Abstract
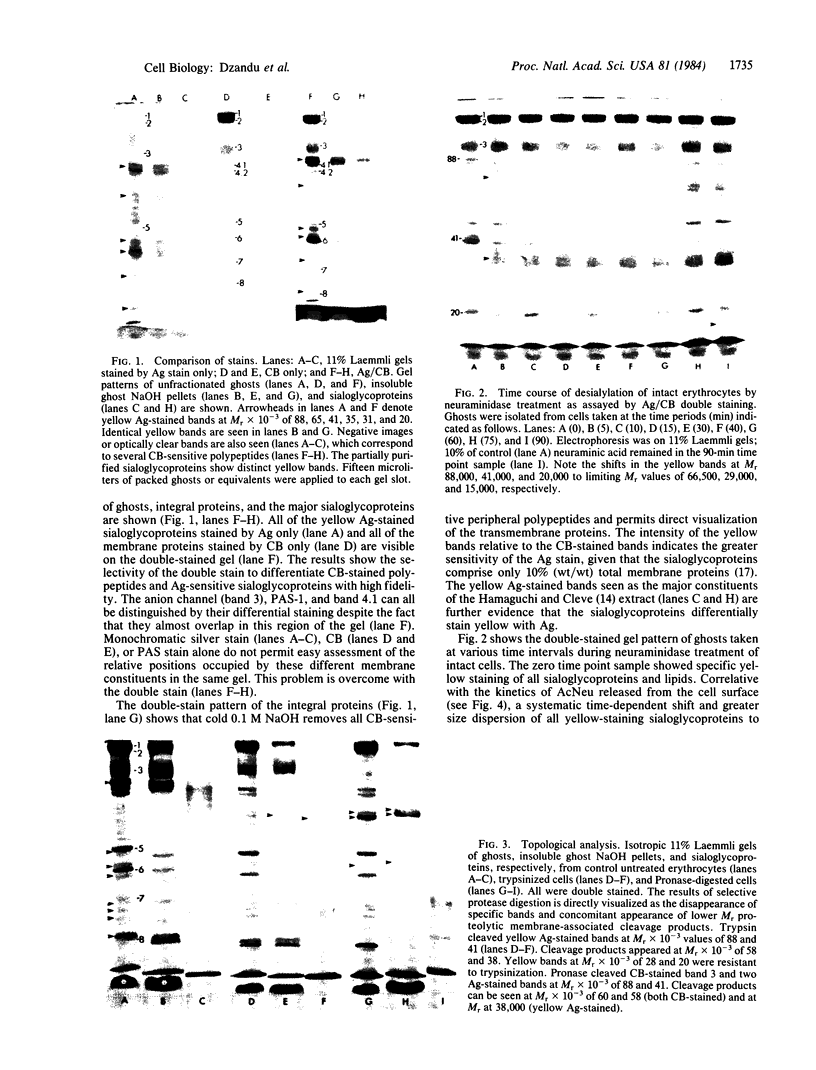
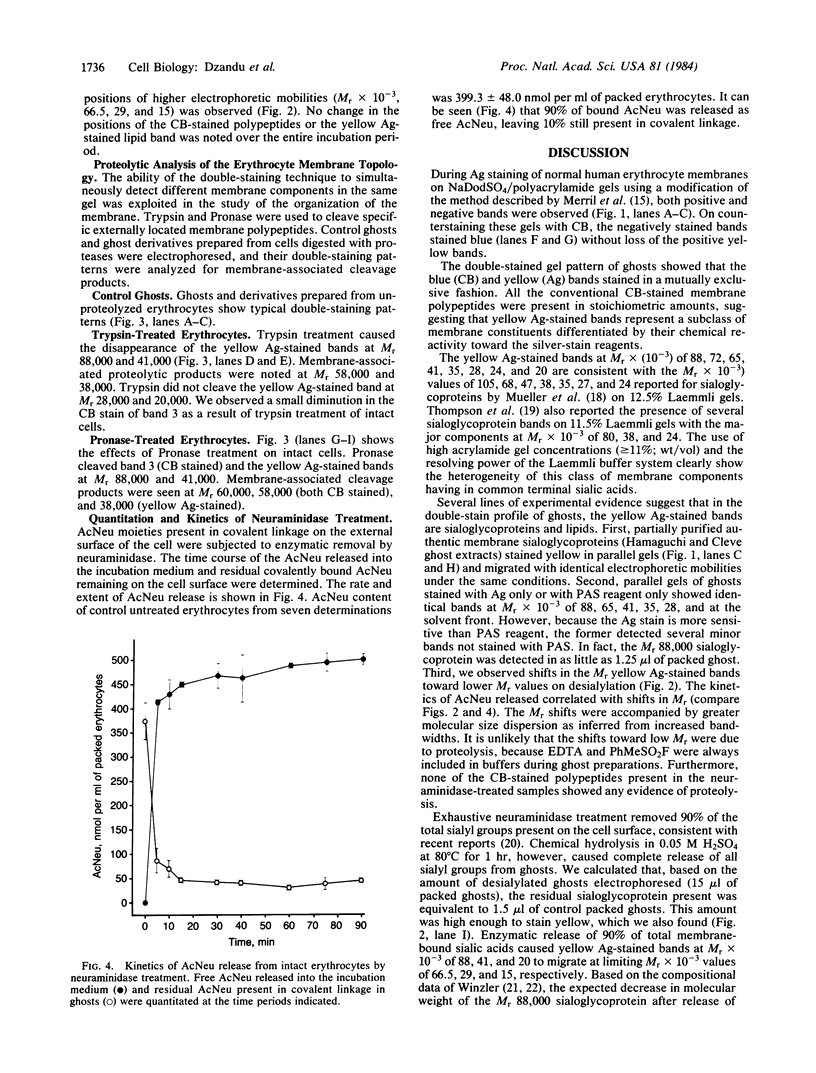
A silver/Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 staining technique that permits a color-coded differentiation of erythrocyte membrane proteins, sialoglycoproteins, and lipids in a single one-dimensional NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel has been described. Gels stained first with silver stain and then with Coomassie blue (CB) showed the characteristic blue staining of all conventional CB-sensitive membrane polypeptides, whereas periodic acid-Schiff reagent-sensitive sialoglycoproteins and lipids stained yellow. Several yellow Ag-stained bands corresponding to major and minor sialoglycoproteins were detected at Mr X 10(-3) of 88, 72, 65, 41, 35, 31, 28, 24, and 20. Neuraminidase treatment of intact erythrocytes caused shifts in the electrophoretic mobilities of several yellow-stained bands without affecting the CB-stained polypeptide pattern. These observations afforded evidence that the yellow-staining bands were sialoglycoproteins and lipids. The double-staining technique was used in a topological analysis of the membrane surface of the erythrocyte using protease digestion and selective solubilization. Trypsin cleaved the yellow bands at Mr 88,000 and 41,000. Membrane-associated cleavage products were noted at Mr 58,000 and 38,000. Pronase treatment of intact cells gave membrane-associated cleavage products at Mr 38,000 (yellow) and two CB-stained bands at Mr 58,000 and 60,000. These results suggested that the double-staining technique may be applicable in compositional and topological analyses of other biological membranes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aminoff D., Bell W. C., Fulton I., Ibgebrigtsen N. Effect of sialidase on the viability of erythrocytes in circulation. Am J Hematol. 1976;1(4):419–432. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830010407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., West C., Blume K. G. The removal of leukocytes and platelets from whole blood. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Aug;88(2):328–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge J. T., Phillips G. B. Composition of phospholipids and of phospholipid fatty acids and aldehydes in human red cells. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):667–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi H., Cleve H. Solubilization of human erythrocyte membrane glycoproteins and separation of the MN glycoprotein from a glycoprotein with I, S, and A activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 29;278(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie S., Sezaki M., Kato Y. A faithful double stain of proteins in the polyacrylamide gels with Coomassie blue and silver. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 1;126(2):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90526-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., McGowan M. W., Morse P. D., 2nd, Dzandu J. K. Proteolytic analysis of the topological arrangement of red cell phosphoproteins. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 20;21(15):3599–3604. doi: 10.1021/bi00258a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller T. J., Dow A. W., Morrison M. Heterogeneity of the sialoglycoproteins of the normal human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):94–99. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90965-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller T. J., Morrison M. Detection of a variant of protein 3, the major transmembrane protein of the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6573–6576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller T. J., Morrison M. Detection of a variant of protein 3, the major transmembrane protein of the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6573–6576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niehaus W. G., Jr, Wold F. Cross-linking of erythrocyte membranes with dimethyl adipimidate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):170–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Morrison M. Exposed protein on the intact human erythrocyte. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1766–1771. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears D. A., Friedman J. M., George J. N. Topography of the external surface of the human red blood cell membrane studied with a nonpenetrating label, [125I]diazodiiodosulfanilic acid. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):712–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoza L., Mohos S. Stable thiobarbituric acid chromophore with dimethyl sulphoxide. Application to sialic acid assay in analytical de-O-acetylation. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):457–462. doi: 10.1042/bj1590457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V., Richards F. M. Photochemical labeling of the surface proteins of human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 18;13(13):2720–2726. doi: 10.1021/bi00710a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibler H., Borg S. Reduction of the sialic acid and galactose concentrations in erythrocyte membranes in alcoholics. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1982 Sep;10(1):85–98. doi: 10.1016/0376-8716(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S., Rennie C. M., Maddy A. H. A re-evaluation of the surface complexity of the intact erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 14;600(3):756–768. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winzler R. J. Carbohydrates in cell surfaces. Int Rev Cytol. 1970;29:77–125. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]