Abstract
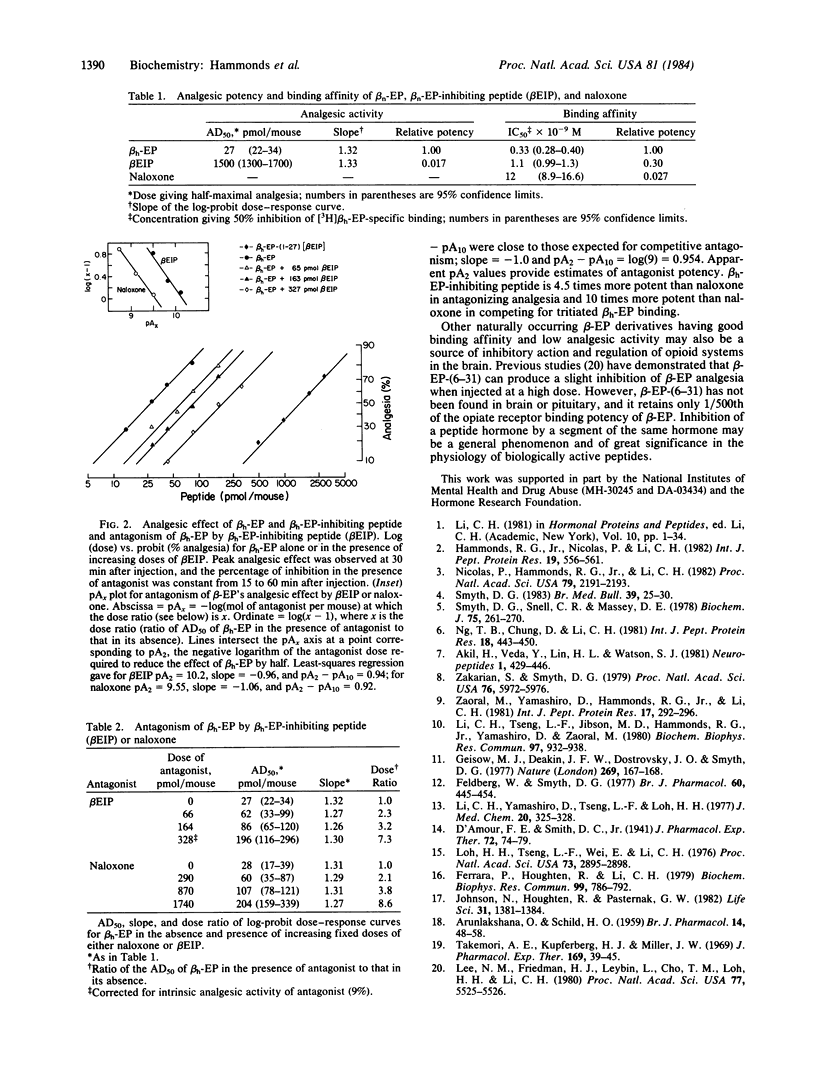
beta h-Endorphin-(1-27), a naturally occurring fragment of human beta-endorphin (beta h-endorphin), diminishes the analgesic effect of beta h-endorphin when coinjected intra-cerebroventricularly into mice. A parallel shift in the dose-response curve of beta h-endorphin in the presence of beta h-endorphin-(1-27) suggests competition at the same site. The potency of beta h-endorphin-(1-27) in antagonizing analgesia is greater than 4 times greater than that of the opiate antagonist naloxone.
Full text
PDF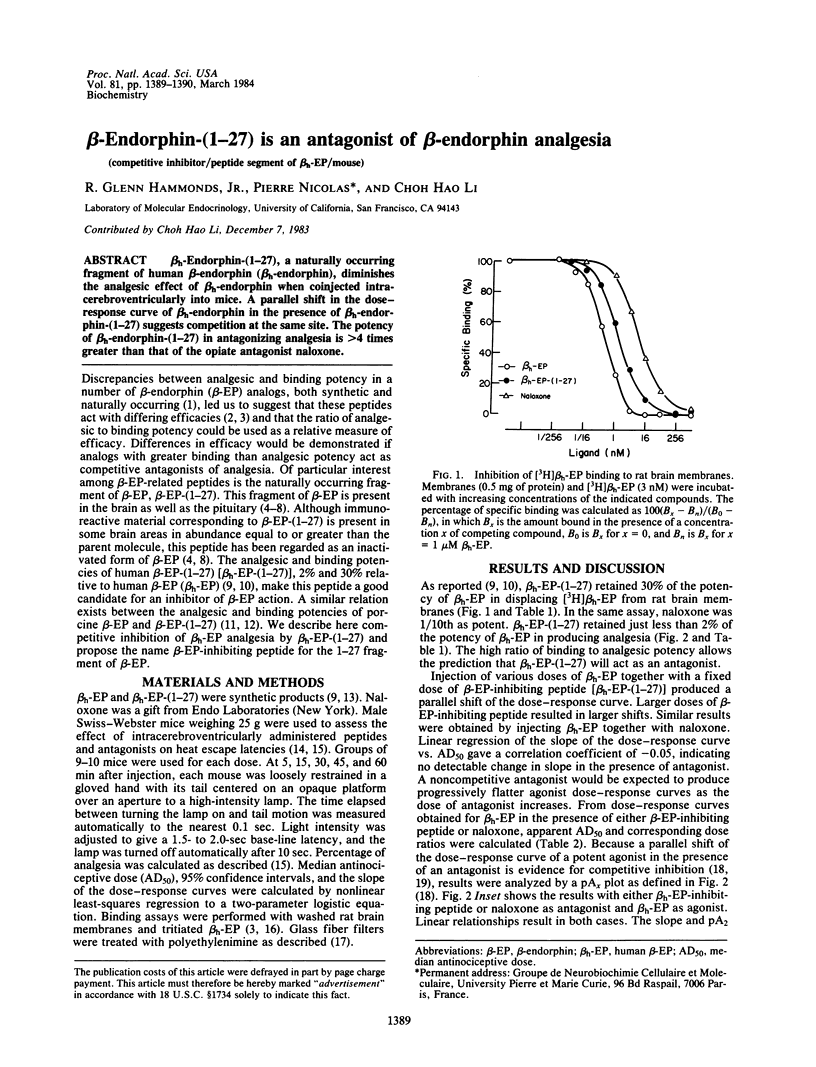
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Smyth D. G. C-fragment of lipotropin--an endogenous potent analgesic peptide. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;60(3):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07521.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara P., Houghten R., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: characteristics of binding sites in the rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):786–792. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91847-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Deakin J. F., Dostrovsky J. O., Smyth D. G. Analgesic activity of lipotropin C fragment depends on carboxyl terminal tetrapeptide. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):167–168. doi: 10.1038/269167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Nicolas P., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: analgesic and receptor binding activity of non-mammalian homologs. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 May;19(5):556–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1982.tb02642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson N., Houghten R., Pasternak G. W. Binding of 3H-beta-endorphin in rat brain. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1381–1384. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N. M., Friedman H. J., Leybin L., Cho T. M., Loh H. H., Li C. H. Peptide inhibitor of morphine- and beta-endorphin-induced analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5525–5526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Tseng L. F., Jibson M. D., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Yamashiro D., Zaoral M. beta-Endorphin- (1-27): acetylation of alpha-amino groups enhances immunoreactivity but diminishes analgesic and receptor-binding activities with no changes in circular dichroism spectra. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 16;97(3):932–938. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91466-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Tseng L. F., Loh H. H. Synthesis and analgesic activity of human beta-endorphin. J Med Chem. 1977 Mar;20(3):325–328. doi: 10.1021/jm00213a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh H. H., Tseng L. F., Wei E., Li C. H. beta-endorphin is a potent analgesic agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2895–2898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. B., Chung D., Li C. H. Isolation and properties of beta-endorphin-(1-27), N alpha-acetyl-beta-endorphin, corticotropin, gamma-lipotropin and neurophysin from equine pituitary glands. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1981 Nov;18(5):443–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1981.tb03005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas P., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. Beta-endorphin: opiate receptor binding activities of six naturally occurring beta-endorphin homologs studied by using tritiated human hormone and naloxone as primary ligands--effects of sodium ion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2191–2193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. G., Snell C. R., Massey D. E. Isolation of the C-fragment and C'-fragment of lipotropin from pig pituitary and C-fragment from brain. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):261–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1750261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. G. beta-Endorphin and related peptides in pituitary, brain, pancreas and antrum. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):25–30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori A. E., Kupferberg H. J., Miller J. W. Quantitative studies of the antagonism of morphine by nalorphine and naloxone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Sep;169(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakarian S., Smyth D. Distribution of active and inactive forms of endorphins in rat pituitary and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5972–5976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaoral M., Yamashiro D., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. Beta-Endorphin: synthesis and radioreceptor binding activity of Beta h-endorphin-(1-27) and its analogs. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1981 Mar;17(3):292–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1981.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



