Abstract
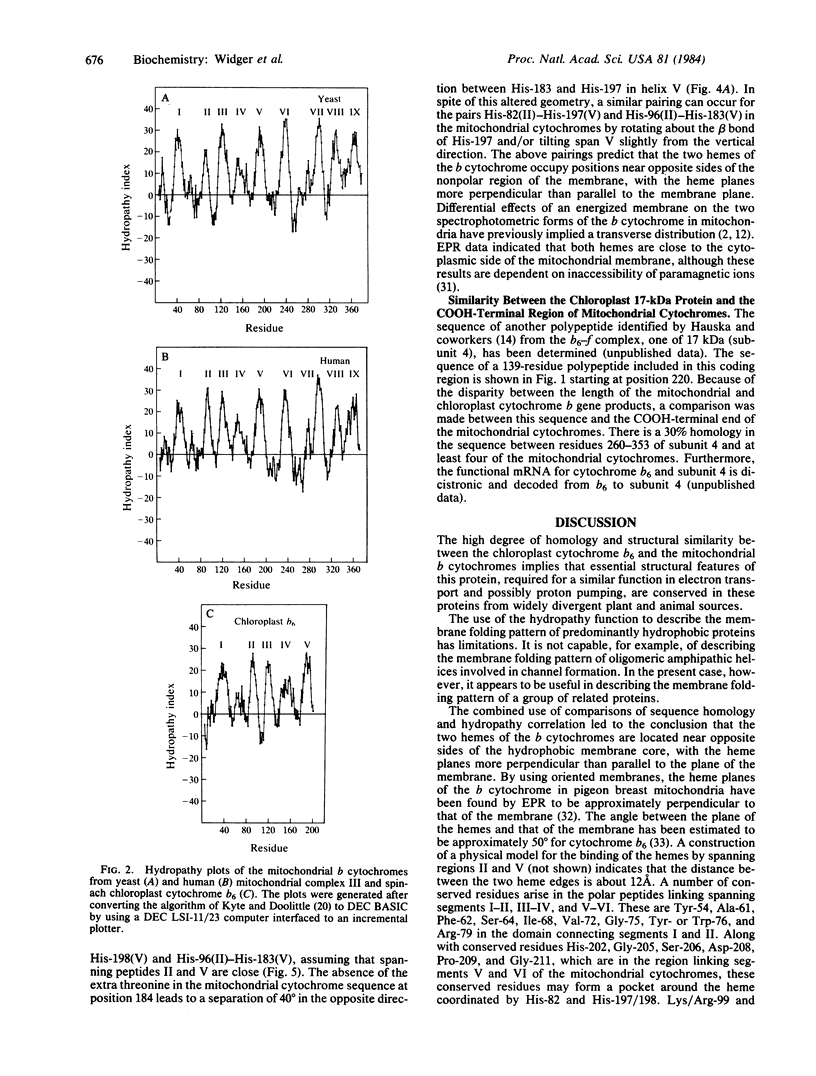
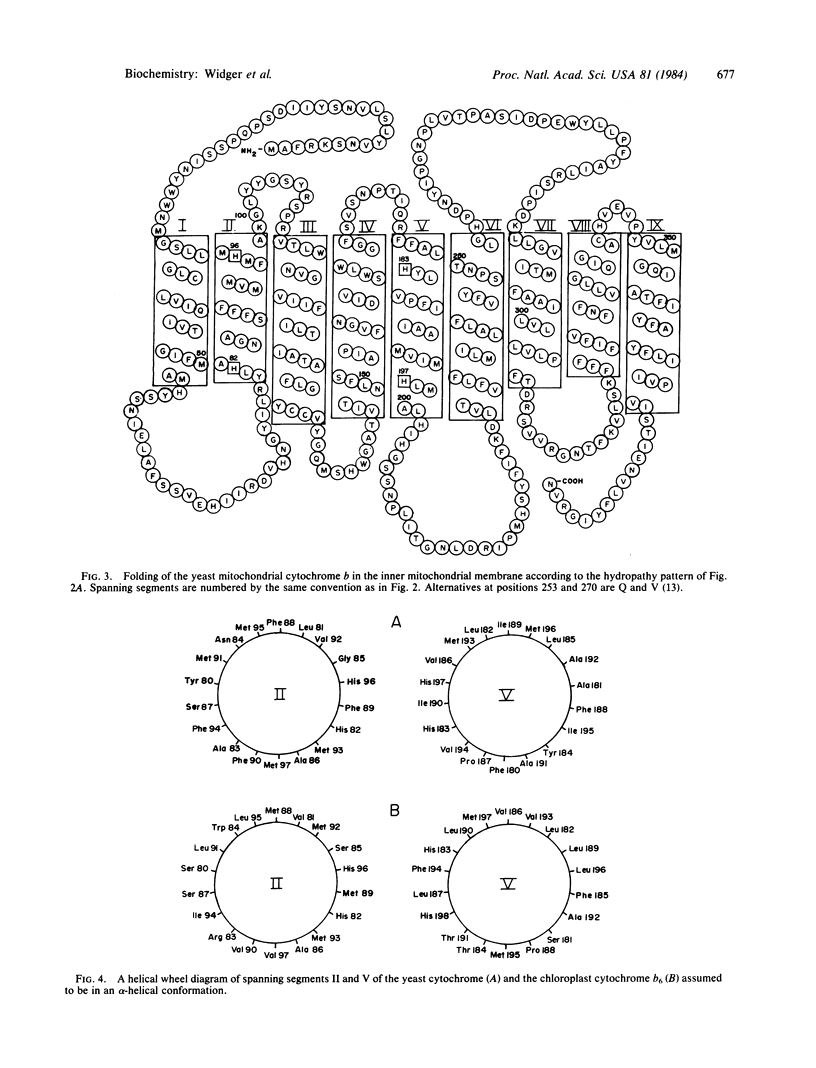
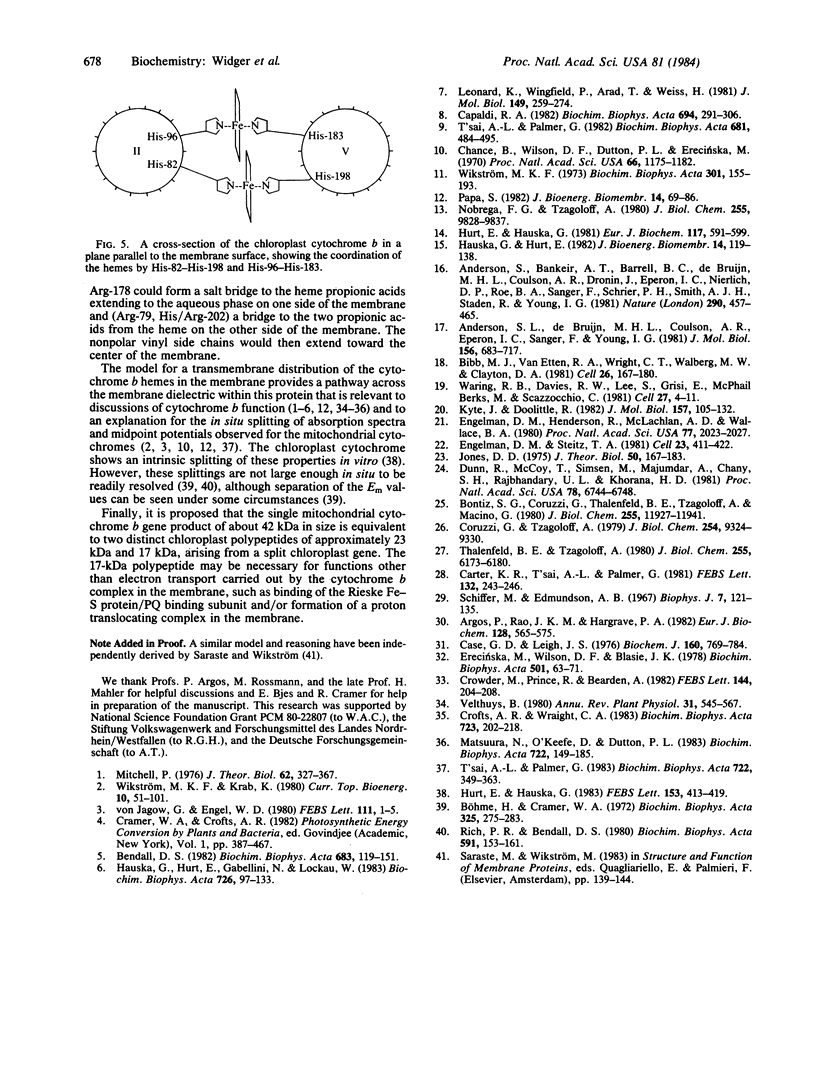
The amino acid sequences of cytochrome b of complex III from five different mitochondrial sources (human, bovine, mouse, yeast, and Aspergillus nidulans) and the chloroplast cytochrome b6 from spinach show a high degree of homology. Calculation of the distribution of hydrophobic residues with a "hydropathy" function that is conserved in this family of proteins implies that the membrane-folding pattern of the 42-kilodalton (kDa) mitochondrial cytochromes involves 8-9 membrane-spanning domains. The smaller 23-kDa chloroplast cytochrome appears to fold in five spanning domains that are similar to the first five of the mitochondria. Four highly conserved histidines are considered to be the likely ligands for the two hemes. The positions of the histidines along the spanning segments and in a cross section of the membrane-spanning alpha helices implies that two ligand pairs, His-82-His-197/198 and His-96-His-183, bridge the spanning peptides II and V, and the two hemes reside on opposite sides of the hydrophobic membrane core. In addition, the 17-kDa protein of the chloroplast b6-f complex appears to contain one or more of the functions of the COOH-terminal end of the mitochondrial cytochrome b polypeptide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Eperon I. C., Sanger F., Young I. G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):683–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Rao J. K., Hargrave P. A. Structural prediction of membrane-bound proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Van Etten R. A., Wright C. T., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonitz S. G., Coruzzi G., Thalenfeld B. E., Tzagoloff A., Macino G. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for subunit 1 of yeast cytochrme oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11927–11941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme H., Cramer W. A. Uncoupler-dependent decrease in midpoint potential of the chloroplast cytochrome b6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 22;325(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A. Arrangement of proteins in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;694(3):291–306. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K. R., Tsai A., Palmer G. The coordination environment of mitochondrial cytochromes b. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case G. D., Leigh J. S., Jr Intramitochondrial positions of cytochrome haem groups determined by dipolar interactions with paramagnetic cations. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):769–783. doi: 10.1042/bj1600769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Wilson D. F., Dutton P. L., Erecińska M. Energy-coupling mechanisms in mitochondria: kinetic, spectroscopic, and thermodynamic properties of an energy-transducing form of cytochrome b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1175–1182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. DNA sequence of subunit 2 of yeast cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9324–9330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn R., McCoy J., Simsek M., Majumdar A., Chang S. H., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. The bacteriorhodopsin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6744–6748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Henderson R., McLachlan A. D., Wallace B. A. Path of the polypeptide in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2023–2027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecińska M., Wilson D. F., Blasie J. K. Studies on the orientations of the mitochondrial redox carriers. II. Orientation of the mitochondrial chromophores with respect to the plane of the membrane in hydrated, oriented mitochondrial multilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 11;501(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauska G., Hurt E., Gabellini N., Lockau W. Comparative aspects of quinol-cytochrome c/plastocyanin oxidoreductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 15;726(2):97–133. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E., Hauska G. A cytochrome f/b6 complex of five polypeptides with plastoquinol-plastocyanin-oxidoreductase activity from spinach chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(3):591–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. D. Amino acid properties and side-chain orientation in proteins: a cross correlation appraoch. J Theor Biol. 1975 Mar;50(1):167–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(75)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard K., Wingfield P., Arad T., Weiss H. Three-dimensional structure of ubiquinol:cytochrome c reductase from Neurospora mitochondria determined by electron microscopy of membrane crystals. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90301-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Possible molecular mechanisms of the protonmotive function of cytochrome systems. J Theor Biol. 1976 Oct 21;62(2):327–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobrega F. G., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. DNA sequence and organization of the cytochrome b gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae D273-10B. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9828–9837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S. Molecular mechanism of proton translocation by the cytochrome system and the ATPase of mitochondria. Role of proteins. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1982 Apr;14(2):69–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00745021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich P. R., Bendall D. S. The redox potentials of the b-type cytochromes of higher plant chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 10;591(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- T'sai A. L., Palmer G. Potentiometric studies on yeast complex III. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 17;722(2):349–363. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(83)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- T'sai A. L., Palmer G. Purification and characterization of highly purified cytochrome b from complex III of baker's yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 15;681(3):484–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(82)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalenfeld B. E., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Sequence of the oxi 2 gene of yeast mitochondrial DNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6173–6180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W., Lee S., Grisi E., Berks M. M., Scazzocchio C. The mosaic organization of the apocytochrome b gene of Aspergillus nidulans revealed by DNA sequencing. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):4–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M. K. The different cytochrome b components in the respiratory chain of animal mitochondria and their role in electron transport and energy conservation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 7;301(2):155–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(73)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Jagow G., Engel W. D. A model for the cytochrome b dimer of the ubiquinol: cytochrome c oxidoreductase as a proton translocator. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80748-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



