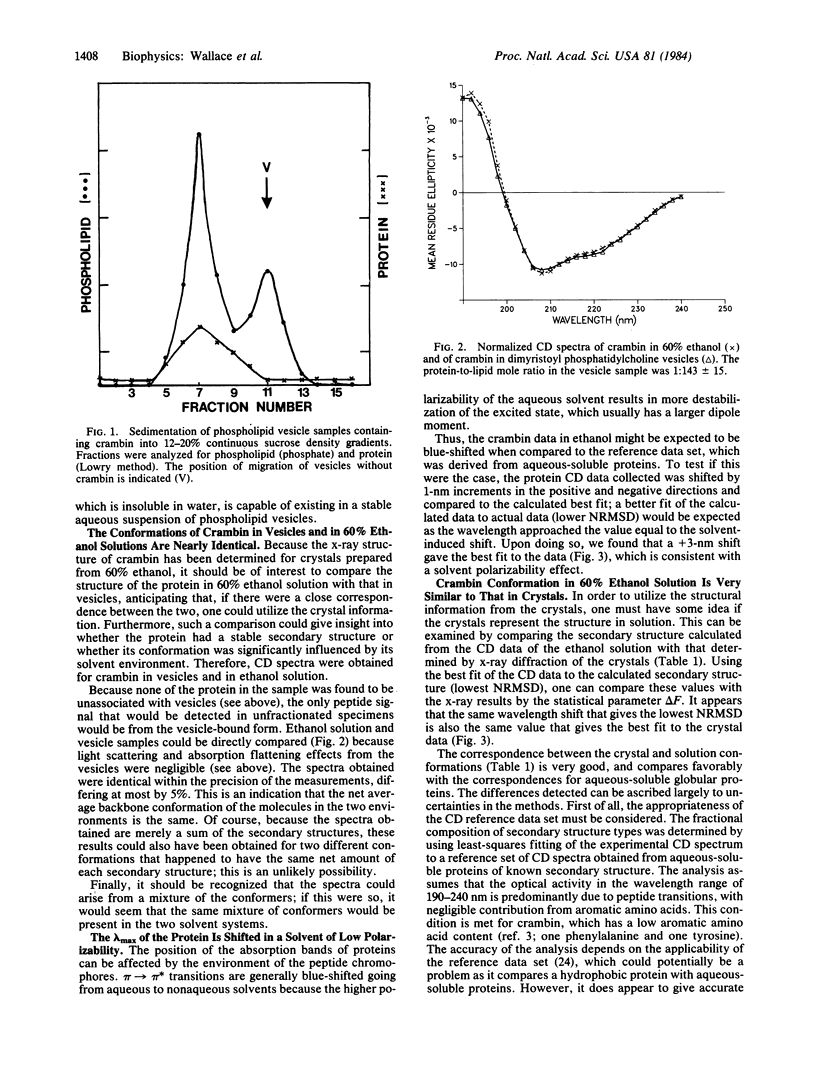
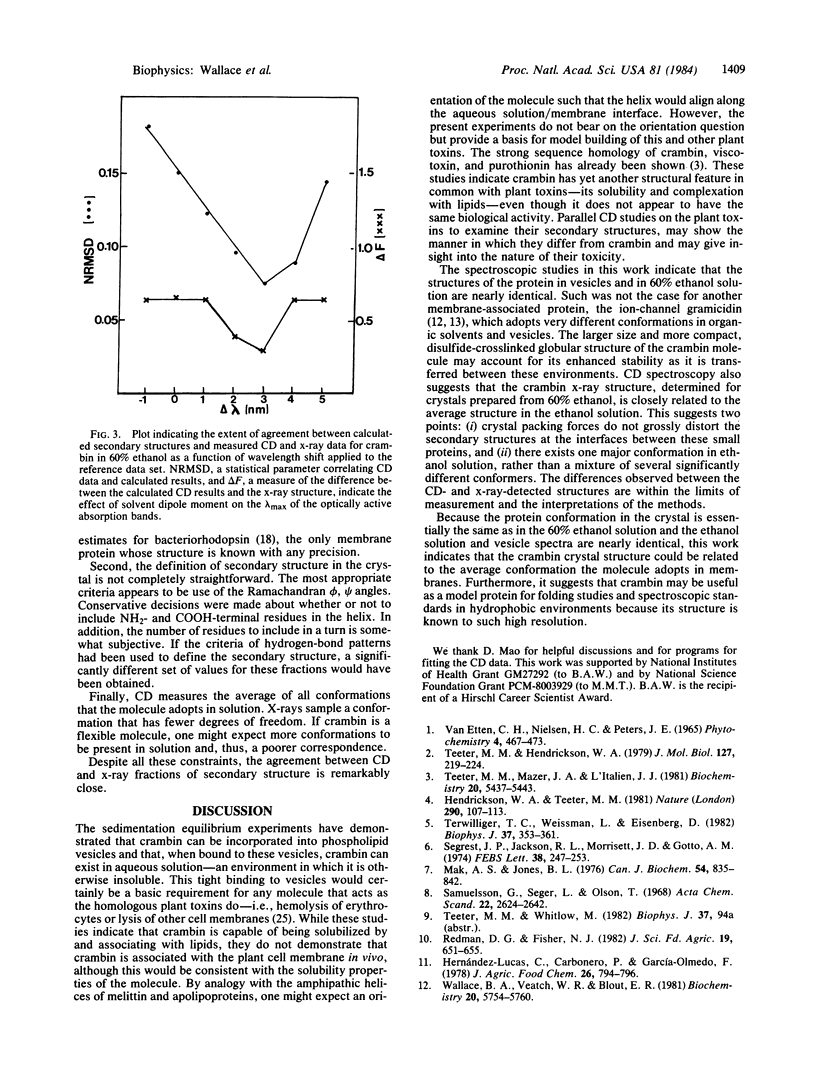
Abstract
Crambin, a hydrophobic plant seed protein that exhibits sequence homology to membrane-active plant toxins, was incorporated into phospholipid vesicles. Circular dichroism spectroscopy indicates that its structure in vesicles is nearly identical to its structure in 60% ethanol solution, the solvent from which the protein was crystallized. The secondary structure predicted from the circular dichroism data of the ethanol solution closely resembles that determined by x-ray diffraction of the crystals. This agreement suggests that the x-ray structure may form a useful basis for modeling the structure and behavior of lipophilic plant toxins. Finally, because the structure of crambin has been determined in an organic solvent medium, it provides a protein standard for examination of the effect of solvent dipole moment on the circular dichroism spectra of proteins, which may be important for interpretation of data for membrane proteins.
Keywords: membrane proteins, secondary structure, plant toxins
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Isenberg I. On the analysis of circular dichroic spectra of proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):629–634. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Vázquez D., Hernández-Lucas C., Carbonero P., García-Olmedo F. Thionins: plant peptides that modify membrane permeability in cultured mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):185–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. T., Wu C. S., Yang J. T. Circular dichroic analysis of protein conformation: inclusion of the beta-turns. Anal Biochem. 1978 Nov;91(1):13–31. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90812-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak A. S., Jones B. L. The amino acid sequence of wheat beta-purothionin. Can J Biochem. 1976 Oct;54(10):835–842. doi: 10.1139/o76-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao D., Wachter E., Wallace B. A. Folding of the mitochondrial proton adenosinetriphosphatase proteolipid channel in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):4960–4968. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. D., Wallace B. A. Binding of fibronectin to phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3327–3331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson G., Seger L., Olson T. The amino acid sequence of oxidized viscotoxin A3 from the European mistletoe (Viscum album L, Loranthaceae). Acta Chem Scand. 1968;22(8):2624–2642. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.22-2624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A. S., Harmatz D. An experimental method correcting for absorption flattening and scattering in suspensions of absorbing particles: circular dichroism and absorption spectra of hemoglobin in situ in red blood cells. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4158–4162. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Morrisett J. D., Gotto A. M., Jr A molecular theory of lipid-protein interactions in the plasma lipoproteins. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jan 15;38(3):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teeter M. M., Hendrickson W. A. Highly ordered crystals of the plant seed protein crambin. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 15;127(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teeter M. M., Mazer J. A., L'Italien J. J. Primary structure of the hydrophobic plant protein crambin. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 15;20(19):5437–5443. doi: 10.1021/bi00522a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Weissman L., Eisenberg D. The structure of melittin in the form I crystals and its implication for melittin's lytic and surface activities. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):353–361. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84683-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Blout E. R. Conformation of an oligopeptide in phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1775–1779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Veatch W. R., Blout E. R. Conformation of gramicidin A in phospholipid vesicles: circular dichroism studies of effects of ion binding, chemical modification, and lipid structure. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5754–5760. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



