppm)): 4.68 (s, 1H) 3.05 (s, 2H), 2.63 (q, J = 7.40 Hz, 2H), 1.38 (m, 15H), 1.28 (m, 2H), 1.13 (s, 1H). 13C NMR (150 MHz, d6-DMSO, δ (ppm)): 155.9, 79.8, 41.9, 40.3, 33.3, 29.8, 28.3, 23.9; HRMS (TOF, ES+) C10H22N2O2 [M + H]+m/z 203.1760, measured 203.1758.
tert-Butyl (5-Cyanamidopentyl)carbamate (11)
tert-Butyl (5-aminopentyl)carbamate 10 (1.52 g, 7.51 mmol) was dissolved in 20 mL of THF, and sodium carbonate (2.38 g, 22.5 mmol) was added. The resulting suspension was cooled to 0 °C. Cyanogen bromide (3.15 g, 30.05 mmol) was added as a solution in 20 mL of chloroform via an addition funnel over the course of 30 min. The solution was stirred for 12 h and monitored by thin layer chromatography. Upon completion, the solution was transferred to a separatory funnel and extracted 3× with 25 mL of DCM. The combined organic layers were dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure to yield a colorless oil. The product was purified on silica (1:1 ethyl acetate/hexanes); yield, 1.32 g (75%) of 11 as a colorless solid. 1H NMR (400.1 MHz, CD3OD, δ (ppm)): 4.67 (s, 1 H), 4.58 (t, J = 5.10 Hz, 1H), 3.04 (m, 4H), 1.59 (m, 2H) 1.47 (m, 2H) 1.40 (m, 12H). 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ (ppm)): 156.2, 116.7, 79.2, 45.8, 40.0, 29.5, 29.0, 28.6, 23.1. HRMS (TOF, ES+) C11H21N3O2 [M + H]+m/z 228.1712, measured 228.1710.
tert-Butyl (5-(2-Hydroxyguanidino)pentyl)carbamate (12)
tert-Butyl (5-cyanamidopentyl)carbamate 11 (657 mg, 2.89 mmol) was dissolved in absolute ethanol. Sodium bicarbonate (485 mg, 5.78 mmol) and hydroxylamine HCl (221 mg, 3.18 mmol) were added, and the reaction was stirred at 25 °C for 4 h. Product formation was monitored by thin layer chromatography (80:18:2 CHCl3/MeOH/NH4OH) visualized with I2 stain. Upon consumption of starting material, the reaction mixture was concentrated and purified on silica (CHCl3 to 80:18:2 CHCl3/MeOH/NH4OH) and isolated as a colorless solid 641 mg (85%). 1H NMR (400.1 MHz, CDCl3, δ (ppm)): 5.75 (br m, 3H) 5.17 (S, 1H) 2.99 (m, 4H), 1.36 (m, 13H), 1.27 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3, δ (ppm)):156.5, 156.1, 78.9, 57.7, 49.9, 41.9, 41.2, 40.3, 29.5, 29.1, 28.3, 23.9, 18.1; HRMS (TOF, ES+) C11H24N4O3 [M + H]+m/z 261.1927, measured 261.1926.
5-((6-Bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)pentane-1,5-diamine (13)
A flask was charged with 6 (105 mg, 0.599 mmol), HATU (227.7 mg, 0.599 mmol), DIEA (174 uL, 0.658 mmol), and DCM (2 mL). The solution was stirred for 30 min, transferred via pipet, and added dropwise to a stirred solution of 12 (171 mg, 0.658 mmol) in DCM (2 mL). The reaction was stirred 1 h and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude mixture was dissolved in DCE (5 mL). The flask was fitted with a reflux condenser, and the reaction was heated to 100 °C for 1 h. The reaction mixture was cooled, and a 1:1 solution of DCM/TFA (5 mL total volume) was added. The flask was heated to 50 °C for 3 h, monitoring reaction progress by LCMS. The mixture was then transferred to a separatory funnel and partitioned between water and DCM. The mixture was extracted 3× with 20 mL of DCM, and the combined organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. The product was purified by reverse phase HPLC using acetonitrile and 0.1% TFA/water (gradient 10:90 to 90:10) yielding 119 mg (74%) 13 as a brown glassy solid. 1H NMR (400.1 MHz, CD3OD, δ (ppm)): 7.51 (s, 1H), 7.44 (d, J = 8.50 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (s, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.50 Hz, 1H), 4.18 (s, 2H), 3.16 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 2.88 (t, J = 7.50 Hz, 2H), 1.66 (m, 4H), 1.42 (m, 2H).; 13C NMR (150 MHz, d6-DMSO, δ (ppm)): 176.7, 168.5, 137.0, 125.7, 125.2, 121.4, 120.1, 114.2, 113.9, 107.2, 45.2, 42.1, 27.9, 26.5, 23.2, 22.5; HRMS (TOF, ES+) C16H20BrN5O [M + H]+m/z 378.0929, measured [M 79Br + H], [M 81Br + H] 378.0926, 380.0911.
Phidianidine A (4)
A 50 mL round-bottom flask was charged with 5-((6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)pentane-1,5-diamine 13 (20 mg, 0.0528 mmol), DIEA (20 uL), N,N′-bis(boc)-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxamidine (17.69 mg, 0.058 mmol), and DCM (5 mL). The reaction was stirred 30 min, monitoring progress by LCMS. After completion, a 1:1 solution of DCM/TFA (5 mL total volume) was added, and the reaction was stirred for 8 h. The mixture was then transferred to a separatory funnel, washed with water, and extracted 3× with 25 mL of DCM. The combined organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate before being concentrated under reduced pressure. The brown solid was then purified by reverse phase HPLC using acetonitrile and 0.1% TFA/water (gradient 10:90 to 90:10), yielding 20 mg (90%) of phidianidine A (4) as a glassy golden brown solid. 1H NMR (600 MHz, d6-DMSO, δ (ppm)): 11.18 (s, 1H), 7.56 (d, J = 1.80 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (d, J = 8.50 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (d, J = 2.50, 1H), 7.13 (dd, J = 8.50, 1.78, 1H), 6.72 (t, J = 5.85 Hz, 1H), 4.2 (s, 2H), 3.00 (dq, J = 33.1, 7.0 Hz, 4H) 1.46 (m, 4H), 1.27 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (150 MHz, d6-DMSO, δ (ppm)): 177.1, 168.9, 157.1, 137.4, 126.1, 125.7, 122.0, 120.6, 114.5, 114.4, 107.8, 42.6, 41.0, 28.54, 28.53, 23.8, 22.9; HRMS (TOF, ES+) C17H22BrN7O [M + H]+m/z 420.1147, measured [M 79Br + H], [M 81Br + H] 420.1148, 422.1132.
Cell Proliferation/Cytotoxicity Assay
Cytotoxicity assays were in HEK293 cells using a WST-1 cell proliferation assay kit at both 24 and 48 h time points. 25,000 cells were plated in a 96-well plate in 100 mL of culture medium with DMSO, 4 (10 μM), or 5 (10 μM). Cells were then cultured for either 24 or 48 h in a CO2 incubator at 37 °C. Then, 10 mL of WST-1 mixture was added to each well, mixed on an orbital shaker, and the cells incubated for another 2 h at 37 °C. Then, the absorbance of each sample was measured at 450 nm.
Radioligand Binding and Functional assays
All biological assays were conducted at Ricerca Pharma according to published protocols, and each assay employed established control compounds.19
Functional μOR Assay (GTPγS)19,25
Human recombinant μ-opioid receptors stably expressed in CHO-K1 cells are used. Compounds 4, 5, and 13 were preincubated with the membranes (0.016 mg/mL) and 3 mM GDP in modified HEPES at pH 7.4 buffer for 20 min at 25 °C, and SPA beads are then added for another 60 min at 30 °C. The reaction is initiated by 0.3 nM [35S]GTPγS for an additional 30 min incubation period. Test compound-induced increase of [35S]GTPγS binding by 50% or more (50%) relative to the 10 mM DAMGO response indicates possible μOR agonist activity. Compounds are screened at 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001 mM.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by the Department of Pharmacology and Vanderbilt University. Funding for the NMR instrumentation was provided in part by a grant from NIH (S10 RR019022). Vanderbilt is a member of the MLPCN and houses the Vanderbilt Specialized Chemistry Center for Accelerated Probe Development.
Supporting Information Available
Experimental procedures and spectroscopic data for selected compounds and detailed pharmacology methods. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Author Contributions
C.W.L. conceived and directed the project, and wrote the manuscript. J.T.B. performed all chemical synthesis. S.L.S. performed cytotoxicity assays.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- Koehn F. E.; Carter G. T. (2005) The evolving role of natural products in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 8, 69–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinski T. F.; Dalisay D. S.; Lieven S. L.; Sauldes J. P. (2009) Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 8, 69–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson D. M.; Wilson S. J.; Boggs J. D.; Xiao W.; Apodaca R.; Barbier A. J.; Lovenberg T. W.; Carruthers N. I. (2006) Aplysamine-1 and related analogs as histamine H3 receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 897–900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierzwa R.; King A.; Conover M. A.; Tozzi S.; Puar M. S.; Patel M.; Coval S. J.; Pomponi S. A. (1994) Verongamine, a novel bromotyrosine-derived histamine H3-antagonist from the marine sponge Verongula gigantea. J. Nat. Prod. 57, 175–177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao C.; Sun M.; Bennani Y. L.; Gopalakrishnan S. M.; Witte D. G.; Miller T. R.; Krueger K. M.; Browman K. E.; Thiffault C.; Wetter J.; Marsh K. C.; Hancock A. A.; Esbenshade T. A.; Cowart M. D. (2008) The alkaloid conessine and analogues as potent histamine H3 receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 51, 5423–5430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy J. P.; Brogan J. T.; Lindsley C. W. (2008) Total synthesis and biological evaluation of the marine bromopyrrole alkaloid dispyrin: elucidation of discrete molecular targets with therapeutic potential. J. Nat. Prod. 71, 1783–1788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy J. P.; Conn P. J.; Lindsley C. W. (2009) A novel class of H3 antagonists derived from the natural product guided synthesis of unnatural analogs of the marine bromopyrrole alkaloid dispyrin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19, 3204–3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leurs R.; Bakker R. A.; Timmerman H.; de Esch I. J. P. (2005) The histamine H3 receptor: from gene cloning to H3 receptor drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 4, 107–120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudkins R. L.; Raddatz R. (2008) Recent advances in drug discovery of histamine H3 antagonist. Annu. Rep. Med. Chem. 42, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- LeBois E. P.; Jones C. K.; Lindsley C. W. (2011) The Evolution of Histamine H3 Antagonists/Inverse Agonists’. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 11, 648–660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogan J. T.; Stoops S. L.; Crews B. C.; Marnett L. J.; Lindsley C. W. (2011) Total synthesis of (+)-7-bromotrypargine and unnatural analogues: Biological evaluation uncovers activity at CNS targets of therapeutic relevance. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2, 633–639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone M.; Li Y.; Mollo E.; Castelluccio F.; Di Pascale A.; Cimino G.; Santamaria R.; Guo Y.-W.; Gavagnin M. (2011) Stucture and cytotoxicity of phidiadinines A and B. First findings of 1,2,4-oxadiazole system in a marine natural product. Org. Lett. 13, 2516–2519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H.-Y.; Snider B. B. (2012) Synthesis of phidiadinines A and B. J. Org. Chem. 77, 4832–4836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dratz E., and Grieco P. (2010) Novel optical labeling molecules for proteomics and other biological analyses, U.S. Pat. Appl. Publ., 20100252433. See Supporting Information for full details.
- See Supporting Information for full details.
- Stoops S. L.; Pearson S. A.; Weaver C.; Waterson A. G.; Days E.; Farmer C.; Brady S.; Weaver C. D.; Beauchamp R. D.; Lindsley C. W. (2011) Identification and optimization of small molecules that restore E-cadherin expression and reduce invasion in colorectal cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 6, 452–465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A.-M.; Assalian A. (1996) Microcat: A novel cell proliferation and cytotoxicity assay based on WST-1. Biochemica 3, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- For information of the WST-1 assay kit employed, see http://www.caymanchem.com/pdfs/10008883.
- For information on the Lead Profiling Screen (68 targets in radioligand binding assays) and the GTPγS fucntiopnal assay employed, see www.ricerca.com.
- Howell L. L.; Kimmel H. L. (2008) Monoamine transporters and psychostimulant addiction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 75, 196–217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raehal K. M.; Schmid C. L.; Groer C. E.; Bohn L. M. (2011) Functional selectivity at the μ-opioid receptor: Implications for understanding opioid analgesia and tolerance. Pharmacol. Rev. 63, 1001–1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colasanti A.; Rabiner E. A.; Lingford-Hughes A.; Nutt D. J. (2012) Opioids and anxiety. J. Psychopharmacology 25, 1415–1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melancon B. J.; Hopkins C. R.; Wood M. R.; Emmitte K. A.; Niswender C. M.; Christopoulos A.; Conn P. J.; Lindsley C. W. (2012) Allosteric modulation of 7 transmembrane spanning receptors: Theory, practice and opportunities for CNS drug discovery. J. Med. Chem. 55, 1445–1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. E.; Koeppe R. A.; Young E. A.; Zubieta J. K. (2006) Dyregul;ation of endogenous opioid emotion regulation circuitry in major depression in women. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 63, 1199–1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt A.; Mansour A.; Medzihhradsky F.; Traynor J. R.; Woods J. H. (1998) Stimulation of guanosine −5′-O-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate binding by endogenous opioids acting at a cloned mu receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 286(1), 282–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozano O.; Blessley G.; Martinez del Campo T.; Thompson A. L.; Giuffredi G. T.; Bettati M.; Walker M.; Borman R. (2011) Organocatalyzed Enantioselective Fluorocyclizations. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 50, 8105–8109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.