Abstract
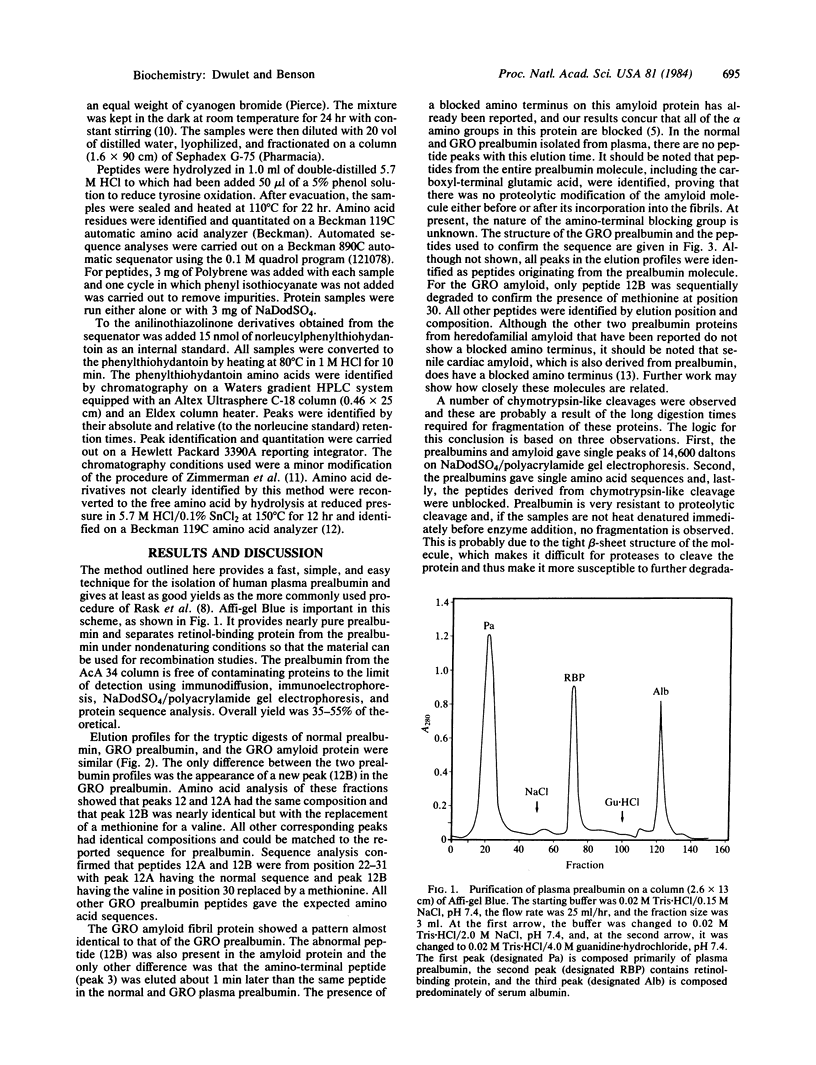
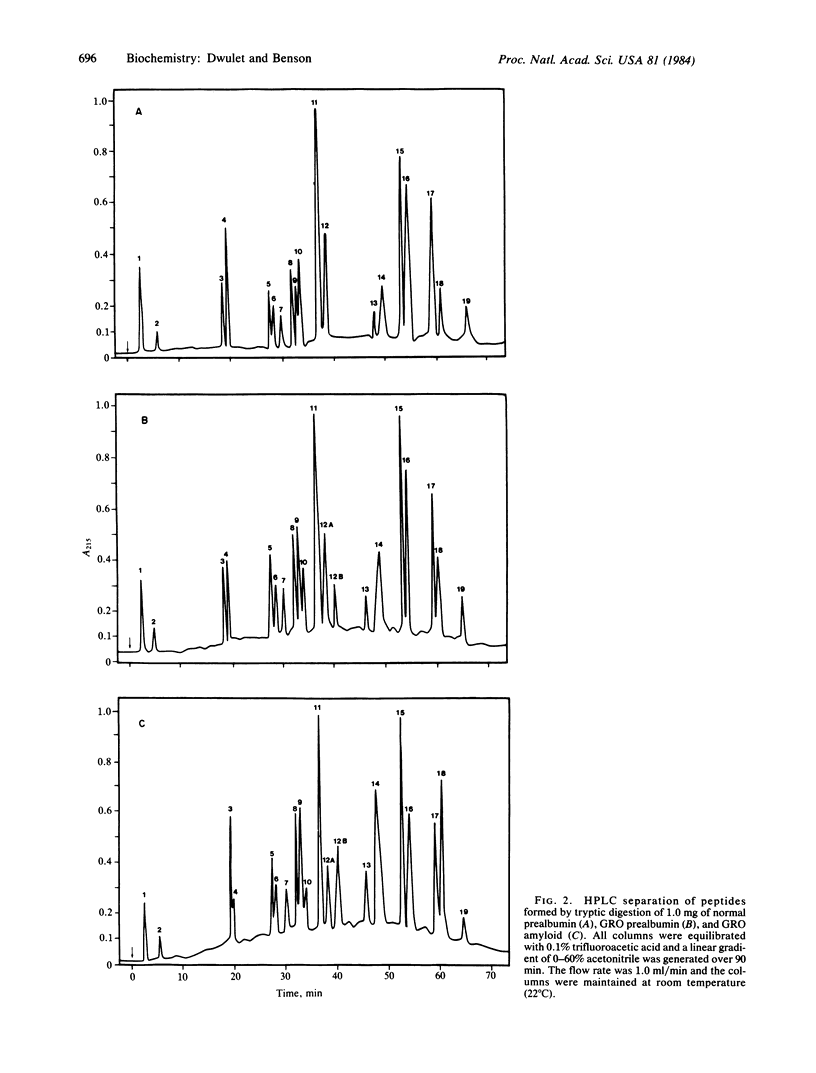
Prealbumin from an individual with heredofamilial amyloid polyneuropathy of Swedish origin was isolated from plasma by using a three-step procedure involving ion exchange, Affi-gel Blue affinity chromatography, and gel filtration. This prealbumin and its associated amyloid fibril subunit protein were digested with trypsin and the resulting peptides were separated by high performance liquid chromatography. Comparison with normal prealbumin peptides showed that an amino acid substitution of a methionine for a valine had occurred at position 30. In the plasma prealbumin, the abnormal residue accounted for 1/3rd of the material while in the amyloid fibrils it accounted for 2/3rds. From this sequence information and the known three-dimensional structure of the prealbumin molecule, a mechanism for the amyloid formation is proposed. It involves formation of the amyloid fibrils by addition of prealbumin dimers or tetramers to the aggregate. Each dimer must contain at least one variant peptide chain while the tetramer must contain at least two abnormal chains. Either of these models can account for the observed amount of normal prealbumin in amyloid fibrils. No proteolytic processing of this molecule is required because the entire undegraded prealbumin molecule is found in the fibrils.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRADE C. A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy; familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain. 1952 Sep;75(3):408–427. doi: 10.1093/brain/75.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade C., Araki S., Block W. D., Cohen A. S., Jackson C. E., Kuroiwa Y., Nissim J., Sohar E., McKusick V. A., Van Allen M. W. Hereditary amyloidosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):902–915. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D. Partial amino acid sequence homology between an heredofamilial amyloid protein and human plasma prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1035–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI110114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Geisow M. J., Oatley S. J., Rérat B., Rérat C. Structure of prealbumin: secondary, tertiary and quaternary interactions determined by Fourier refinement at 1.8 A. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):339–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa P. P., Figueira A. S., Bravo F. R. Amyloid fibril protein related to prealbumin in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4499–4503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1283–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda Y., Goodman D. S., Canfield R. E., Morgan F. J. The amino acid sequence of human plasma prealbumin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6796–6805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez E., Lai C. Y. Regeneration of amino acids from thiazolinones formed in the Edman degradation. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90677-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Franklin E. C., Prelli F., Frangione B. A variant of prealbumin from amyloid fibrils in familial polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):989–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Prelli F., Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Primary structure of an amyloid prealbumin variant in familial polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):539–542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask L., Peterson P. A., Nilsson S. F. The subunit structure of human thyroxine-binding prealbumin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):6087–6097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Cohen A. S. The prealbumin nature of the amyloid protein in familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP)-swedish variety. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1326–1332. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Westermark P., Natvig J. B. Senile cardiac amyloid is related to prealbumin. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(6):503–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman C. L., Appella E., Pisano J. J. Rapid analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1977 Feb;77(2):569–573. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



