Abstract
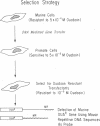
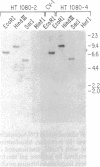
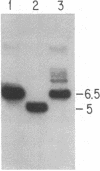
DNA prepared from ouabain-resistant mouse cells was able to transform ouabain-sensitive CV-1 cells to ouabain resistance after DNA-mediated gene transfer. The murine DNA fragment responsible for ouabain resistance was detected on the background of CV-1 DNA by virtue of a repetitive DNA sequence element that reacts positively with a mouse repeat DNA clone. CV-1 DNA is nonreactive with this probe. Southern analysis of several independently derived ouabain-resistant transformants indicates that the mouse ouaR gene is located on a 6.5-kilobase EcoRI restriction fragment. The 6.5-kilobase DNA fragment was initially isolated from a lambda phage library made from a ouabain-resistant secondary transformant and subsequently was subcloned in the plasmid vector pAT153. This plasmid was able to transform wild-type CV-1 cells to ouabain resistance at a frequency of about 10 cells per ng of DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Competence for DNA transfer of ouabain resistance and thymidine kinase: clonal variation in mouse L-cell recipients. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):617–630. doi: 10.1007/BF01549663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. Split genes and RNA splicing. Science. 1979 Apr 20;204(4390):264–271. doi: 10.1126/science.373120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. THE ACTION OF CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES ON ION MOVEMENTS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Dec;16:381–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. Isolation of beta-globin-related genes from a human cosmid library. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy I., Pellicer A., Jackson J. F., Sim G. K., Silverstein S., Axel R. Isolation of transforming DNA: cloning the hamster aprt gene. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):817–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90558-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Lipsich L., Wigler M. Isolation of the chicken thymidine kinase gene by plasmid rescue. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):207–210. doi: 10.1038/285207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Perucho M., Kurtz D., Dana S., Pellicer A., Axel R., Silverstein S. Transformation of mammalian cells with an amplifiable dominant-acting gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3567–3570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder J. I., Ganesan A. T. Procaryotic genomic DNA inhibits mammalian cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):956–959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]