Abstract
A cDNA sequence coding for mouse mast-cell growth-factor (MCGF) has been cloned from a cDNA library prepared from mRNA derived from a concanavalin A-activated mouse T-cell clone. Cloning was achieved using the pcD vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. The DNA sequence codes for a polypeptide of 166 amino acid residues including a putative signal peptide. The supernatant fluid obtained after transfection of COS-7 monkey cells with the pcD-MCGF plasmid had mouse MCGF activity. The MCGF amino acid sequence between amino acids 33 and 41, deduced from the nucleotide sequence of its cDNA, is identical to the NH2-terminal sequence of the mouse lymphokine, interleukin 3, suggesting that MCGF is related to interleukin 3.
Full text
PDF
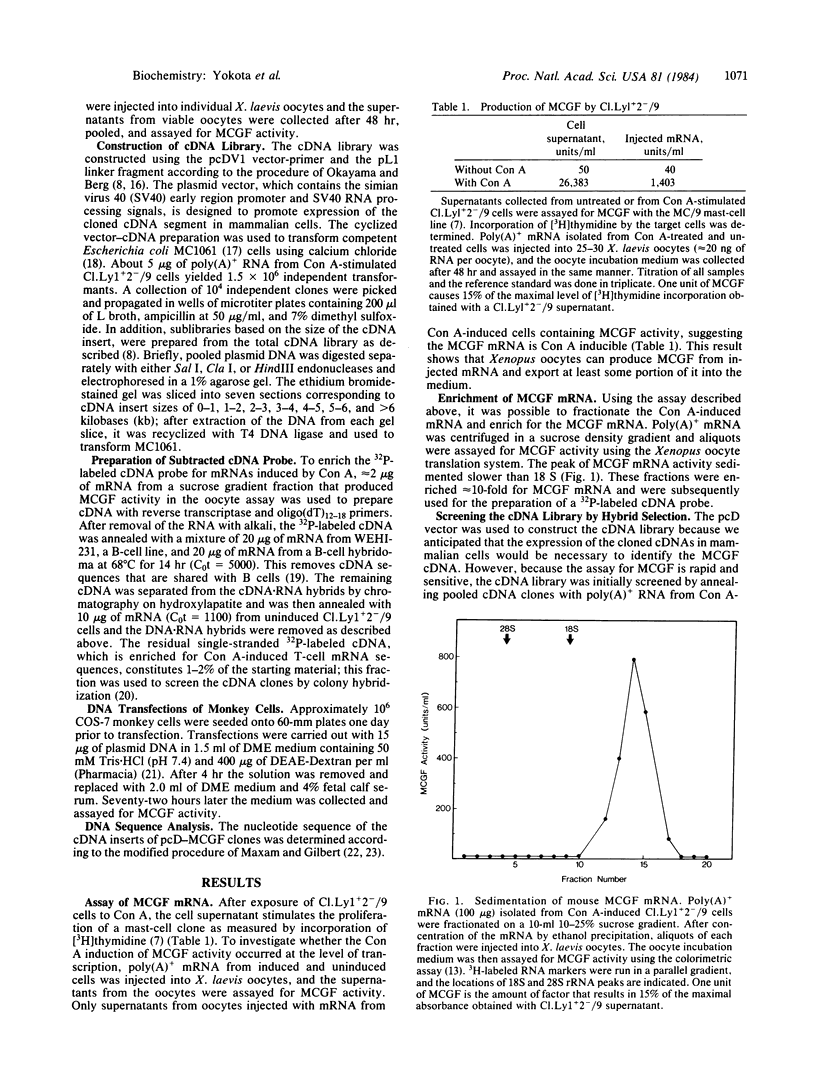
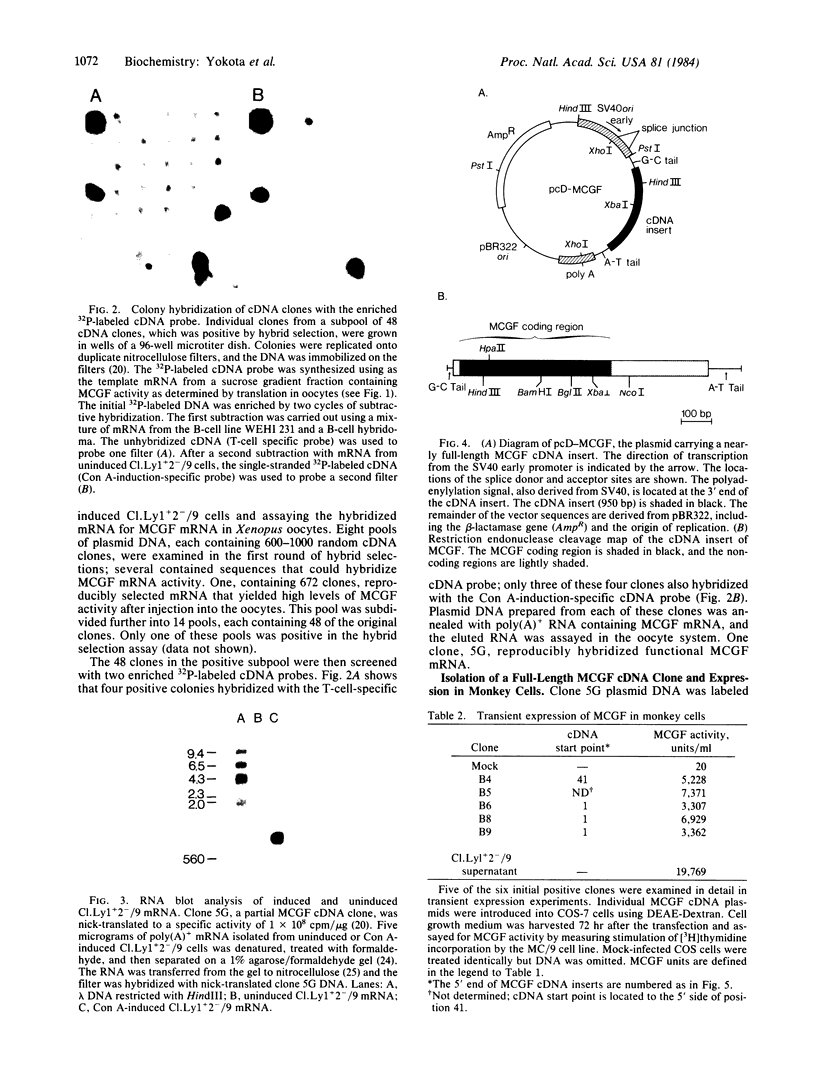


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. II. Cooperation between subclasses of Ly+ cells in the generation of killer activity. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1390–1399. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapel A. J., Lee J. C., Farrar W. L., Ihle J. N. Establishment of continuous cultures of thy1.2+, Lyt1+, 2-T cells with purified interleukin 3. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Henderson L., Klein F., Palaszynski E. Procedures for the purification of interleukin 3 to homogeneity. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2431–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Fitch F., Prystowsky M. B., Goldwasser E., Schrader J. W., Palaszynski E. Biologic properties of homogeneous interleukin 3. I. Demonstration of WEHI-3 growth factor activity, mast cell growth factor activity, p cell-stimulating factor activity, colony-stimulating factor activity, and histamine-producing cell-stimulating factor activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Pepersack L., Rebar L. Regulation of T cell differentiation: in vitro induction of 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in splenic lymphocytes from athymic mice by a unique lymphokine. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2184–2189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Fresno M., Chessman A., Cantor H. Use of cloned populations of mouse lymphocytes to analyze cellular differentiation. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90266-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F., Cantor H. Inducer T lymphocytes synthesize a factor that stimulates proliferation of cloned mast cells. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):332–334. doi: 10.1038/291332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Greenberger J. S., Sakakeeny M. A., Cantor H. Multiple biologic activities of a cloned inducer T-cell population. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1157–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. G., Chess L., Hillman D. G., Clarke B., Breard J., Merler E., Housman D. E. Human erythroid burst-forming unit: T-cell requirement for proliferation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):324–339. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Schmid C. W. Pyrimidine-specific chemical reactions useful for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4613–4619. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Röllinghoff M. T-T-cell interactions during the vitro cytotoxic allograft responses. I. Soluble products from activated Lyl+ T cells trigger autonomously antigen-primed Ly23+ T cells to cell proliferation and cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1523–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]