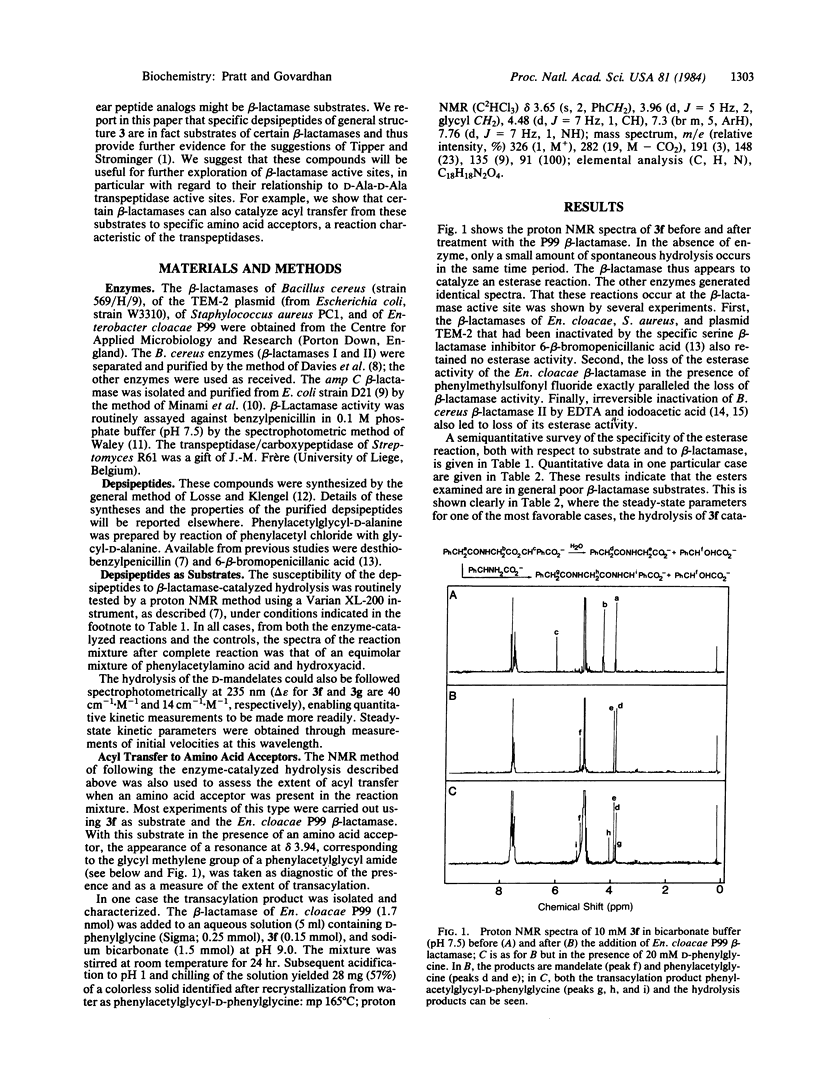
Abstract
beta-Lactamases from all three classes, A, B, and C, catalyze the hydrolysis of specific acyclic depsipeptide (PhCH2CONHCR1R2CO2CHR3CO2H) analogs of acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine peptides. The depsipeptides investigated, which are chemically as reactive toward nucleophiles as penicillins, are in general poor substrates, although differences between the classes of beta-lactamases have been observed: the order of effectiveness seems to be C greater than B greater than A. Certain class A and C beta-lactamases also catalyze phenylacetylglycyl transfer between phenylacetylglycyl depsipeptides and specific amino acid acceptors, a type of reaction hitherto identified more closely with D-alanyl-D-alanine transpeptidases than with beta-lactamases. Preliminary indications of an acyl-enzyme intermediate in these reactions have been obtained. These results support the suggestion [Tipper, D.J. and Strominger, J.L. (1965) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 54, 1133-1141] that beta-lactamases are evolutionary descendants of bacterial cell wall D-alanyl-D-alanine transpeptidases.
Full text
PDF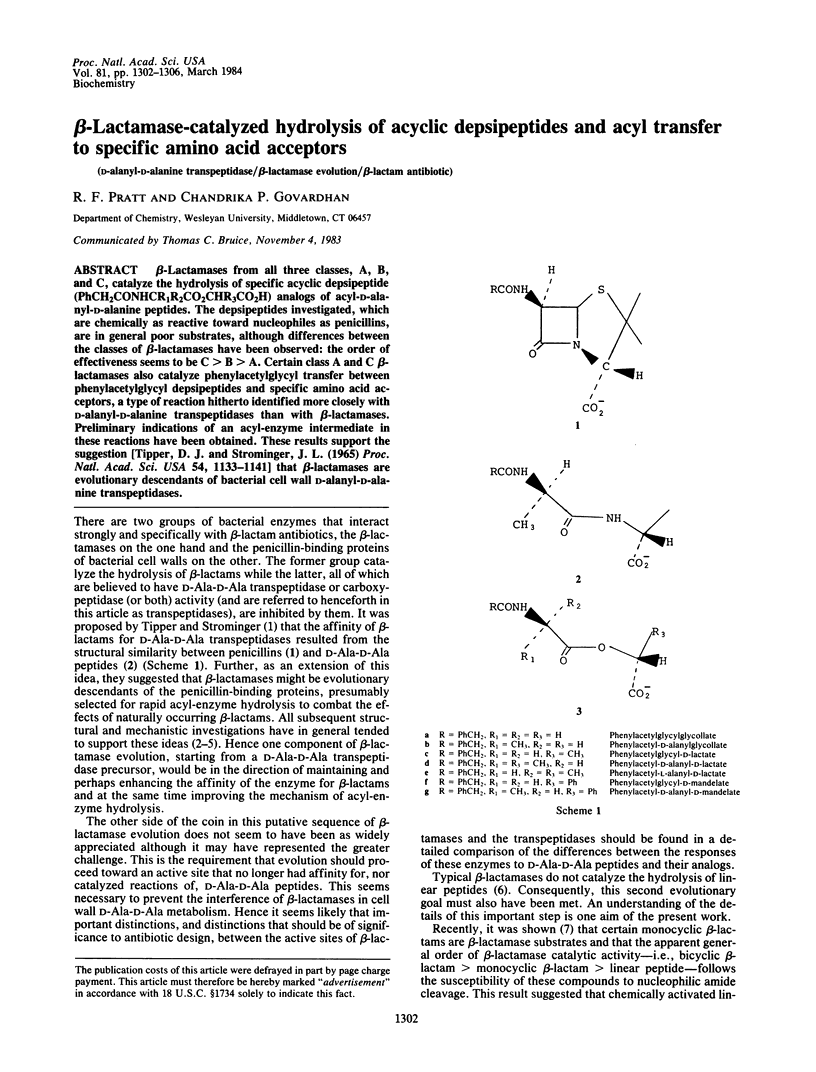


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):321–331. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. G., Pratt R. F. Pre-steady state beta-lactamase kinetics. Observation of a covalent intermediate during turnover of a fluorescent cephalosporin by the beta-lactamase of STaphylococcus aureus PC1. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11401–11404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Olsson O., Normark S. Common evolutionary origin of chromosomal beta-lactamase genes in enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):528–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.528-534.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Eriksson-Grennberg K. G., Normark S., Matsson E. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. IV. Genetic study of mutants resistant to D,L-ampicillin concentrations o 100 mu-g-ml. Genet Res. 1968 Oct;12(2):169–185. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Pratt R. F. Inactivation of Bacillus cereus beta-lactamase I by 6 beta-bromopencillanic acid: mechanism. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 19;19(17):3996–4003. doi: 10.1021/bi00558a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. B., Abraham E. P. Metal cofactor requirements of beta-lactamase II. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):129–135. doi: 10.1042/bj1430129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. B., Abraham E. P. Separation, purification and properties of beta-lactamase I and beta-lactamase II from Bacillus cereus 569/H/9. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1430115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J., Belasco J. G., Khosla S., Knowles J. R. beta-Lactamase proceeds via an acyl-enzyme intermediate. Interaction of the Escherichia coli RTEM enzyme with cefoxitin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2895–2901. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M., Frère J. M., Leyh-Bouille M., Coyette J., Dusart J., Nguyen-Distèche M. Use of model enzymes in the determination of the mode of action of penicillins and delta 3-cephalosporins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:73–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T. ampC cephalosporinase of Escherichia coli K-12 has a different evolutionary origin from that of beta-lactamases of the penicillinase type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. A., Moews P. C., Knox J. R., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M. Penicillin target enzyme and the antibiotic binding site. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):479–481. doi: 10.1126/science.7123246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott-Hunziker V., Petursson S., Waley S. G., Jaurin B., Grundström T. The acyl-enzyme mechanism of beta-lactamase action. The evidence for class C Beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 1;207(2):315–322. doi: 10.1042/bj2070315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozarich J. W., Strominger J. L. A membrane enzyme from Staphylococcus aureus which catalyzes transpeptidase, carboxypeptidase, and penicillinase activities. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1272–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of a cephalosporinase from Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):853–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Distèche M., Leyh-Bouille M., Ghuysen J. M. Isolation of the membrane-bound 26 000-Mr penicillin-binding protein of Streptomyces strain K15 in the form of a penicillin-sensitive D-alanyl-D-alanine-cleaving transpeptidase. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 1;207(1):109–115. doi: 10.1042/bj2070109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. J., Ghuysen J. M., Linder R., Salton M. R., Perkins H. R., Nieto M., Leyh-Bouille M., Frere J. M., Johnson K. Transpeptidase activity of Streptomyces D-alanyl-D carboxypeptidases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):662–666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R. F., Anderson E. G., Odeh I. Certain monocyclic beta-lactams are beta-lactamase substrates: nocardicin A and desthiobenzylpenicillin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1266–1273. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90626-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R. F., Loosemore M. J. 6-beta-bromopenicillanic acid, a potent beta-lactamase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4145–4149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen J. R., Strominger J. L. Utilization of a depsipeptide substrate for trapping acyl-enzyme intermediates of penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. W. Beta-lactamase (Enterobacter species). Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:678–687. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAZ A. K., LOWERY D. L., JACKSON L. J. Staphylococcal penicillinase. I. Inhibition and stimulation of activity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Aug;82:298–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.2.298-304.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Finland M. Thiol-group binding of zinc to a beta-lactamase of Bacillus cereus: differential effects on enzyme activity with penicillin and cephalosporins as substrates. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1513–1519. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1513-1519.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of action of penicillins: a proposal based on their structural similarity to acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. A spectrophotometric assay of beta-lactamase action on penicillins. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):789–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


