Abstract
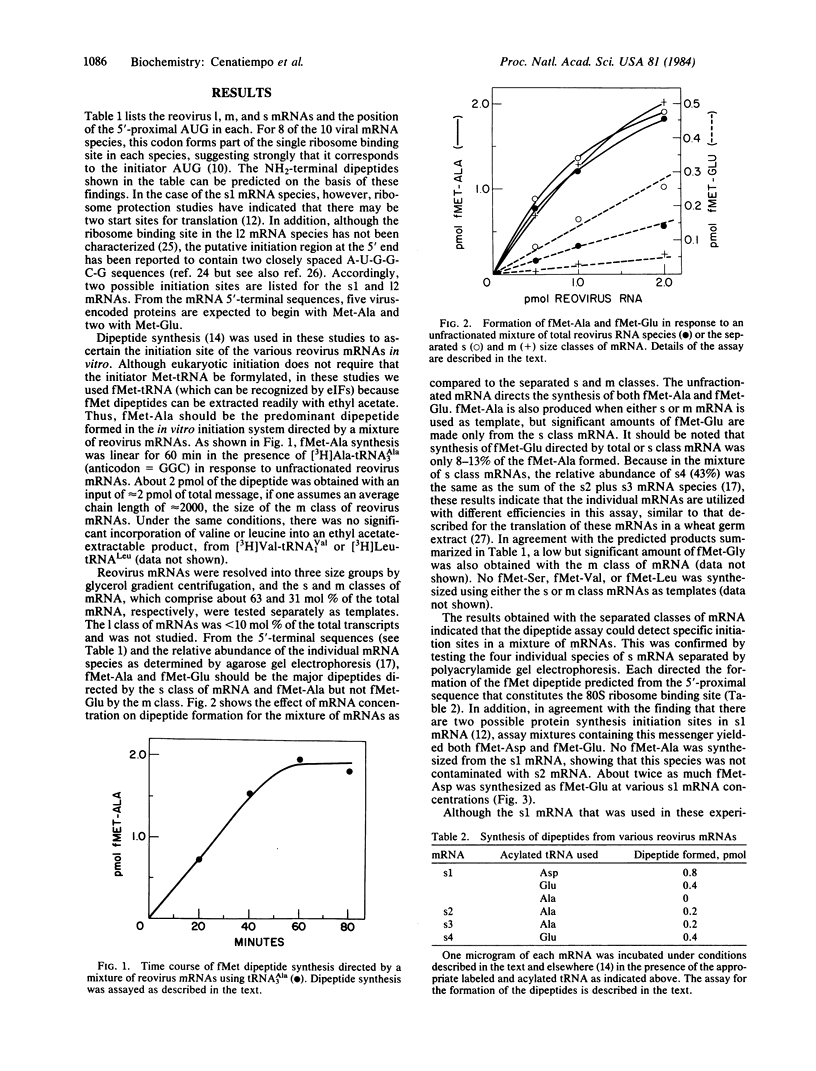
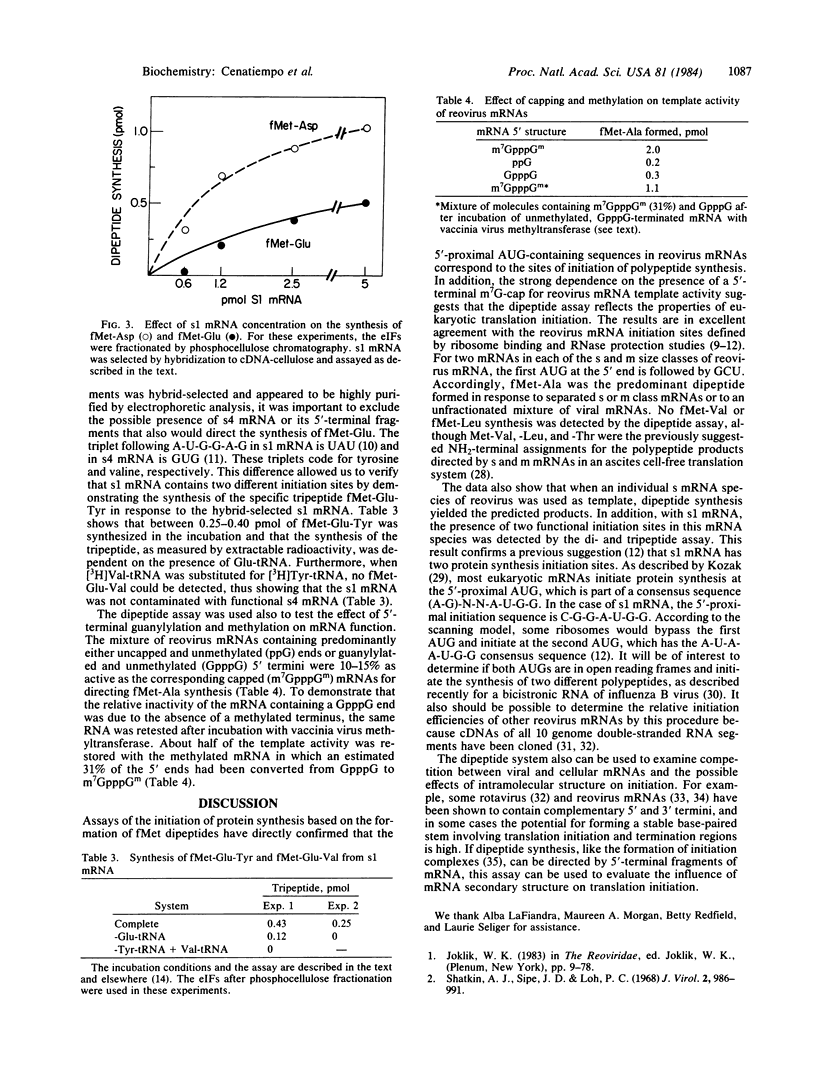
Reovirus mRNAs directed the synthesis of fMet dipeptides in a translation initiation system reconstituted from rabbit reticulocyte initiation and elongation factors, Artemia salina 80S ribosomes, yeast fMet-tRNAiMet and Escherichia coli3H-labeled aminoacyl tRNAs. As predicted from the GC(U,G) codon that follows the 5'-proximal AUG in half of the viral mRNA species, fMet-Ala was the predominant dipeptide product obtained in response to a mixture of mRNAs or to the separated size classes of medium (m) and small (s) mRNA. The four individual small mRNA species each directed the synthesis of an fMet dipeptide that was consistent with the utilization of the 5'-proximal AUG for initiation. In addition to fMet-Asp, the s1 mRNA also directed fMet-Glu synthesis indicative of initiation in a second reading frame at the 5'-penultimate AUG. The tripeptide fMet-Glu-Tyr was also synthesized from s1 mRNA, which further verified this second initiation site. mRNAs containing 5'-terminal GpppG were 10-15% as active as the corresponding m7G-capped templates. The dipeptide assay provides a rapid method for determining initiation sites in individual mRNAs or in mixtures of mRNAs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antczak J. B., Chmelo R., Pickup D. J., Joklik W. K. Sequence at both termini of the 10 genes of reovirus serotype 3 (strain Dearing). Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Graham A. F. Reovirus: RNA polymerase activity in purified virions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashdollar L. W., Esparza J., Hudson G. R., Chmelo R., Lee P. W., Joklik W. K. Cloning the double-stranded RNA genes of reovirus: sequence of the cloned S2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7644–7648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenatiempo Y., Twardowski T., Redfield B., Reid B. R., Dauerman H., Weissbach H., Brot N. Simplified in vitro system for study of eukaryotic mRNA translation by measuring di- and tripeptide formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3223–3226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinger M. J., Martin S. A., Paoletti E., Moss B. Modification of the 5'-terminus of mRNA by soluble guanylyl and methyl transferases from vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal m-7G(5')ppp(5')G-m-p in vivo: identification in reovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):742–745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Muthukrishnan S., Tomasz J., Shatkin A. J. Mechanism of formation of reovirus mRNA 5'-terminal blocked and methylated sequence, m7GpppGmpC. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):5043–5053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. Differential synthesis of blocked and unblocked 5'-termini in reovirus mRNA: effect of pyrophosphate and pyrophosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Lifton R. P., Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Isolation of specific RNA's using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:206–220. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings K. E., Millward S. Nucleotide sequences at the 5' termini of reovirus mRNA's. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):490–498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.490-498.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Joklik W. K. Demonstration that the same strand of reovirus genome RNA is transcribed in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):450–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Richardson M. A., Ikegami N., Shatkin A. J., Furuichi Y. Molecular cloning of double-stranded RNA virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):373–377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R. Binding of messenger RNA in initiation of eukaryotic translation. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:380–392. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Analysis of ribosome binding sites from the s1 message of reovirus. Initiation at the first and second AUG codons. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):807–820. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Mechanism of mRNA recognition by eukaryotic ribosomes during initiation of protein synthesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:81–123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Sequences of ribosome binding sites from the large size class of reovirus mRNA. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):467–473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.467-473.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Characterization of ribosome-protected fragments from reovirus messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4259–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Characterization of translational initiation regions from eukaryotic messenger RNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:360–375. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin K. H., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. purification and characterization of the small-sized class mRNAs of reovirus type 3: coding assignments and translational efficiencies. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. K., Keene J. D., Scheible P. P., Joklik W. K. Nature of the 3'-terminal sequences of the plus and minus strands of the S1 gene of reovirus serotypes 1, 2 and 3. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. K., Scheible P. P., Keene J. D., Joklik W. K. The plus strand of reovirus gene S2 is identical with its in vitro transcript. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J. Initiation of reovirus transcription by inosine 5'-triphosphate and properties of 7-methylinosine-capped, inosine-substituted messenger ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):5960–5966. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Utilization of the guanylyltransferase and methyltransferases of vaccinia virus to modify and identify the 5'-terminals of heterologous RNA species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):374–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus genome RNA segments: resistance to S-1 nuclease. Virology. 1975 Mar;64(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock S., Cenatiempo Y., Robakis N., Brot N., Weissbach H. In vitro synthesis of the first dipeptide of the beta subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4609–4612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pett D. M., Vanaman T. C., Joklik W. K. Studies on the amino and carboxyl terminal amino acid sequences of reovirus capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):174–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa M. D., Sigler P. B. Isolation and characterization of two methionine: tRNA ligases from wheat germ. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):141–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Joklik W. K. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. Initiation of reovirus messenger RNA translation in vitro and identification of methionyl-x initiation peptides. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D., Loh P. Separation of ten reovirus genome segments by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.986-991.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. RNA polymerase activity in purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. W., Choppin P. W., Lamb R. A. A previously unrecognized influenza B virus glycoprotein from a bicistronic mRNA that also encodes the viral neuraminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4879–4883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



