Abstract
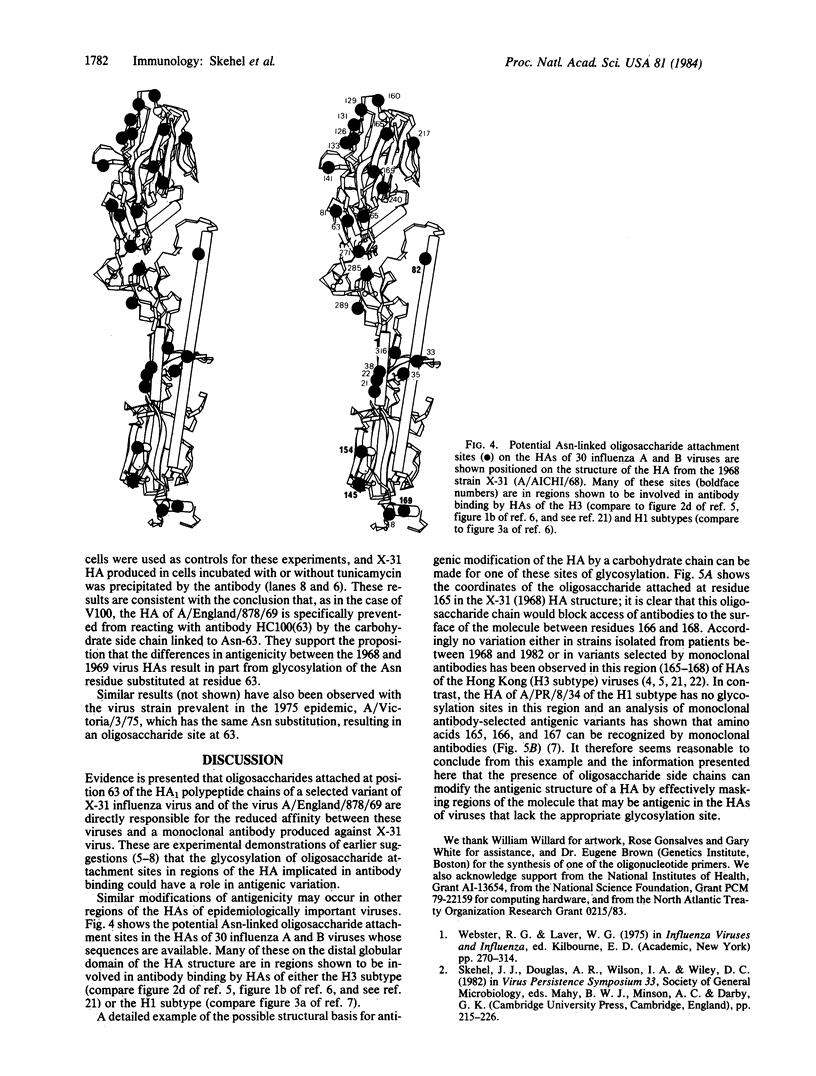
A single amino acid substitution, Asp-63 to Asn-63, was detected in the hemagglutinin of an antigenic variant of the 1968 Hong Kong (H3) influenza virus that was selected by growth of the wild-type virus in the presence of a monoclonal antibody. The mutation generates an oligosaccharide attachment site, Asn-Cys-Thr at residues 63-65, that is glycosylated. Immunoprecipitation experiments with extracts from variant virus-infected cells prepared in the presence or absence of tunicamycin, which inhibits glycosylation, demonstrate that addition of the new oligosaccharide side chain is required to prevent reaction with the monoclonal antibody. Similar experiments with the virus of the 1969 Hong Kong influenza epidemic, A/England/878/69, which also contains a hemagglutinin glycosylated at residue 63, support this conclusion and provide evidence for the epidemiological significance of carbohydrate-mediated modifications of hemagglutinin antigenicity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Both G. W., Sleigh M. J. Conservation and variation in the hemagglutinins of Hong Kong subtype influenza viruses during antigenic drift. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):663–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.663-672.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caton A. J., Brownlee G. G., Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W. The antigenic structure of the influenza virus A/PR/8/34 hemagglutinin (H1 subtype). Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Analyses of the antigenicity of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH optimum for virus-mediated membrane fusion. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1657–1662. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. D. Future influenza vaccines and the use of genetic recombinants. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(3):643–645. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Dopheide T. A., Ward C. W. Amino acid sequence changes in the haemagglutinin of A/Hong Kong (H3N2) influenza virus during the period 1968--77. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):454–457. doi: 10.1038/283454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel T. P., Millican T. A., Bose C. C., Titmas R. C., Mock G. A., Eaton M. A. Improvements to solid phase phosphotriester synthesis of deoxyoligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5605–5620. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond F. L., Caton A. J., Cox N. J., Kendal A. P., Brownlee G. G. Antigenicity and evolution amongst recent influenza viruses of H1N1 subtype. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7191–7203. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Wiley D. C. Antigenic and amino acid sequence variations in the haemagglutinins of type A influenza viruses recently isolated from human subjects. Bull World Health Organ. 1983;61(4):671–676. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J., Both G. W., Underwood P. A., Bender V. J. Antigenic drift in the hemagglutinin of the Hong Kong influenza subtype: correlation of amino acid changes with alterations in viral antigenicity. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):845–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.845-853.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeyen M., Fang R., Jou W. M., Devos R., Huylebroeck D., Saman E., Fiers W. Antigenic drift between the haemagglutinin of the Hong Kong influenza strains A/Aichi/2/68 and A/Victoria/3/75. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):771–776. doi: 10.1038/286771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]