Abstract
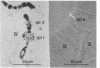
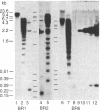
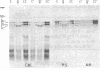
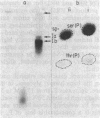
Balbiani rings (BR), giant puffs in Chironomus larval salivary glands, code for giant secretory proteins. As shown earlier, the normally dominant BR2 is turned off with its putative translation product during exposure of larvae to compounds that diminish the stores of Pi. A BR6 develops from a compact chromosome band, and a new giant protein appears in the secretion as the major component. We have determined the sequence of cloned DNA fragments representative for large parts of BR1 and BR2 (normally active) and the inducible BR6. There is an excess of positive charges and high contents of serine/threonine in the coded amino acid composition for the BR1 and BR2 sequences. The coded amino acid sequence for the BR6 clone shares homologies with the others but has an excess of negative charges and lacks serine/threonine. This suggested that the Pi effects observed earlier could be related to differences in phosphorylation between the normal proteins and the BR6 product. This could be confirmed by measurements of phosphorylation, which occurs in the normal giant proteins mainly at seryl residues. P export with giant secretory protein is normally quantitatively important. Thus, BR6 activation should decrease P loss when Pi pools are lowered because of inducer action.
Keywords: cloned DNA, repetitive sequences, secretory proteins, amino acid composition, phosphoserine
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERMANN W. [A Balbiani ring as locus of a salivary gland mutation]. Chromosoma. 1961;12:1–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00328911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beermann W. Directed changes in the pattern of Balbiani ring puffing in Chironomus: effects of a sugar treatment. Chromosoma. 1973;41(3):297–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00344024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäumlein H., Wobus U., Gerbi S., Kafatos F. C. Characterization of a 249-bp tandemly repetitive, satellite-like repeat in the translated portion of Balbiani ring c of Chironomus thummi. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):641–647. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case S. T., Daneholt B. The size of the transcription unit in Balbiani ring 2 of Chironomus tentans as derived from analysis of the primary transcript and 75 S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):223–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case S. T., Summers R. L., Jones A. G. A variant tandemly repeated nucleotide sequence in Balbiani ring 2 of Chironomus tentans. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):555–562. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90436-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B., Anderson K., Fagerlind M. Large-sized polysomes in Chironomus tentans salivary glands and their relation to Balbiani ring 75S RNA. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):149–160. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B. Giant RNA transcript in a Balbiani ring. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 20;240(103):229–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio240229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström J. E., Rydlander L., Francke C. Concomitant induction of a Balbiani ring and a giant secretory protein in Chironomus salivary glands. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):115–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00292426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström J. E., Sierakowska H., Burvall K. Dependence of Balbiani ring induction in Chironomus salivary glands on inorganic phosphate. Dev Biol. 1982 May;91(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Ansorge W. Improvements of DNA sequencing gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbach U. Chromosomen-Aktivitat und biochemische Zelldifferenzierung in den Speicheldrüsen von Camptochironomus. Chromosoma. 1969;28(2):136–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00331528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäckle H., Almeida J. C., Galler R., Kluding H., Lehrach H., Edström J. E. Constant and variable parts in the Balbiani ring 2 repeat unit and the translation termination region. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):883–888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer-Safer P. R., Levine M., Ward D. C. Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumo D. E., Kleinsmith L. J. Methods for the assessment of nonhistone phosphorylation (acid-stable, alkali-labile linkages). Methods Cell Biol. 1978;19:119–126. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringborg U., Rydlander L. Nucleolar-derived ribonucleic acid in chromosomes, nuclear sap, and cytoplasm of Chironomus tentans salivary gland cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Nov;51(21):355–368. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydlander L., Edström J. E. Large sized nascent protein as dominating component during protein synthesis in Chironomus salivary glands. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):85–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00292424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydlander L., Pigon A., Edström J. E. Sequences translated by Balbiani ring 75S RNA in vitro are present in giant secretory protein from Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):101–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00292425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH D. W., AMES B. N. PHOSPHORIBOSYLADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE, AN INTERMEDIATE IN HISTIDINE BIOSYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:3056–3063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sümegi J., Wieslander L., Daneholt B. A hierarchic arrangement of the repetitive sequences in the Balbiani ring 2 gene of Chironomus tentans. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L., Lendahl U. The Balbiani ring 2 gene in Chironomus tentans is built from two types of tandemly arranged major repeat units with a common evolutionary origin. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1169–1175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L., Sümegi J., Daneholt B. Evidence for a common ancestor sequence for the Balbiani ring 1 and Balbiani ring 2 genes in Chironomus tentans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6956–6960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]