Abstract
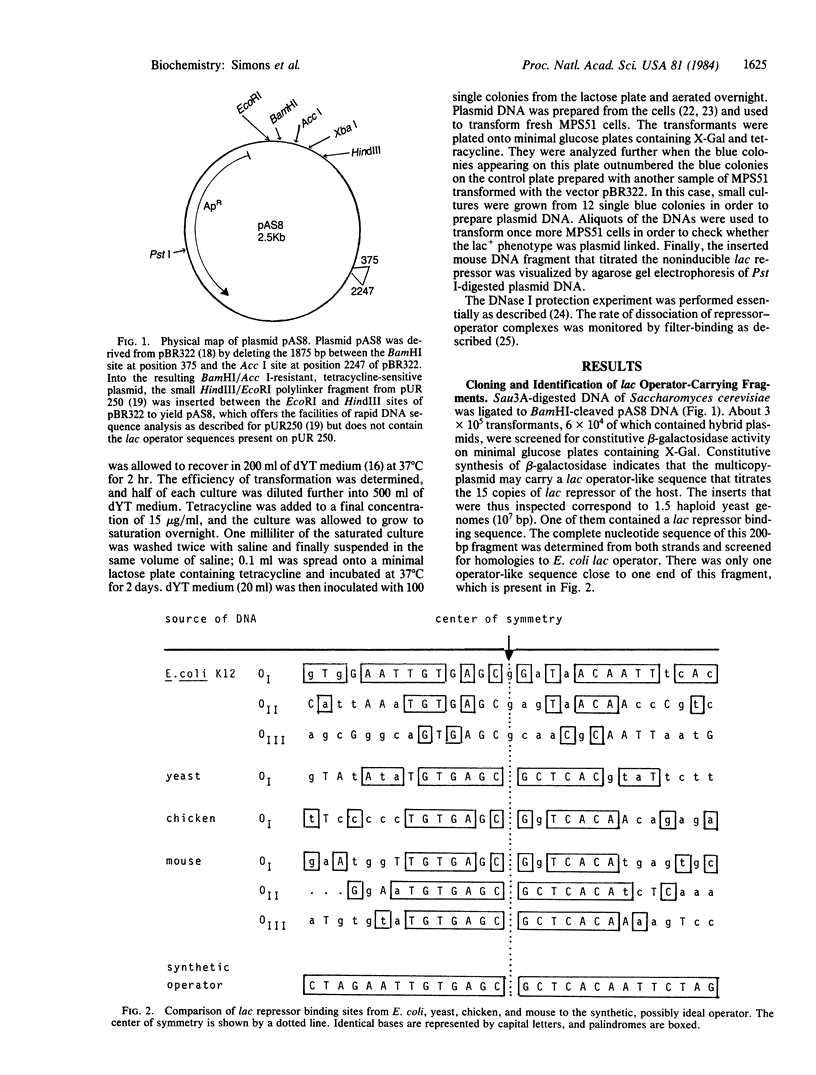
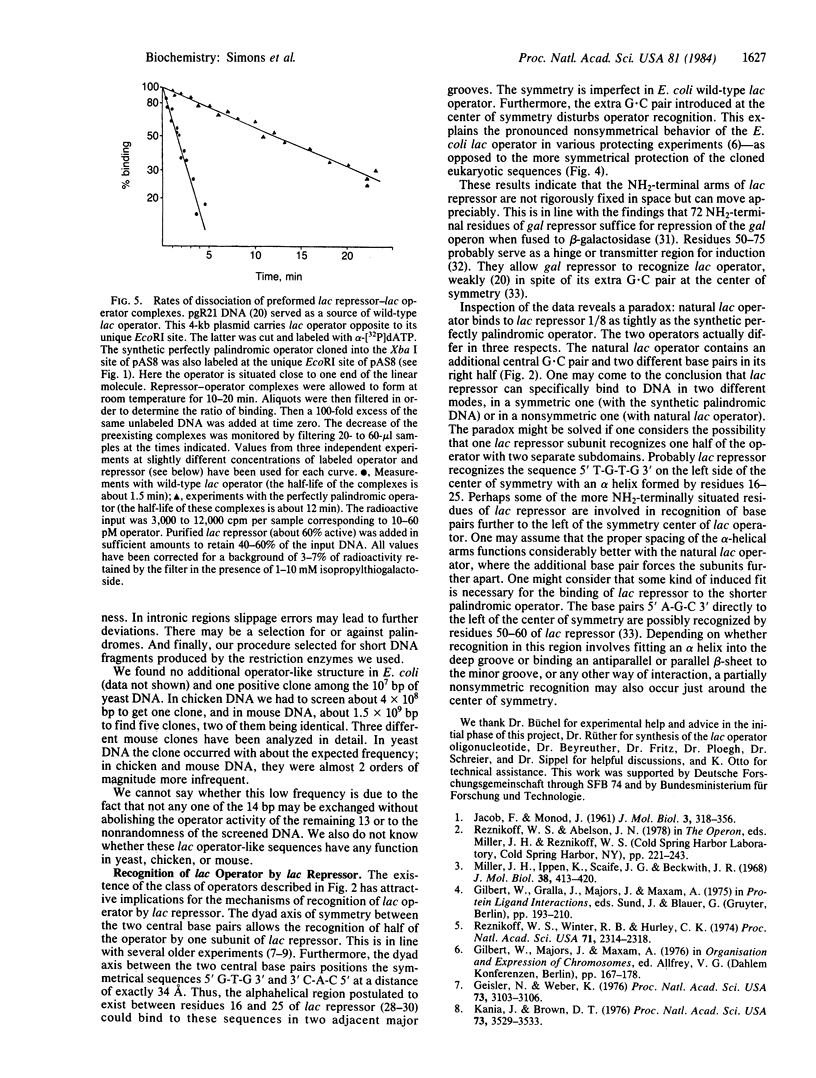
Five DNA fragments have been cloned from yeast, chicken, and mouse DNA that titrate lac repressor in an Escherichia coli lac+ I+Z+ wild-type strain when on a multi-copy plasmid. The five repressor-binding sequences have been identified by DNA sequence determinations and DNase cleavage-inhibition patterns. They share the 14-base-pair symmetrical consensus sequence 5' T-G-T-G-A-G-C:G-C-T-C-A-C-A 3' (the colon represents the center of symmetry), which is an inverted repeat of 7 base pairs of the left half of the E. coli lac operator. A similar perfect palindromic DNA fragment--an 11-base-pair inverted repeat of the left half of the lac operator--was synthesized. The cloned synthetic DNA 5' G-A-A-T-T-G-T-G-A-G-C:G-C-T-C-A-C-A-A-T-T-C 3' binds lac repressor 8-fold more tightly than does wild-type E. coli lac operator DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler K., Beyreuther K., Fanning E., Geisler N., Gronenborn B., Klemm A., Müller-Hill B., Pfahl M., Schmitz A. How lac repressor binds to DNA. Nature. 1972 Jun 9;237(5354):322–327. doi: 10.1038/237322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahl C. P., Wu R., Stawinsky J., Narang S. A. Minimal length of the lactose operator sequence for the specific recognition by the lactose repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):966–970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchel D. E., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of the lactose permease gene. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):541–545. doi: 10.1038/283541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Kahmann R., Kamp D. Electron microscopic characterization of DNAs of non-defective deletion mutants of bacteriophage Mu. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 15;113(4):591–609. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte M. A., Fangman W. L. Naturally occurring cross-links in yeast chromosomal DNA. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):425–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Isolation of a set of hybrid lac repressors made in vitro between normal lac repressor and its homogeneous tryptic core. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3103–3106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Yansura D. G., Caruthers M. H. How lac repressor recognizes lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3578–3582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kania J., Brown D. T. The functional repressor parts of a tetrameric lac repressor-beta-galactosidase chimaera are organized as dimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3529–3533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kania J., Müller-Hill B. Construction, isolation and implications of repressor-galactosidase - beta-galactosidase hybrid molecules. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):381–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., Riggs A. D. Lac repressor binding to non-operator DNA: detailed studies and a comparison of eequilibrium and rate competition methods. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):671–690. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Takeda Y. Structure of the DNA-binding region of lac repressor inferred from its homology with cro repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1428–1432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Ippen K., Scaife J. G., Beckwith J. R. The promoter-operator region of the lac operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B. Lac repressor and lac operator. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1975;30(2-3):227–252. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(76)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl M., Stockter C., Gronenborn B. Genetic analysis of the active sites of lac repressor. Genetics. 1974 Apr;76(4):669–679. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.4.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Winter R. B., Hurley C. K. The location of the repressor binding sites in the lac operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2314–2318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Bourgeois S., Cohn M. The lac repressor-operator interaction. 3. Kinetic studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):401–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U. pUR 250 allows rapid chemical sequencing of both DNA strands of its inserts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5765–5772. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Pabo C. O., Meyer B. J., Ptashne M., Backman K. C. Regulatory functions of the lambda repressor reside in the amino-terminal domain. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):396–400. doi: 10.1038/279396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A. Cyclic AMP receptor proteins interacts with lactose operator DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):277–292. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Koenen M., Griesser H. W., Müller-Hill B. 72 residues of gal repressor fused to beta-galactosidase repress the gal operon of E. coli. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1271–1274. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of galR gene indicates a common evolutionary origin of lac and gal repressor in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]