Abstract
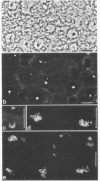
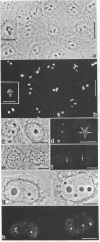
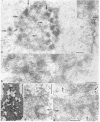
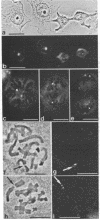
Rabbit antibodies to RNA polymerase I from a rat hepatoma have been used to localize the enzyme in a variety of cells at the light and electron microscopic level. In interphase cells the immunofluorescence pattern indicated that polymerase I is contained exclusively within the nucleolus. That this fluorescence, which appeared punctated rather than uniform, represented transcriptional complexes of RNA polymerase I and rRNA genes was suggested by the observation that it was enhanced in regenerating liver and in a hepatoma and was markedly diminished in cells treated with actinomycin D. Electron microscopic immunolocalization using gold-coupled second antibodies showed that transcribed rRNA genes are located in, and probably confined to, the fibrillar centers of the nucleolus. In contrast, the surrounding dense fibrillar component, previously thought to be the site of nascent pre-rRNA, did not contain detectable amounts of polymerase I. During mitosis, polymerase I molecules were detected by immunofluorescence microscopy at the chromosomal nucleolus organizer region, indicating that a considerable quantity of the enzyme remains bound to the rRNA genes. From this we conclude that rRNA genes loaded with polymerase I molecules are transmitted from one cell generation to the next one and that factors other than the polymerase itself are involved in the modulation of transcription of DNA containing rRNA genes during the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolph K. W. Isolation and structural organization of human mitotic chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1980;76(1):23–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00292223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona M., Scheer U., Bautz E. K. Antibodies of RNA polymerase II (B) inhibit transcription in Lampbrush chromosomes after microinjection into living amphibian oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):81–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Bernhard W. Localisation of rapidly and slowly labelled nuclear RNA as visualized by high resolution autoradiography. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jul;67(1):129–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goessens G. High resolution autoradiographic studies of ehrlich tumour cell nucleoli. Nucleolar labelling after [3H]actinomycin D binding to DNA or after [3H]TdR or [3H]uridine incorporation in nucleic acids. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jun;100(1):88–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goessens G., Lepoint A. The fine structure of the nucleolus during interphase and mitosis in Ehrlich tumour cells cultivated in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Jul;87(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90527-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodpasture C., Bloom S. E. Visualization of nucleolar organizer regions im mammalian chromosomes using silver staining. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 20;53(1):37–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00329389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A. Biogenesis of ribosomes in eukaryotes. Subcell Biochem. 1980;7:1–80. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7948-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Verdun D., Hubert J., Bourgeois C. A., Bouteille M. Ultrastructural localization of Ag-NOR stained proteins in the nucleolus during the cell cycle and in other nucleolar structures. Chromosoma. 1980;79(3):349–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00327325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu T. C., Spirito S. E., Pardue M. L. Distribution of 18+28S ribosomal genes in mammalian genomes. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 20;53(1):25–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00329388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Stick R., Kleinschmidt J. A., Moll R., Franke W. W., Hausen P. Immunological localization of a major karyoskeletal protein in nucleoli of oocytes and somatic cells of Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):749–754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S. I., Weinfeld H., Sandberg A. A. Quantitative conservation of chromatin-bound RNA polymerases I and II in mitosis. Implications for chromosome structure. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):451–464. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Beatty B. R. Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirre C., Stahl A. Peripheral RNA synthesis of fibrillar center in nucleoli of Japanese quail oocytes and somatic cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1978 Sep;64(3):377–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(78)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirre C., Stahl A. Ultrastructural organization, sites of transcription and distribution of fibrillar centres in the nucleolus of the mouse oocyte. J Cell Sci. 1981 Apr;48:105–126. doi: 10.1242/jcs.48.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott D. M. Cellular sites of RNA synthesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1964;3:33–57. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60738-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvion-Dutilleul F., Bachellerie J. P. Ribosomal transcriptional complexes in subnuclear fractions of Chinese hamster ovary cells after short-term actinomycin D treatment. J Ultrastruct Res. 1979 Feb;66(2):190–199. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(79)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recher L., Whitescarver J., Briggs L. The fine structure of a nucleolar constituent. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Oct;29(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)80052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Stetler D. A., Jacob S. T. Protein kinase activity of RNA polymerase I purified from a rat hepatoma: probable function of Mr 42,000 and 24,600 polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Trendelenburg F., Franke W. W. Effects of actinomycin D on the association of newly formed ribonucleoproteins with the cistrons of ribosomal RNA in Triturus oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):163–179. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]