Abstract
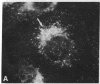
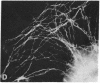
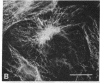
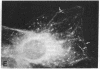
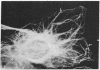
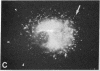
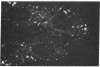
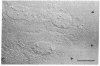
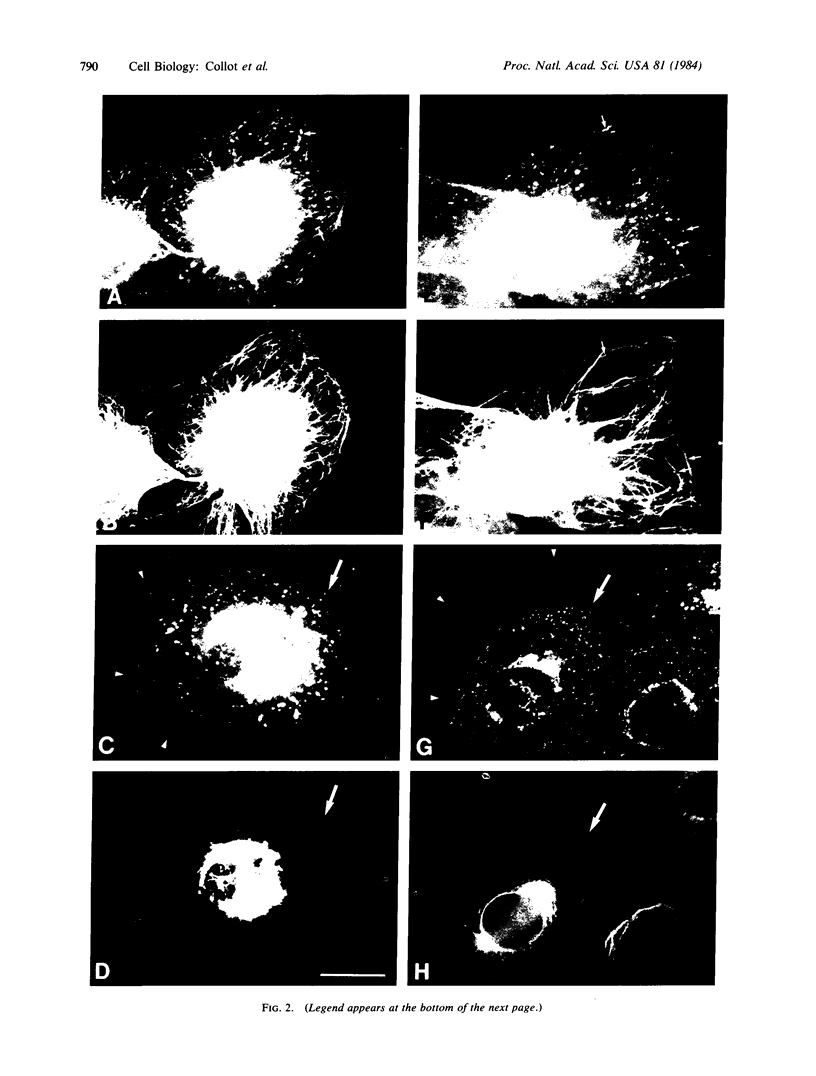
Double immunofluorescent labeling experiments for lysosomes and either microtubules or vimentin intermediate filaments in cultured well-spread fibroblasts show a remarkable degree of superposition of the lysosomes and the microtubules. Under two different sets of conditions where the microtubules and intermediate filaments are well segregated from one another, the lysosomes remain codistributed with the microtubules. It is suggested that this specific association of lysosomes with microtubules reflects some type(s) of linkage(s) between them and that such linkages may play an important role in the location and intracellular transport of lysosomes inside cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball E. H., Singer S. J. Association of microtubules and intermediate filaments in normal fibroblasts and its disruption upon transformation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6986–6990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball E. H., Singer S. J. Mitochondria are associated with microtubules and not with intermediate filaments in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):123–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrendt H. Effect of anabolic steroids on rat heart muscle cells. I. Intermediate filaments. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 May 31;180(3):303–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00227598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Vallee R. B. Association of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP 2) with microtubules and intermediate filaments in cultured brain cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1523–1531. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couchman J. R., Rees D. A. Organelle-cytoskeleton relationships in fibroblasts: mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum in phases of movement and growth. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;27(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Ferreira K. L., David-Ferreira J. F. Association between intermediate-sized filaments and mitochondria in rat Leydig cells. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1980 Jul;4(7):655–662. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(80)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Granett S., Rosenbaum J. L. Ultrastructural localization of the high molecular weight proteins associated with in vitro-assembled brain microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):237–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Porter K. R. Microtrabecular structure of the axoplasmic matrix: visualization of cross-linking structures and their distribution. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):464–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrans V. J., Roberts W. C. Intermyofibrillar and nuclear-myofibrillar connections in human and canine myocardium. An ultrastructural study. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1973 Jun;5(3):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(73)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed J. J., Lebowitz M. M. The association of a class of saltatory movements with microtubules in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 May;45(2):334–354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.2.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Singer S. J. Association of microtubules and intermediate filaments in chicken gizzard cells as detected by double immunofluorescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4769–4773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotlieb A. I., Heggeness M. H., Ash J. F., Singer S. J. Mechanochemical proteins, cell motility and cell-cell contacts: the localization of mechanochemical proteins inside cultured cells at the edge of an in vitro "wound". J Cell Physiol. 1979 Sep;100(3):563–578. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden J. H., Allen R. D., Goldman R. D. Cytoplasmic transport in keratocytes: direct visualization of particle translocation along microtubules. Cell Motil. 1983;3(1):1–19. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Simon M., Singer S. J. Association of mitochondria with microtubules in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3863–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Wang K., Singer S. J. Intracellular distributions of mechanochemical proteins in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3883–3887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Cross-linker system between neurofilaments, microtubules, and membranous organelles in frog axons revealed by the quick-freeze, deep-etching method. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):129–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein S., Goldstein I. M., Weissmann G. Role of microtubule assembly in lysosomal enzyme secretion from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. A reevaluation. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):242–256. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Binder L. I., Rosenbaum J. L. The periodic association of MAP2 with brain microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):266–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leterrier J. F., Liem R. K., Shelanski M. L. Interactions between neurofilaments and microtubule-associated proteins: a possible mechanism for intraorganellar bridging. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):982–986. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Reggio H., Warren G. Antibodies to the Golgi complex and the rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):92–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. L., Bank H. L., Brissie N. T., Spicer S. S. Association of microfilament bundles with lysosomes in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):659–666. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Borisy G. G. Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Like A. A., Amherdt M., Blondel B., Kanazawa Y., Marliss E. B., Lambert A. E., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E. Monolayer cell culture of neonatal rat pancreas: an ultrastructural and biochemical study of functioning endocrine cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 May;43(3):270–297. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)80039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papasozomenos S. C., Yoon M., Crane R., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Redistribution of proteins of fast axonal transport following administration of beta,beta'-iminodipropionitrile: a quantitative autoradiographic study. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):672–675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phaire-Washington L., Silverstein S. C., Wang E. Phorbol myristate acetate stimulates microtubule and 10-nm filament extension and lysosome redistribution in mouse macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):641–655. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Wiche G. High molecular weight polypeptides (270,000-340,000) from cultured cells are related to hog brain microtubule-associated proteins but copurify with intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4808–4812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS E., GONATAS N. K. HISTOCHEMICAL AND ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDIES ON HELA CELL CULTURES EXPOSED TO SPINDLE INHIBITORS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE INTERPHASE CELL. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Sep;12:704–711. doi: 10.1177/12.9.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Chen L. B., Murphy J. R., Fields B. N. Specific disruption of vimentin filament organization in monkey kidney CV-1 cells by diphtheria toxin, exotoxin A, and cycloheximide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7267–7271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. S., Järlfors U., Cayer M. L. Structural cross-bridges between microtubules and mitochondria in central axons of an insect (Periplaneta americana). J Cell Sci. 1977;27:255–272. doi: 10.1242/jcs.27.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suprenant K. A., Dentler W. L. Association between endocrine pancreatic secretory granules and in-vitro-assembled microtubules is dependent upon microtubule-associated proteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):164–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T., Dutton A. H., Singer S. J. Immunoelectron microscopic studies of desmin (skeletin) localization and intermediate filament organization in chicken cardiac muscle. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1736–1742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T., Dutton A. H., Singer S. J. Immunoelectron microscopic studies of desmin (skeletin) localization and intermediate filament organization in chicken skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1727–1735. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Cross R. K., Choppin P. W. Involvement of microtubules and 10-nm filaments in the movement and positioning of nuclei in syncytia. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):320–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Goldman R. D. Functions of cytoplasmic fibers in intracellular movements in BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):708–726. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]