Abstract
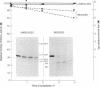
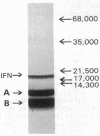
To attempt to locate functionally important regions of the interferon (IFN) molecule, recombinant human IFN-alpha 2 was subjected to proteolytic digestion. The bacterial proteinase thermolysin produced two major complementary fragments, HuIFN-alpha 2-(1-110) and HuIFN-alpha 2-(111-153). After reduction with 2-mercaptoethanol and separation of the two major fragments on NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, antiviral activity persisted in the larger, Mr 12,000, fragment consisting of the amino-terminal 110 amino acids.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheiter H., Ohno M., Smith M., Gutte B., Zoon K. C. Orientation of a human leukocyte interferon molecule on its cell surface receptor: carboxyl terminus remains accessible to a monoclonal antibody made against a synthetic interferon fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2539–2543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter H., Thomas R. M., Leist T., Fountoulakis M., Gutte B. Physicochemical and antigenic properties of synthetic fragments of human leukocyte interferon. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):278–280. doi: 10.1038/294278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bewley T. A., Levine H. L., Wetzel R. Structural features of human leukocyte interferon A as determined by circular dichroism spectroscopy. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Jul;20(1):93–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1982.tb02658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose S., Gurari-Rotman D., Ruegg U. T., Corley L., Anfinsen C. B. Apparent dispensability of the carbohydrate moiety of human interferon for antiviral activity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1659–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braude I. A., Lin L. S., Stewart W. E., 2nd Differential inactivation and separation of homologous and heterologous antiviral activity of human leukocyte interferon by a proteolytic enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 27;89(2):612–619. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90674-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braude I. A., Lin L. S., Stewart W. E., 2nd Isolation of a Biologically active fragment of human alpha interferon. J Interferon Res. 1981 Feb;1(2):245–251. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke A. E., Shepard H. M., Houck C. M., Leung D. W., Goeddel D. V., Lawn R. M. Carboxyterminal region of hybrid leukocyte interferons affects antiviral specificity. DNA. 1982;1(3):223–230. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1982.1.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Leung D. W., Dull T. J., Gross M., Lawn R. M., McCandliss R., Seeburg P. H., Ullrich A., Yelverton E., Gray P. W. The structure of eight distinct cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNAs. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):20–26. doi: 10.1038/290020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Protein sequence analysis: automated microsequencing. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):650–659. doi: 10.1126/science.6687410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy W. P., Rubinstein M., Shively J., Del Valle U., Lai C. Y., Moschera J., Brink L., Gerber L., Stein S., Pestka S. Amino acid sequence of a human leukocyte interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6186–6190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto M. J., Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. Enzymatic modifications of human fibroblast and leukocyte interferons. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):390–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.390-399.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehberg E., Kelder B., Hoal E. G., Pestka S. Specific molecular activities of recombinant and hybrid leukocyte interferons. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11497–11502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard H. M., Leung D., Stebbing N., Goeddel D. V. A single amino acid change in IFN-beta1 abolishes its antiviral activity. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):563–565. doi: 10.1038/294563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Chudzio T., Lin L. S., Wiranowska-Stewart M. Interferoids: in vitro and in vivo conversion of native interferons to lower molecular weight forms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4814–4818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Hall A., Boll W., Stewart W. E., 2nd, Nagata S., Weissmann C. Target cell specificity of two species of human interferon-alpha produced in Escherichia coli and of hybrid molecules derived from them. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Nagata S., Weissmann C. At least three human type alpha interferons: structure of alpha 2. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1343–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.6158094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Apperson S., May L., Stebbing N. Comparison of the antiviral activities of various cloned human interferon-alpha subtypes in mammalian cell cultures. J Gen Virol. 1981 Nov;57(Pt 1):233–237. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-1-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel R. Assignment of the disulphide bonds of leukocyte interferon. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):606–607. doi: 10.1038/289606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Buckler C. E., Bridgen P. J., Gurari-Rotman D. Production of human lymphoblastoid interferon by Namalva cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):44–51. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.44-51.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Smith M. E., Bridgen P. J., zur Nedden D., Anfinsen C. B. Purification and partial characterization of human lymphoblast interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5601–5605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K., Zur Nedden D., Arnheiter H. Specific binding of human alpha interferon to a high affinity cell surface binding site on bovine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4695–4697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]