Abstract
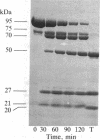
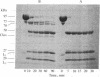
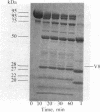
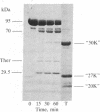
Because the proteolytic cleavage of a folded polypeptide depends not only on the specificity of the protease but on the nature of the folding, we investigated the cleavage of (chymotryptically produced) subfragment 1 (designated "S-1") or "head" segment of myosin by seven proteases with different specificities. All seven produced approximately the same three fragments of S-1--namely, fragments (from the NH2 terminus) of 27, 50, and 20 kilodaltons, suggesting that in intact S-1 these fragments are distinct domains. The same proteases were used to hydrolyze the MgADP complex of S-1. All failed to do so except trypsin, which, as found earlier [Hozumi, T. (1983) Biochemistry 22, 799-804], makes two additional cleavages. This result suggests that the conformational change induced by MgADP opens up only a small stretch of polypeptide chain, which stretch happens to be vulnerable to trypsin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botts J., Muhlrad A., Takashi R., Morales M. F. Effects of tryptic digestion on myosin subfragment 1 and its actin-activated adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6903–6905. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M., Sivaramakrishnan M. Subunit interactions of skeletal muscle myosin and myosin subfragment 1. Formation and properties of thermal hybrids. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5908–5913. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bálint M., Wolf I., Tarcsafalvi A., Gergely J., Sréter F. A. Location of SH-1 and SH-2 in the heavy chain segment of heavy meromyosin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):793–799. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaussepied P., Bertrand R., Audemard E., Pantel P., Derancourt J., Kassab R. Selective cleavage of the connector segments within the myosin-S1 heavy chain by staphylococcal protease. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 5;161(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80735-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R. Protease from Staphyloccus aureus. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:469–475. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais M., Corazzin S., Risler Y. How the loss of several residues, at the level of one interglobule junction, modulates the lactate dehydrogenase activity of yeast flavocytochrome b2: a study of the nicked enzymes resulting from clostripain and trypsin action. Biochimie. 1982 Jul;64(7):509–522. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozumi T., Muhlrad A. Reactive lysyl of myosin subfragment 1: location on the 27K fragment and labeling properties. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2945–2950. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozumi T. Structure and function of myosin subfragment 1 as studied by tryptic digestion. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):799–804. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassab R., Mornet D., Pantel P., Bertrand R., Audemard E. Structural aspects of actomyosin interaction. Biochimie. 1981 Apr;63(4):273–289. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. P., Mornet D., Vandest P., Kassab R. Proximity of alkali light chains to 27K domain of the heavy chain in myosin subfragment 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):466–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER H., PERRY S. V. The degradation of heavy meromyosin by trypsin. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:431–439. doi: 10.1042/bj0850431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marianne-Pépin T., Mornet D., Audemard E., Kassab R. Structural and actin-binding properties of the trypsin-produced HMM and S1 from gizzard smooth muscle myosin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 8;159(1-2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80448-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R. U., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Proteolytic approach to structure and function of actin recognition site in myosin heads. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2110–2120. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Structure of the actin-myosin interface. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):301–306. doi: 10.1038/292301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. The limited tryptic cleavage of chymotryptic S-1: an approach to the characterization of the actin site in myosin heads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91867-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhlrad A., Morales M. F. Isolation and partial renaturation of proteolytic fragments of the myosin head. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1003–1007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offer G., Moos C., Starr R. A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extractions, purification and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):653–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto Y., Okamoto M., Sekine T. Two opposite effects of ATP on the chymotryptic cleavages in smooth muscle myosin head. Determination of cleavable points and their characterization. J Biochem. 1980 Aug;88(2):361–371. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope B. J., Wagner P. D., Weeds A. G. Heterogeneity of myosin heavy chains in subfragment-1 isoenzymes rabbit skeletal myosin. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):470–473. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub M. C., Watterson J. G., Waser P. G. Conformational differences in myosin, IV.[1-3] Radioactive labeling of specific thiol groups as influenced by ligand binding. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Mar;356(3):325–339. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.1.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Mapping of actin-binding sites on the heavy chain of myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilagyi L., Balint M., Sreter F. A., Gergely J. Photoaffinity labelling with an ATP analog of the N-terminal peptide of myosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):936–945. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P. D., Giniger E. Hydrolysis of ATP and reversible binding to F-actin by myosin heavy chains free of all light chains. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):560–562. doi: 10.1038/292560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Taylor R. S. Separation of subfragment-1 isoenzymes from rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):54–56. doi: 10.1038/257054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Active site trapping of nucleotides by crosslinking two sulfhydryls in myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4966–4970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Yazawa Y., Yasui T. Proteolytic separation of an enzymic active subfragment from the myosin-subfragment (S-1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 17;29(3):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Sekine T. Substructure of myosin subfragment-1 as revealed by digestion with proteolytic enzymes. J Biochem. 1980 Jan;87(1):219–226. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]