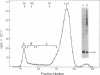
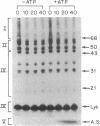
Abstract
Previous studies have indicated that the ATP-requiring conjugation of ubiquitin with proteins plays a role in the energy-dependent degradation of intracellular proteins. To examine whether such conjugates are indeed intermediates in protein breakdown, conjugates of 125I-labeled lysozyme with ubiquitin were isolated and incubated with a fraction of reticulocyte extract that lacks the enzymes that carry out ubiquitin-protein conjugation. ATP markedly stimulated degradation of the lysozyme moiety of ubiquitin conjugates to products soluble in trichloroacetic acid. By contrast, free 125I-labeled lysozyme was not degraded under these conditions, unless ubiquitin and the three enzymes required for ubiquitin conjugation were supplemented. Mg2+ was absolutely required for conjugate breakdown. Of various nucleotides, only CTP replaced ATP. Nonhydrolyzable analogs of ATP were not effective. In the absence of ATP, free lysozyme is released from ubiquitin-lysozyme conjugates by isopeptidases present in the extract. Thus, ATP is involved in both the formation and the breakdown of ubiquitin-protein conjugates.
Full text
PDF
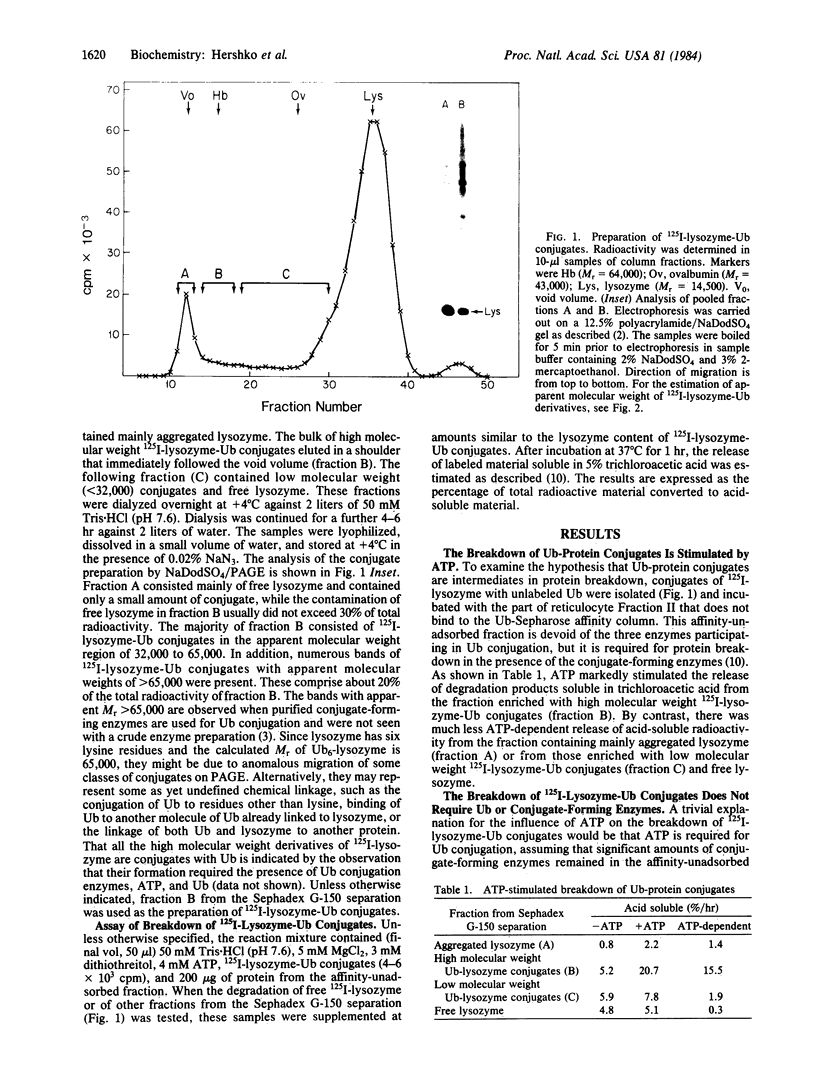

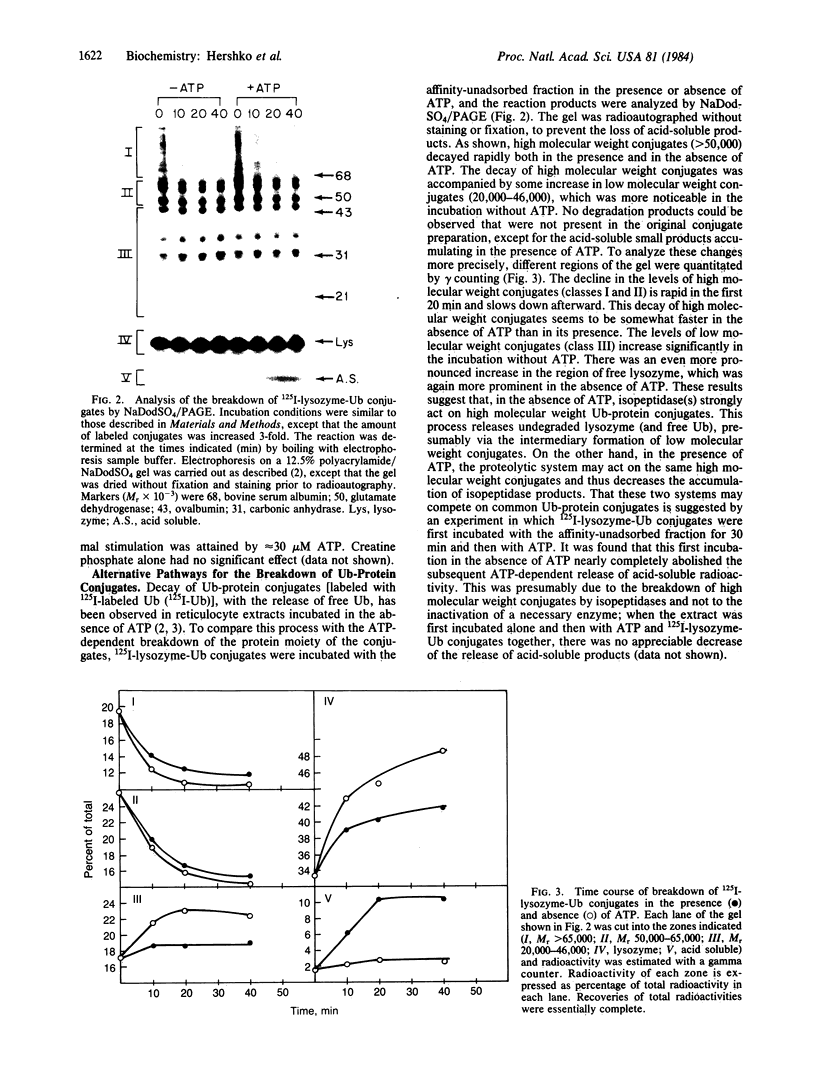

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen M. W., Ballal N. R., Goldknopf I. L., Busch H. Protein A24 lyase activity in nucleoli of thioacetamide-treated rat liver releases histone 2A and ubiquitin from conjugated protein A24. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1100–1104. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. T., Kuehl L., Rechsteiner M. Conjugation of ubiquitin to denatured hemoglobin is proportional to the rate of hemoglobin degradation in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5857–5861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Elias S., Heller H., Ferber S., Hershko A. Characterization of the heat-stable polypeptide of the ATP-dependent proteolytic system from reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7525–7528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Elias S., Heller H., Hershko A. "Covalent affinity" purification of ubiquitin-activating enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2537–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Heller H., Elias S., Haas A. L., Hershko A. ATP-dependent conjugation of reticulocyte proteins with the polypeptide required for protein degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1365–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Heller H., Katz-Etzion R., Hershko A. Activation of the heat-stable polypeptide of the ATP-dependent proteolytic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):761–765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciehanover A., Hod Y., Hershko A. A heat-stable polypeptide component of an ATP-dependent proteolytic system from reticulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1100–1105. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMartino G. N., Goldberg A. L. Identification and partial purification of an ATP-stimulated alkaline protease in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3712–3715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desautels M., Goldberg A. L. Demonstration of an ATP-dependent, vanadate-sensitive endoprotease in the matrix of rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11673–11679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etlinger J. D., Goldberg A. L. A soluble ATP-dependent proteolytic system responsible for the degradation of abnormal proteins in reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):54–58. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etlinger J. D., Goldberg A. L. Control of protein degradation in reticulocytes and reticulocyte extracts by hemin. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4563–4568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. L., Rose I. A. Hemin inhibits ATP-dependent ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis: role of hemin in regulating ubiquitin conjugate degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6845–6848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. L., Warms J. V., Hershko A., Rose I. A. Ubiquitin-activating enzyme. Mechanism and role in protein-ubiquitin conjugation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2543–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A., Heller H., Haas A. L., Rose I. A. Proposed role of ATP in protein breakdown: conjugation of protein with multiple chains of the polypeptide of ATP-dependent proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1783–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. Mechanisms of intracellular protein breakdown. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:335–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A., Rose I. A. Identification of the active amino acid residue of the polypeptide of ATP-dependent protein breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1525–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A., Rose I. A. Resolution of the ATP-dependent proteolytic system from reticulocytes: a component that interacts with ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3107–3110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Eytan E., Ciechanover A., Haas A. L. Immunochemical analysis of the turnover of ubiquitin-protein conjugates in intact cells. Relationship to the breakdown of abnormal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13964–13970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Heller H., Elias S., Ciechanover A. Components of ubiquitin-protein ligase system. Resolution, affinity purification, and role in protein breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8206–8214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larimore F. S., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Studies of the ATP-dependent proteolytic enzyme, protease La, from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4187–4195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S., Sandberg A. A., Negoro S., Seon B. K., Goldstein G. Isopeptidase: a novel eukaryotic enzyme that cleaves isopeptide bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1535–1539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A., Warms J. V., Hershko A. A high molecular weight protease in liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8135–8138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser S., Etlinger J. D. ATP stimulates proteolysis in reticulocyte extracts by repressing an endogenous protease inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3577–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. ATP serves two distinct roles in protein degradation in reticulocytes, one requiring and one independent of ubiquitin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1580–1585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]