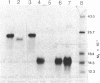
Abstract
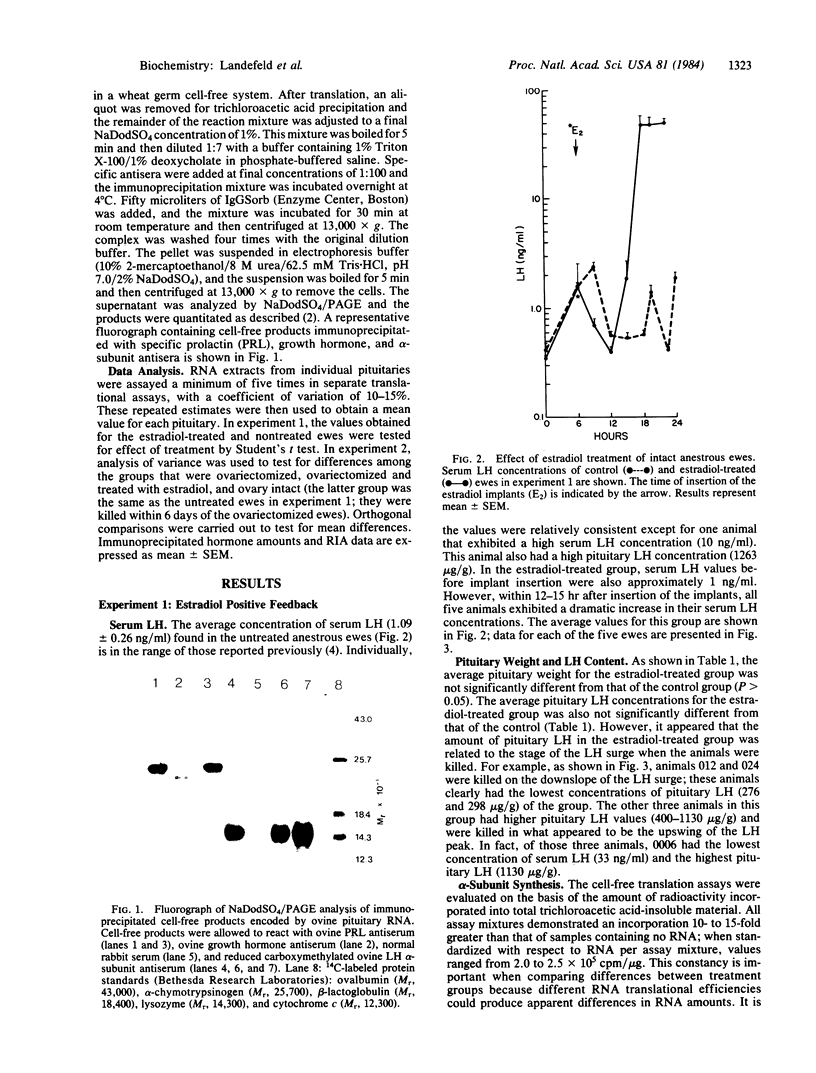
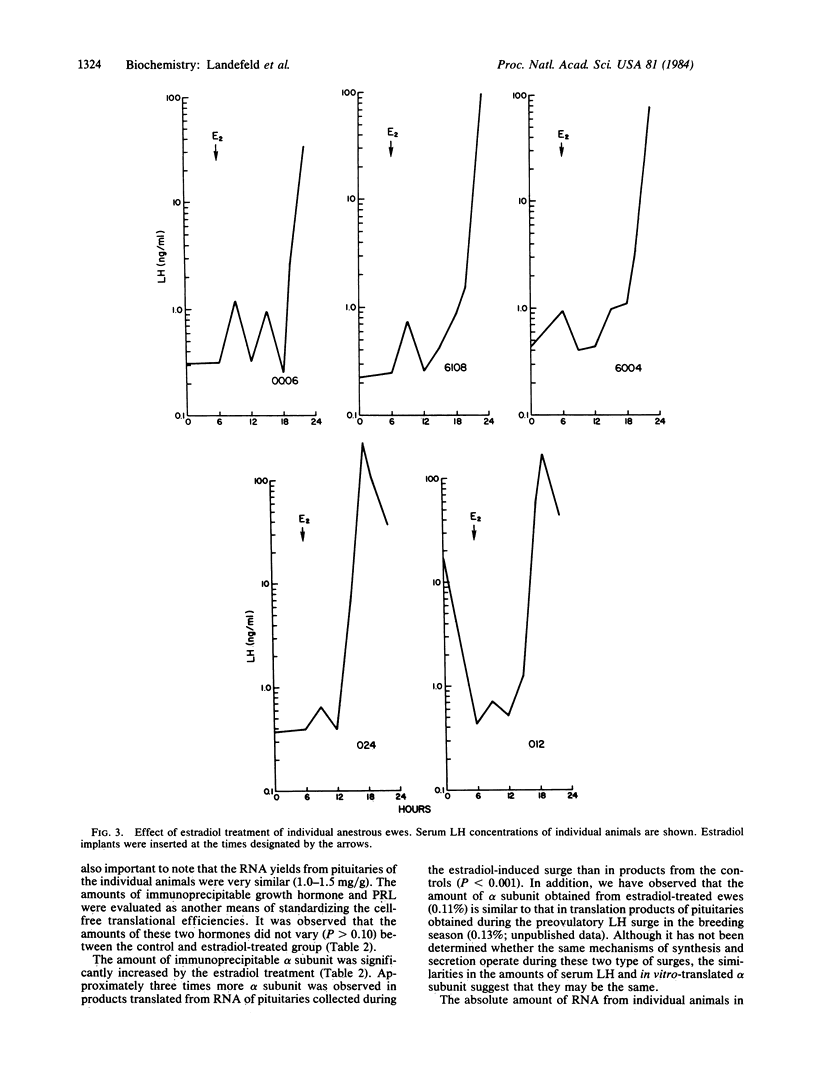
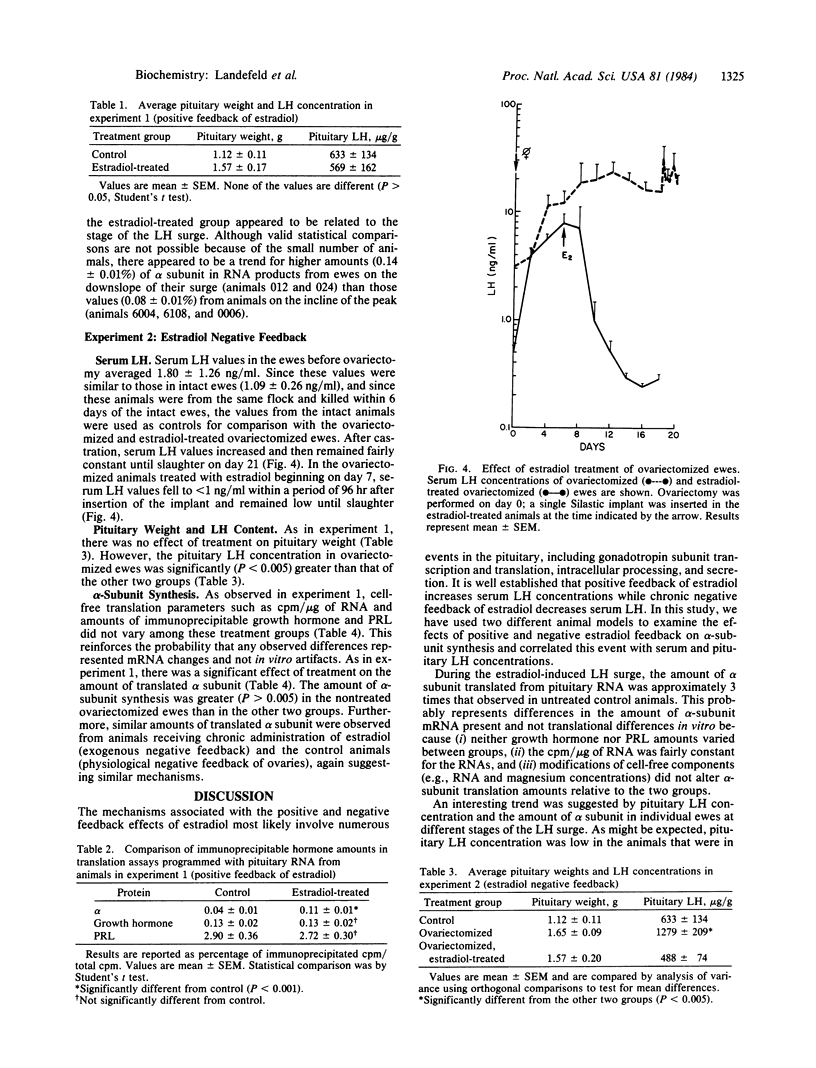
The effects of estradiol feedback on pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH) content, serum LH concentration, and in vitro-translated alpha subunit was examined in the ewe. Three animal models were used representing positive, negative, and no estradiol feedback. Two experiments were carried out: (i) anestrous ewes were treated acutely with five Silastic estradiol implants to induce a LH surge (positive feedback) and (ii) ovariectomized ewes were treated chronically with an estradiol implant (negative feedback) or were not treated (no feedback). Pituitary RNA was prepared and translated in a cell-free system; the alpha subunit was identified by immunoprecipitation and NaDodSO4/PAGE. cpm/microgram of RNA and immunoprecipitated growth hormone and prolactin were used to evaluate possible differences in RNA translational efficiencies among the treatment groups. In experiment 1, significantly higher amounts of the alpha subunit were observed in animals exhibiting an estradiol-induced LH surge than in normal anestrous ewes (P less than 0.001). Examination of values from individual animals suggested a correlation between the stage of the LH surge, pituitary LH, and translated alpha subunit. In experiment 2, the amount of alpha subunit observed in animals exposed to chronic estradiol negative feedback was significantly less (P less than 0.005) than that in the untreated ovariectomized animals (no feedback) and no different from that in intact anestrous ewes. These results suggest that both the negative and the positive feedback effects of estradiol include regulation of the amount of alpha-subunit mRNA.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander D. C., Miller W. L. Regulation of ovine follicle-stimulating hormone beta-chain mRNA by 17 beta-estradiol in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2282–2286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. L., Karsch F. J. Pulsatile secretion of luteinizing hormone: differential suppression by ovarian steroids. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1286–1290. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauger R. L., Karsch F. J., Foster D. L. A new concept for control of the estrous cycle of the ewe based on the temporal relationships between luteinizing hormone, estradiol and progesterone in peripheral serum and evidence that progesterone inhibits tonic LH secretion. Endocrinology. 1977 Sep;101(3):807–817. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-3-807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Miller W. L. Effects of estradiol-17 beta on basal and luteinizing hormone releasing hormone-induced secretion of luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone by ovine pituitary cell culture. Biol Reprod. 1980 Aug;23(1):124–134. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod23.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsch F. J., Dierschke D. K., Weick R. F., Yamaji T., Hotchkiss J., Knobil E. Positive and negative feedback control by estrogen of luteinizing hormone secretion in the rhesus monkey. Endocrinology. 1973 Mar;92(3):799–804. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-3-799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsch F. J., Foster D. L. Sexual differentiation of the mechanism controlling the preovulatory discharge of luteinizing hormone in sheep. Endocrinology. 1975 Aug;97(2):373–379. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller D., Fetherston J., Boime I. Isolation of mRNA from bovine pituitary. The cell-free synthesis of the alpha and beta subunits of luteinizing hormone. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landefeld T. D. Identification of in vitro synthesized pituitary glycoprotein alpha subunit. Translation of a possible precursor. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3685–3688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landefeld T. D., Kepa J., Karsch F. J. Regulation of alpha subunit synthesis by gonadal steroid feedback in the sheep anterior pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2390–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legan S. J., Karsch F. J., Foster D. L. The endocrin control of seasonal reproductive function in the ewe: a marked change in response to the negative feedback action of estradiol on luteinizing hormone secretion. Endocrinology. 1977 Sep;101(3):818–824. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-3-818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. C., Jackson G. L. Effect of in vivo treatment with estrogen on luteinizing hormone synthesis and release by rat pituitaries in vitro. Endocrinology. 1977 May;100(5):1294–1302. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-5-1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar R. P., Rosen H., Badminton M., Pasqualini C., Kerdelhue B. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH) binding to purified rat pituitary nuclei. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 21;153(2):382–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80648-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss G. E., Crowder M. E., Nett T. M. GnRH-receptor interaction. VI. Effect of progesterone and estradiol on hypophyseal receptors for GnRH, and serum and hypophyseal concentrations of gonadotropins in ovariectomized ewes. Biol Reprod. 1981 Dec;25(5):938–944. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod25.5.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss G. E., Nett T. M. GnRH interaction with anterior pituitary. IV. Effect of estradiol-17 beta on GnRH-mediated release of LH from ovine pituitary cells obtained during the breeding season, anestrous season, and period of transition into or out of the breeding season. Biol Reprod. 1980 Sep;23(2):398–403. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod23.2.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niswender G. D., Reichert L. E., Jr, Midgley A. R., Jr, Nalbandov A. V. Radioimmunoassay for bovine and ovine luteinizing hormone. Endocrinology. 1969 May;84(5):1166–1173. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-5-1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Mulvihill E. R., Shepherd J. H., McKnight G. S. Steroid hormone regulation of ovalbumin and conalbumin gene transcription. A model based upon multiple regulatory sites and intermediary proteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7910–7916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter B. S., Johnson L. K., Baxter J. D., Roberts J. L. Differential regulation by glucocorticoids of proopiomelanocortin mRNA levels in the anterior and intermediate lobes of the rat pituitary. Endocrinology. 1982 Apr;110(4):1442–1444. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-4-1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen X. Z., Tsai M. J., Bullock D. W., Woo S. L. Hormonal regulation of rabbit uteroglobin gene transcription. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):871–876. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupnik M. A., Chin W. W., Ross D. S., Downing M. F., Habener J. F., Ridgway E. C. Regulation by thyroxine of the mRNA encoding the alpha subunit of mouse thyrotropin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15120–15124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]